Abstract
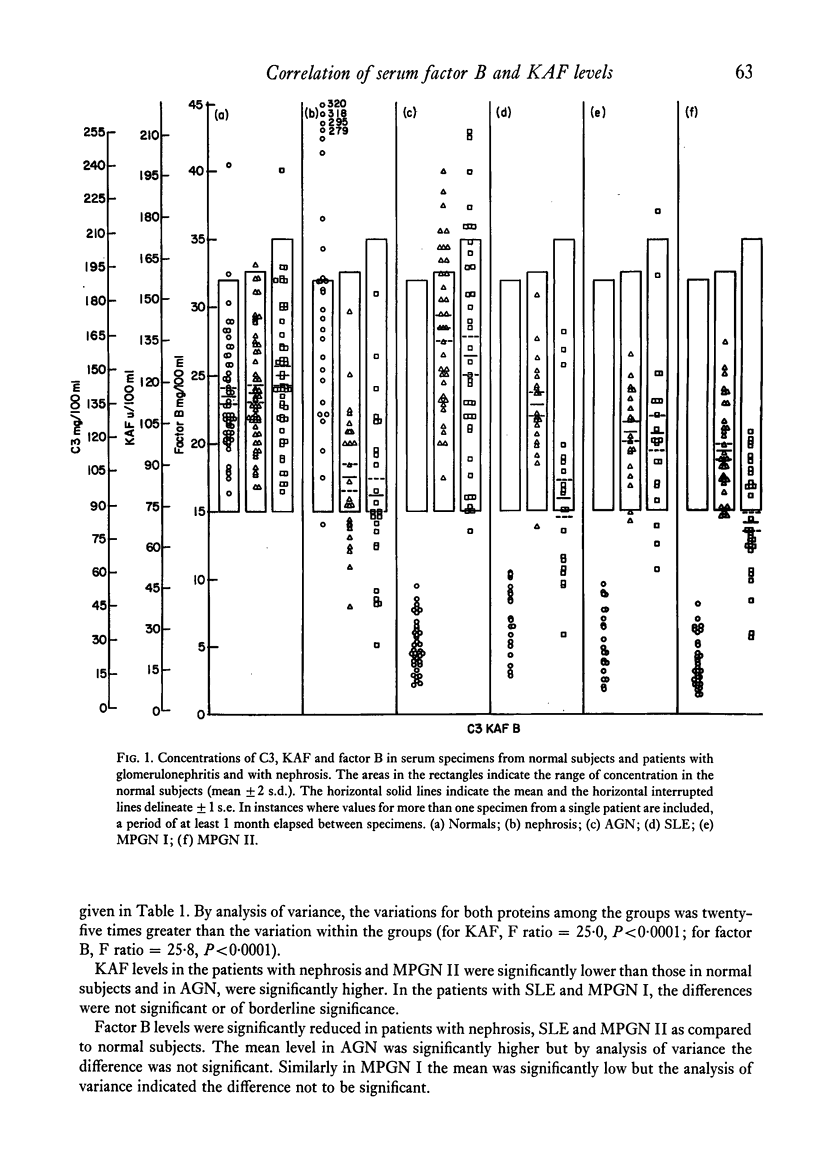
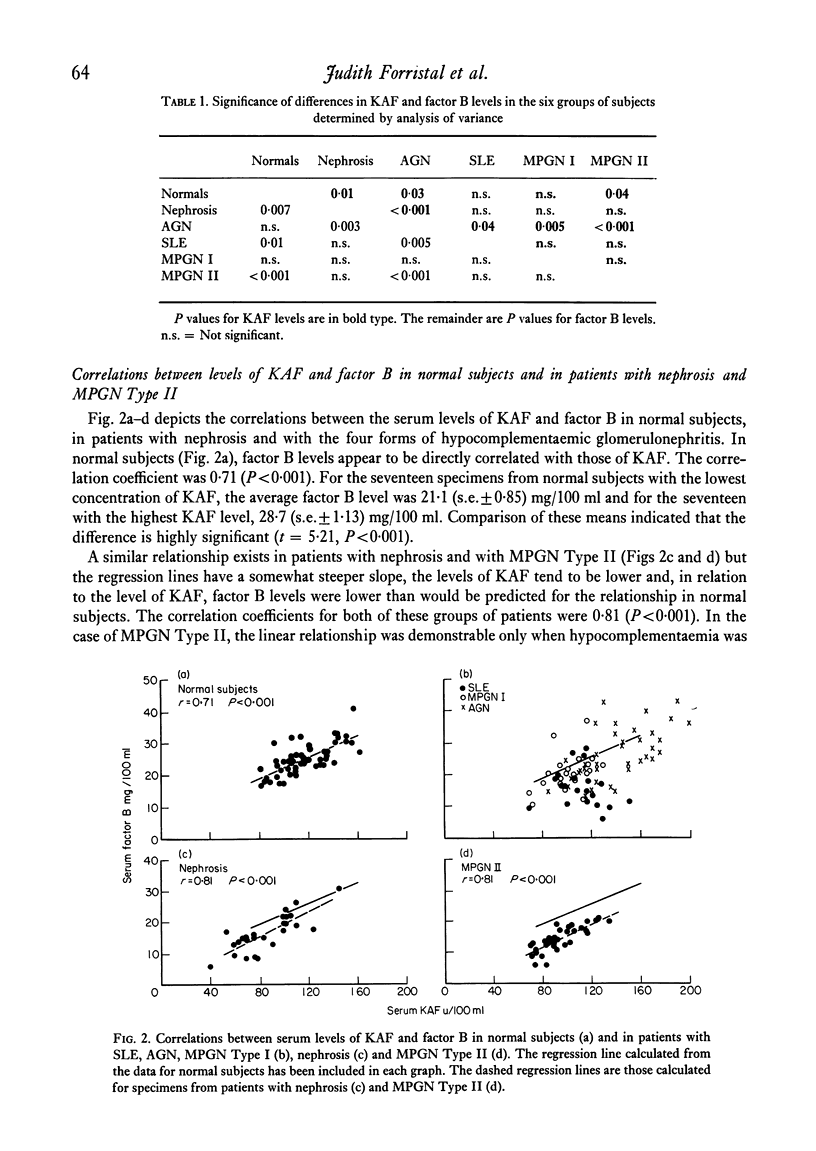
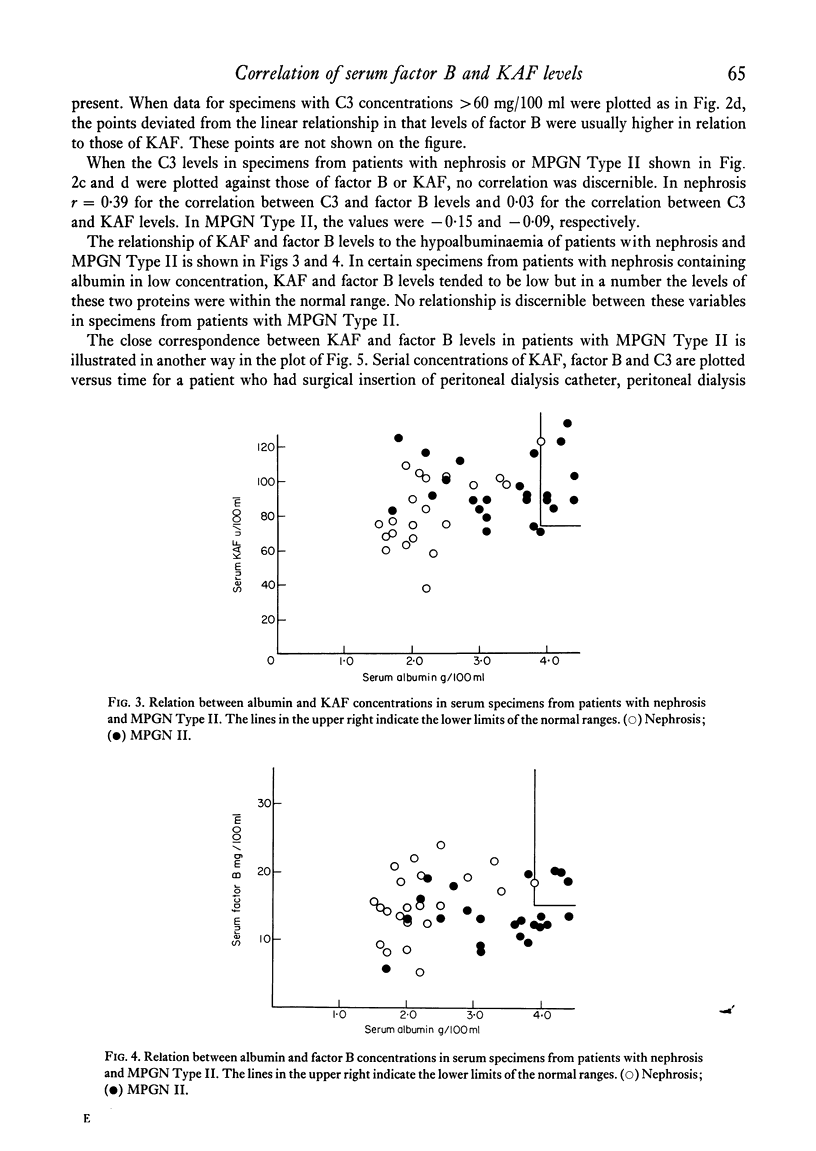
In normal subjects, factor B and C3b inactivator (KAF) levels were linearly related (r = 0-71); factor B levels in subjects with low normal levels of KAF were significantly lower than in those with high normal levels of KAF. This relationship is postulated to be the result of modulation by the level of KAF of the availability of nascent, spontaneously formed, C3b, in turn responsible for a constant low-grade activation of the C3b feedback which determines in part the level of factor B. The correlation did not obtain in patients with infections; levels of KAF and, to a greater extent, factor B were elevated. In patients with glomerulonephritis and hypocomplementaemic because of in vivo classical pathway activation, KAF and factor B levels were also poorly correlated, presumably because many factors were influencing the levels of these proteins transcending the modulating effect of the concentration of KAF. On the other hand, in patients with nephrosis and with MPGN Type II, KAF and factor B levels were low but were directly correlated. In nephrosis the correlation may be the combined result of an equal rate of catabolism of these proteins and of modulation of factor B levels by the level of KAF as in normal subjects. In MPGN Type II, the correlation may reflect the fact, noted in in vitro studies, that with alternative pathway activation, the level of KAF influences the extent of factor B and C3 conversion to a greater extent than when complement is activated by the classical pathway.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramson N., Alper C. A., Lachmann P. J., Rosen F. S., Jandl J. H. Deficiency of C3 inactivator in man. J Immunol. 