Abstract
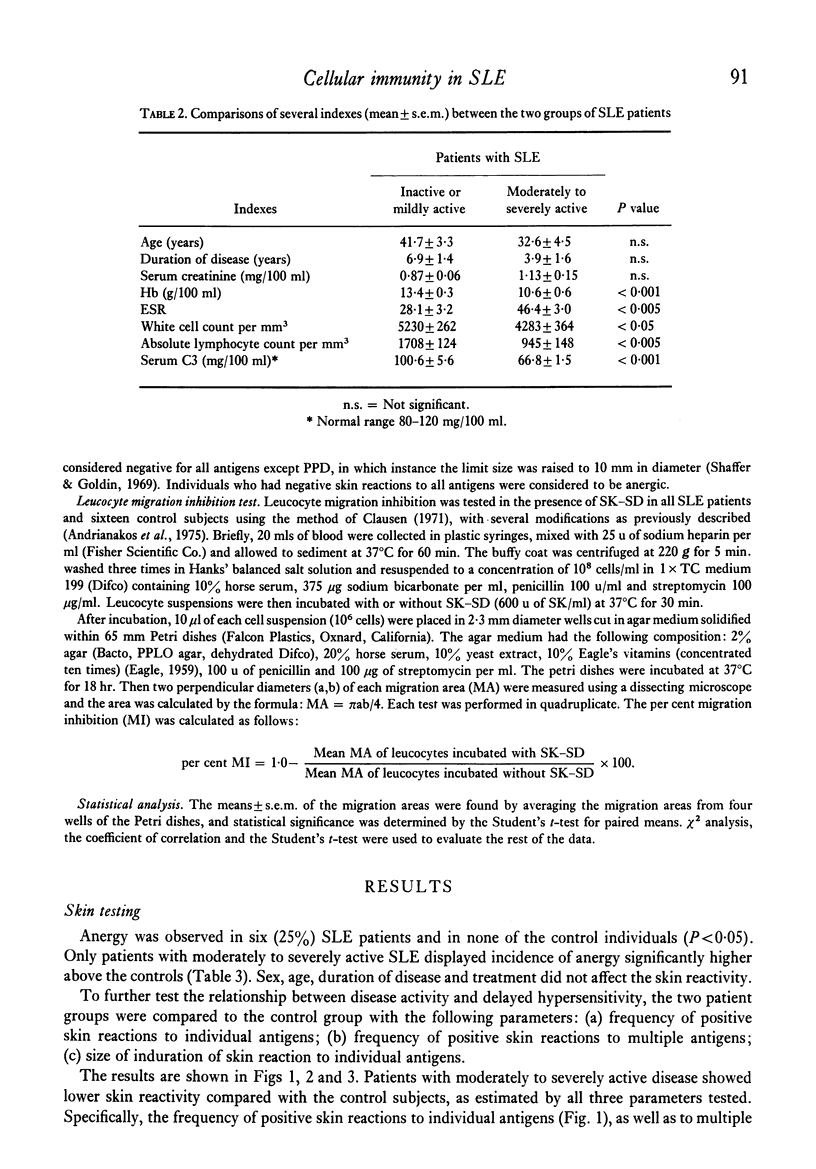
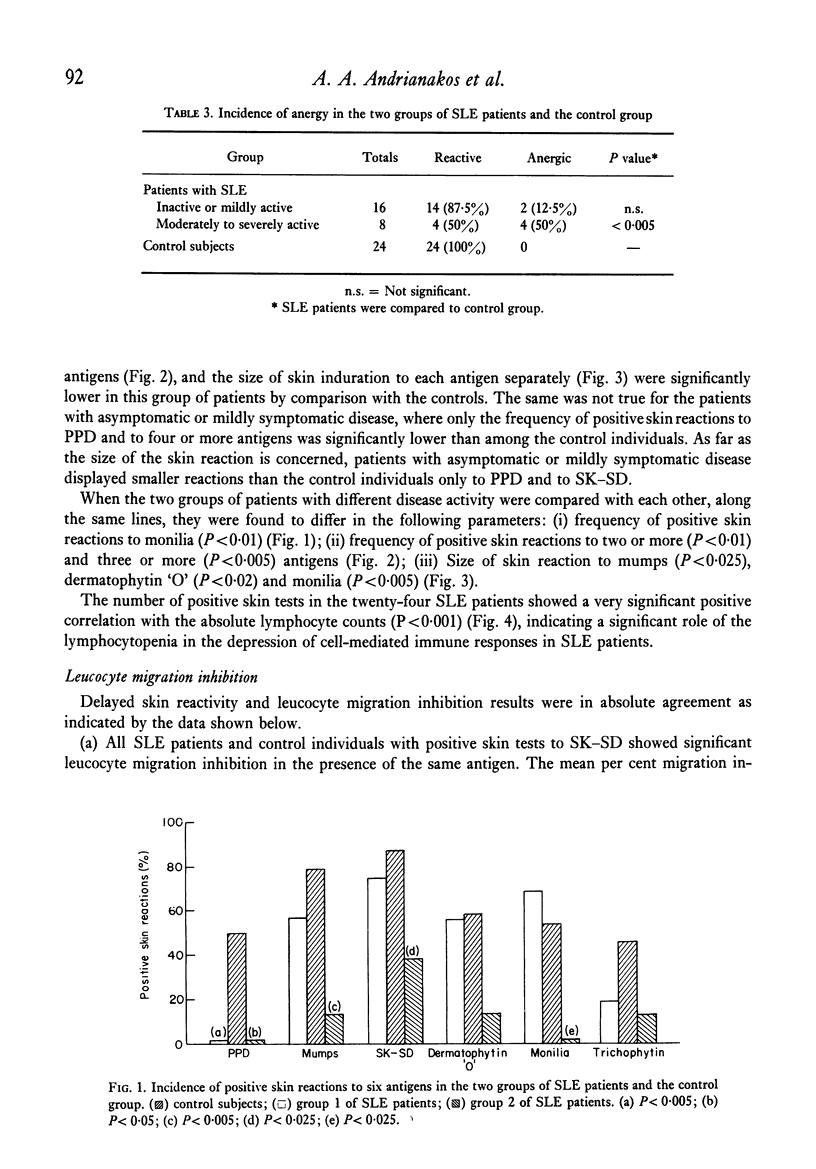
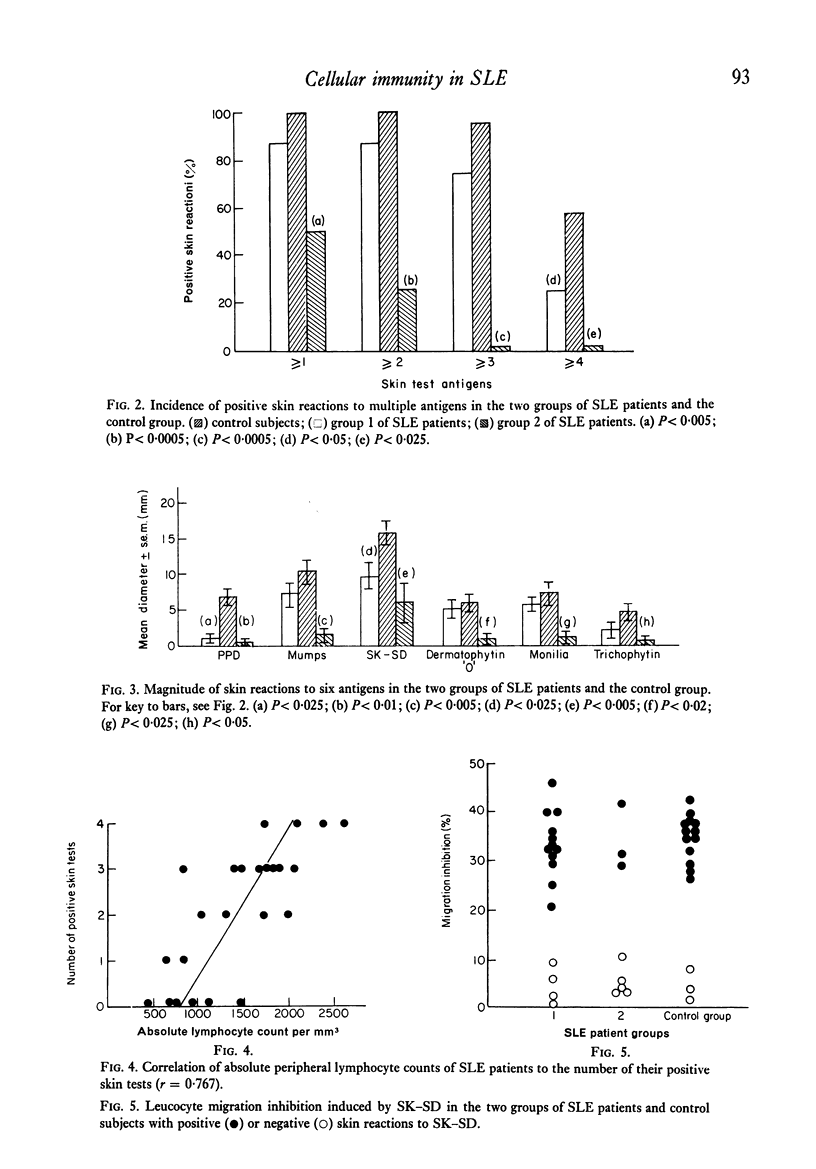
Cell-mediated immunity in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) was assessed by skin testing with six common antigens and by streptokinase-streptodornase (SK–SD) induced leucocyte migration inhibition in twenty-four SLE patients, who were age- and sex-matched with twenty-four healthy subjects or patients with diseases not known to be associated with immunological abnormalities. 25% of SLE patients were anergic, and the migration of their leucocytes was not inhibited in the presence of SK–SD. Depressed cell-mediated immune responses were significantly related to disease activity. Patients with inactive or mildly active SLE exhibited selective hyporeactivity to purified protein derivative (PPD), while those with moderately to severely active SLE had marked depression of cell-mediated immunity, as manifested by both skin testing with common antigens and leucocyte migration inhibition in response to stimulation by SK–SD. A significant positive correlation was found between absolute peripheral lymphocyte counts of the SLE patients and the number of their positive skin tests. Peripheral lymphocyte counts were significantly decreased in the anergic SLE patients and in those with moderate to severe disease activity. The correlation found between skin test reactivity and absolute lymphocyte count suggests lymphocytopenia as the mechanism of the immune suppression. On the other hand, lymphocytopenia alone cannot explain the depression of the leucocyte migration inhibition response to SK–SD observed in the SLE patients, because in this system a relatively constant number of lymphocytes is employed. In conclusion, the depression of cell-mediated immune responses in SLE is caused by both lymphocytopenia and lymphocyte hyporeactivity.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe T., Homma M. Immunological reactivity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Humoral antibody and cellular immune responses. Acta Rheumatol Scand. 