Abstract
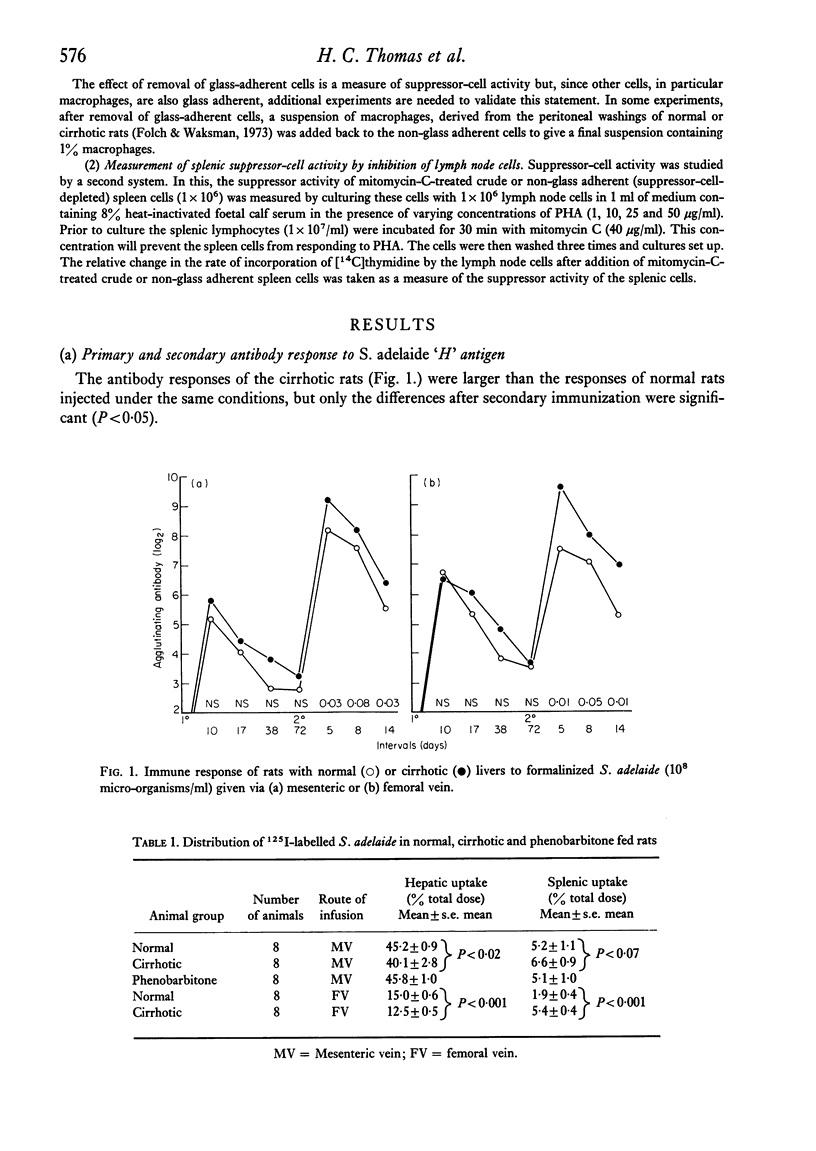
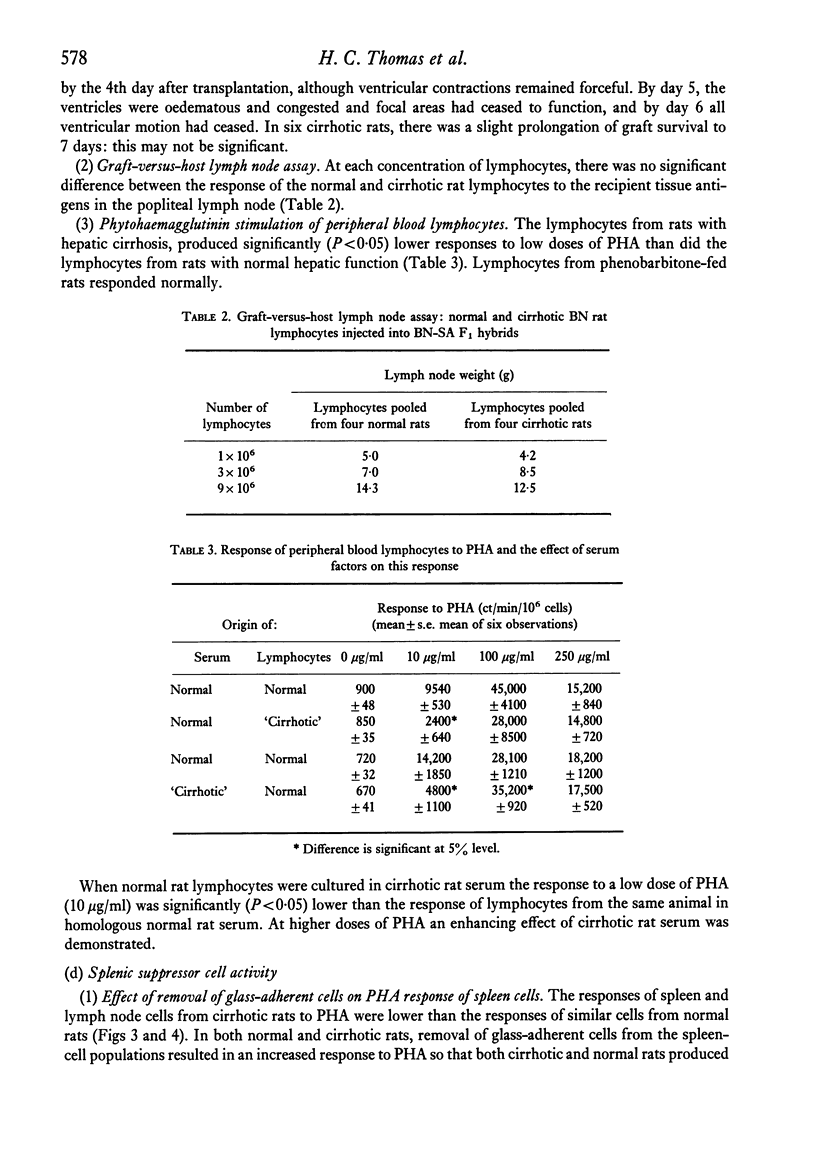
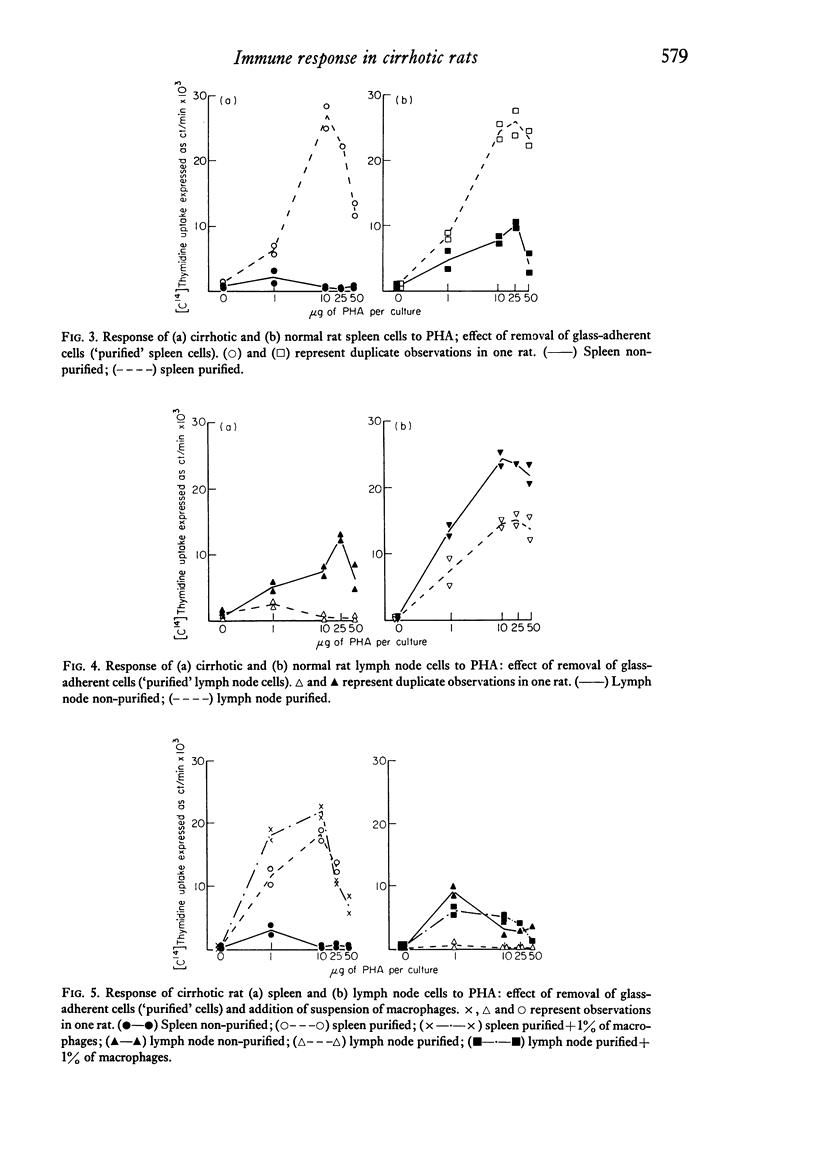
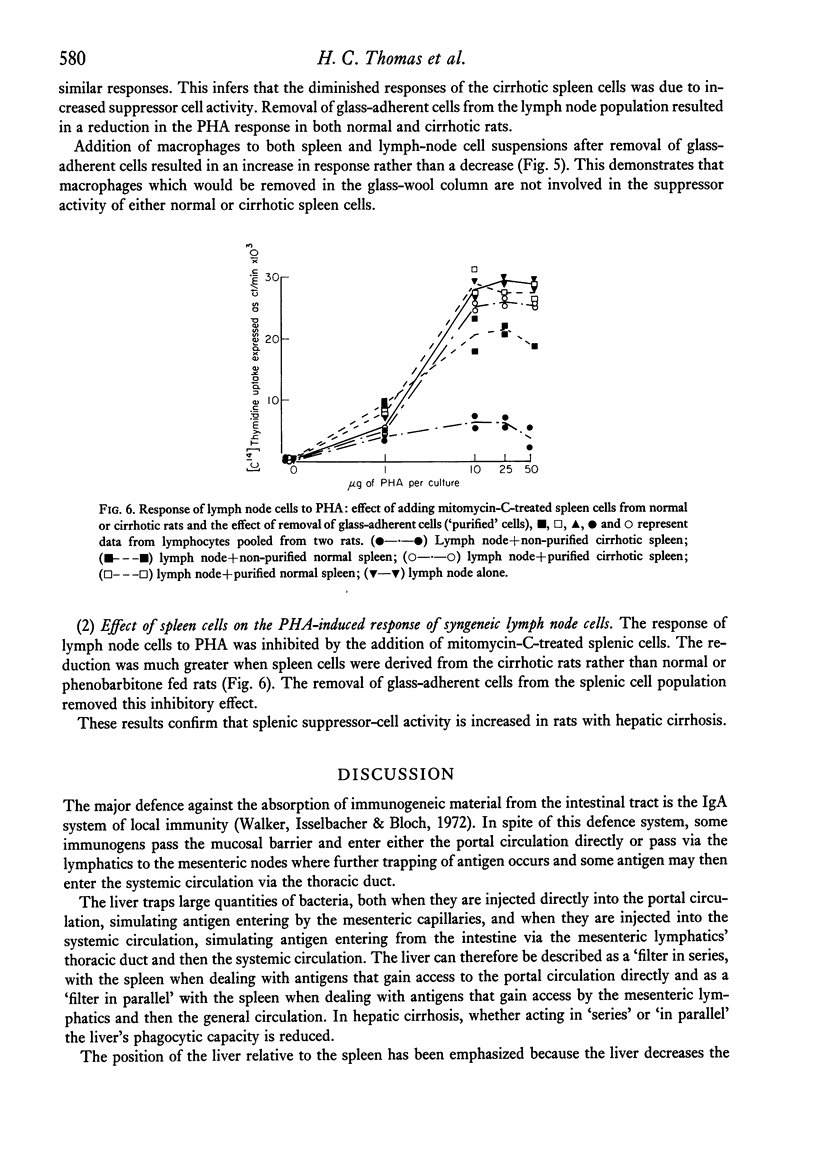
The immunological disturbances occurring as a result of liver disease have been studied in an animal model of cirrhosis. The mononuclear phagocytic cells of the normal liver phagocytose large amounts of antigen irrespective of whether that antigen is injected directly into the portal or into the systemic circulations. The liver therefore acts as a filter 'in series' and 'in parallel' with the spleen and reduces the immunogenicity of antigens entering the organism by either of these routes. In rats with hepatic cirrhosis, there is a reduction in the capacity of the liver to phagocytose the flagellar antigen of Salmonella adelaide. This results in increased stimulation of splenic lymphoid tissue and in an increased antibody response to this thymus-independent antigen. The increased antigenic stimulus to the spleen may also be responsible for the increased suppressor-cell activity which has been demonstrated in these rats, and may be the mechanism of the diminished cell-mediated immune response both in this animal model of cirrhosis and in the human disease state. These studies suggest that many of the immunological disturbances associated with chronic liver disease may be the result of maldistribution of antigen occurring because of impaired hepatic phagocytic capacity.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bash J. A., Waksman B. H. The suppressive effect of immunization on the proliferative responses of rat T cells in vitro. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 2):782–787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berenyi M. R., Straus B., Cruz D. In vitro and in vivo studies of cellular immunity in alcoholic cirrhosis. Am J Dig Dis. 1974 Mar;19(3):199–205. doi: 10.1007/BF01072535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorneboe M. Anti-salmonella agglutinins in chronic active liver disease. Lancet. 1971 Aug 28;2(7722):484–485. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92644-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorneboe M., Prytz H., Orskov F. Antibodies to intestinal microbes in serum of patients with cirrhosis of the liver. Lancet. 1972 Jan 8;1(7741):58–60. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)90060-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorneboe M., Prytz H. Relation between Australia antigen and autoimmune hepatitis. Lancet. 1972 Jun 17;1(7764):1335–1336. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91058-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANZL R. E. Immunogenic sub-cellular particles obtained from spleens of antigen-injected mice. Nature. 1962 Aug 4;195:457–458. doi: 10.1038/195457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folch H., Waksman B. H. Regulation of lymphocyte responses in vitro. V. Suppressor activity of adherent and nonadherent rat lymphoid cells. Cell Immunol. 1973 Oct;9(1):12–24. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(73)90163-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford W. L., Burr W., Simonsen M. A lymph node weight assay for the graft-versus-host activity of rat lymphoid cells. Transplantation. 