1971 Jul;107(1):19–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alper C. A., Rosen F. S., Lachmann P. J. Inactivator of the third component of complement as an inhibitor in the properdin pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):2910–2913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
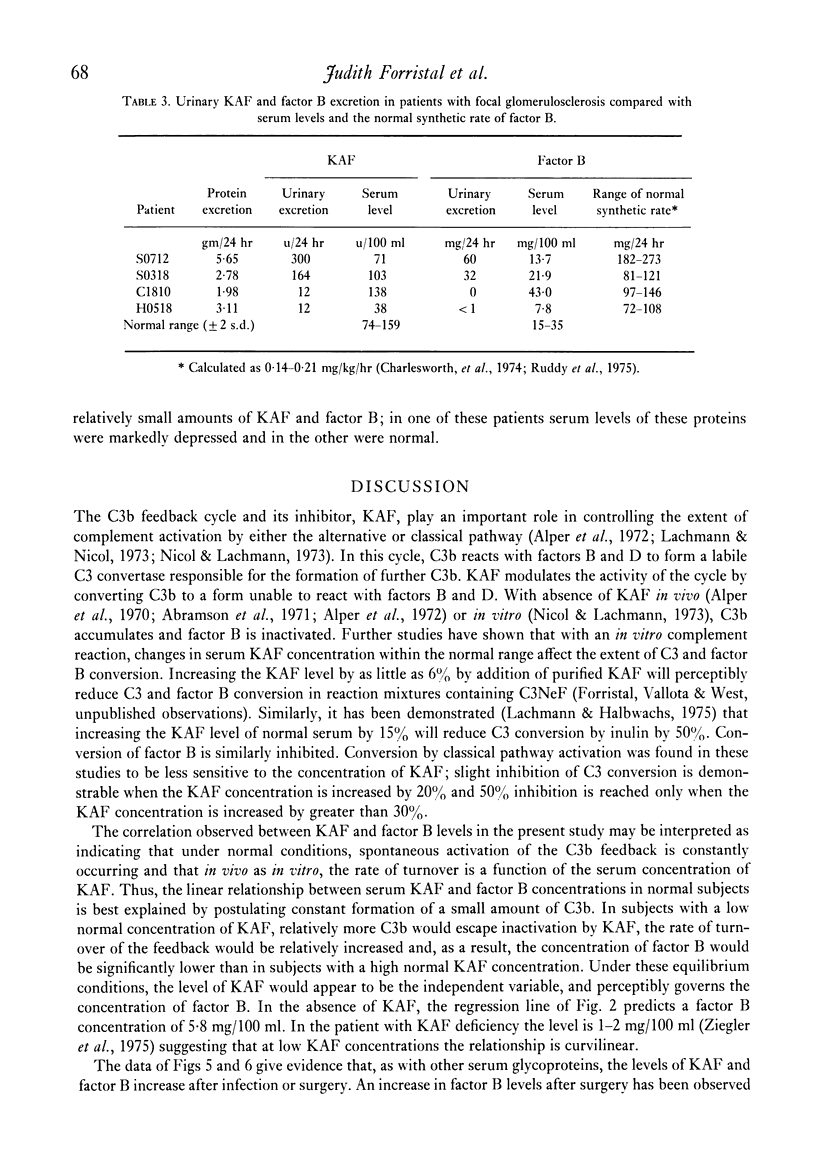
- Charlesworth J. A., Williams D. G., Sherington E., Lachmann P. J., Peters D. K. Metabolic studies of the third component of complement and the glycine-rich beta glycoprotein in patients with hypocomplementemia. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jun;53(6):1578–1587. doi: 10.1172/JCI107708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GITLIN D., JANEWAY C. A., FARR L. E. Studies on the metabolism of plasma proteins in the nephrotic syndrome. I. Albumin, gamma-globulin and iron-binding globulin. J Clin Invest. 1956 Jan;35(1):44–56. doi: 10.1172/JCI103251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOA J. A micro biuret method for protein determination; determination of total protein in cerebrospinal fluid. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1953;5(3):218–222. doi: 10.3109/00365515309094189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habib R., Loirat C., Gubler M., Levy M. Morphology and serum complement levels in membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis. Adv Nephrol Necker Hosp. 1974;4:109–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ J., SELLERS A. L., BONORRIS G. EFFECT OF NEPHRECTOMY ON PLASMA ALBUMIN CATABOLISM IN EXPERIMENTAL NEPHROSIS. J Lab Clin Med. 1964 Apr;63:680–686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. J., Halbwachs L. The influence of C3b inactivator (KAF) concentration on the ability of serum to support complement activation. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Jul;21(1):109–114. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. J., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The demonstration in human serum of "conglutinogen-activating factor" and its effect on the third component of complement. J Immunol. 1968 Apr;100(4):691–698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. J., Nicol P. Reaction mechanism of the alternative pathway of complement fixation. Lancet. 1973 Mar 3;1(7801):465–467. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91886-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis E. J., Carpenter C. B., Schur P. H. Serum complement component levels in human glomerulonephritis. Ann Intern Med. 1971 Oct;75(4):555–560. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-75-4-555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean R. H., Michael A. F. Properdin anc C3 proactivator: alternate pathway components in human glomerulonephritis. J Clin Invest. 1973 Mar;52(3):634–644. doi: 10.1172/JCI107225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicol P. A., Lachmann P. J. The alternate pathway of complement activation. The role of C3 and its inactivator (KAF). Immunology. 1973 Feb;24(2):259–275. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddy S., Austen K. F. C3 inactivator of man. I. Hemolytic measurement by the inactivation of cell-bound C3. J Immunol. 1969 Mar;102(3):533–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schutte M., DiCamelli R., Murphy P., Sadove M., Gewurz H. C3 proactivator (C3PA) as an acute phase reactant. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Oct;18(2):251–256. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strife C. F., McDonald B. M., Ruley E. J., McAdams A. J., West C. D. Shunt nephritis: the nature of the serum cryoglobulins and their relation to the complement profile. J Pediatr. 1976 Mar;88(3):403–413. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)80254-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West C. D., Ruley E. J., Forristal J., Davis N. C. Mechanisms of hypocomplementemia in glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 1973 Feb;3(2):116–125. doi: 10.1038/ki.1973.18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West C., Davis N. C., Forristal J., Herbst J., Spitzer R. Antigenic determinants of human beta-1c and beta-1g-globulins. J Immunol. 1966 Apr;96(4):650–658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whaley K., Schur P. H., Ruddy S. C3b inactivator in the rheumatic diseases. Measurement by radial immunodiffusion and by inhibition of formation of properdin pathway C3 convertase. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jun;57(6):1554–1563. doi: 10.1172/JCI108426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. G., Peters D. K., Fallows J., Petrie A., Kourilsky O., Morel-Maroger L., Cameron J. S. Studies of serum complement in the hypocomplementaemic nephritides. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Nov;18(3):391–405. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler J. B., Alper C. A., Rosen R. S., Lachmann P. J., Sherington L. Restoration by purified C3b inactivator of complement-mediated function in vivo in a patient with C3b inactivator deficiency. J Clin Invest. 1975 Mar;55(3):668–672. doi: 10.1172/JCI107975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