1971;17(1):35–46. doi: 10.3109/rhe1.1971.17.issue-1-4.06. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrianakos A. A., Sharp J. T., Person D. A., Lidsky M. D., Duffy J. Cell-mediated immunity in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1977 Feb;36(1):13–20. doi: 10.1136/ard.36.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitter T. Systemic lupus erythematosus: antinuclear serology and cell-mediated immunity in the light of clinico-hematologic diagnostic criteria. Preliminary communication. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1971 Feb 13;101(6):181–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block S. R., Gibbs C. B., Stevens M. B., Shulman L. E. Delayed hypersensitivity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 1968 Jul;27(4):311–318. doi: 10.1136/ard.27.4.311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen J. E. Tuberculin-induced migration inhibition of human peripheral leucocytes in agarose medium. Acta Allergol. 1971 Feb;26(1):56–80. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1971.tb01399.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Amino acid metabolism in mammalian cell cultures. Science. 1959 Aug 21;130(3373):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3373.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foad B. S., Khullar S., Freimer E. H., Kirsner A. B., Sheon R. P. Cell-mediated immunity in systemic lupus erythematosus: alterations with advancing age. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Jan;85(1):132–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman J. A., Litwin A., Adams L. E., Krueger R. C., Hess E. V. Cellular immunity to nuclear antigens in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1972 Oct;51(10):2669–2677. doi: 10.1172/JCI107085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn B. H., Bagby K. K., Osterland C. K. Abnormalities of delayed hypersensitivity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Med. 1973 Jul;55(1):25–31. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(73)90146-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz D. A., Cousar J. B. A relationship between impaired cellular immunity humoral suppression of lymphocyte function and severity of systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Med. 1975 Jun;58(6):829–835. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(75)90639-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz D. A. Impaired delayed hypersensitivity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1972 Jul-Aug;15(4):353–359. doi: 10.1002/art.1780150406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes P., Holt S., Rowell N. R. Leucocyte migration-inhibition in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 1974 Jan;33(1):48–52. doi: 10.1136/ard.33.1.48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lies R. B., Messner R. P., Williams R. C., Jr Relative T-cell specificity of lymphocytotoxins from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1973 May-Jun;16(3):369–375. doi: 10.1002/art.1780160312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockshin M. D., Eisenhauer A. C., Kohn R., Weksler M., Block S., Mushlin S. B. Cell-mediated immunity in rheumatic diseases. II. Mitogen responses in RA, SLE, and other illnesses: correlation with T- and B-lymphocyte populations. Arthritis Rheum. 1975 May-Jun;18(3):245–250. doi: 10.1002/art.1780180308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messner R. P., Lindström F. D., Williams R. C., Jr Peripheral blood lymphocyte cell surface markers during the course of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1973 Dec;52(12):3046–3056. doi: 10.1172/JCI107503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittal K. K., Rossen R. D., Sharp J. T., Lidsky M. D., Butler W. T. Lymphocyte cytotoxic antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Nature. 