1970 Sep;10(3):258–266. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197009000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu C. C., Leevy C. M. Inhibition of PHA-stimulated lymphocyte transformation by plasma from patients with advanced alcoholic cirrhosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 May;8(5):749–760. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inchley C. J. The actvity of mouse Kupffer cells following intravenous injection of T4 bacteriophage. Clin Exp Immunol. 1969 Jul;5(1):173–187. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacSween R. N., Thomas M. A. Lymphocyte transformation by phytohaemagglutinin (PHA) and purified protein derivative (PPD) in primary biliary cirrhosis. Evidence of serum inhibitory factors. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Dec;15(4):523–533. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean E. K., McLean A. E., Sutton P. M. Instant cirrhosis. An improved method for producing cirrhosis of the liver in rats by simultaneous administration of carbon tetrachloride and phenobarbitone. Br J Exp Pathol. 1969 Oct;50(5):502–506. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono K., Lindsey E. S. Improved technique of heart transplantation in rats. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1969 Feb;57(2):225–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherlock S., Fox R. A., James D. G., Scheuer P. J., Sharma O. Impaired delayed hypersensitivity in primary biliary cirrhosis. Lancet. 1969 May 10;1(7602):959–962. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)91860-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souhami R. L. The effect of colloidal carbon on the organ distribution of sheep red cells and the immune response. Immunology. 1972 Apr;22(4):685–694. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas H. C., McSween R. N., White R. G. Role of the liver in controlling the immunogenicity of commensal bacteria in the gut. Lancet. 1973 Jun 9;1(7815):1288–1291. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91300-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triger D. R., Alp M. H., Wright R. Bacterial and dietary antibodies in liver disease. Lancet. 1972 Jan 8;1(7741):60–63. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)90061-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker W. A., Isselbacher K. J., Bloch K. J. Intestinal uptake of macromolecules: effect of oral immunization. Science. 1972 Aug 18;177(4049):608–610. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4049.608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willems F. T., Melnick J. L., Rawls W. E. Viral inhibition of the phytohemagglutinin response of human lymphocytes and application to viral hepatitis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Feb;130(2):652–661. doi: 10.3181/00379727-130-33628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolochow H., Hildebrand G. J., Lamanna C. Translocation of microorganisms across the intestinal wall of the rat: effect of microbial size and concentration. J Infect Dis. 1966 Oct;116(4):523–528. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.4.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