1970 Mar 28;225(5239):1255–1256. doi: 10.1038/2251255a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrucco A., Rothfield N. F., Hirschhorn K. The response of cultured lymphocytes from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus to DNA. Arthritis Rheum. 1967 Feb;10(1):32–37. doi: 10.1002/art.1780100105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paty J. G., Jr, Sienknecht C. W., Townes A. S., Hanissian A. S., Miller J. B., Masi A. T. Impaired cell-mediated immunity in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). A controlled study of 23 untreated patients. Am J Med. 1975 Dec;59(6):769–779. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(75)90462-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal C. J., Franklin E. C. Depression of cellular-mediated immunity in systemic lupus erythematosus. relation to disease activity. Arthritis Rheum. 1975 May-Jun;18(3):207–217. doi: 10.1002/art.1780180303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan J. L., Arbeit R. D., Dickler H. B., Henkart P. A. Inhibition of lymphocyte mitogenesis by immobilized antigen-antibody complexes. J Exp Med. 1975 Oct 1;142(4):814–826. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.4.814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheinberg M. A., Cathcart E. S. B cell and T cell lymphopenia in systemic lupus erythematosus. Cell Immunol. 1974 May;12(2):309–314. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(74)90083-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senyk G., Hadley W. K., Attias M. R., Talal N. Cellular immunity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1974 Sep-Oct;17(5):553–562. doi: 10.1002/art.1780170509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stastny P., Ziff M. Antibodies against cell membrane constituents in systemic lupus erythematosus and related diseases. I. Cytotoxic effect of serum from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) for allogeneic and for autologous lymphocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Apr;8(4):543–550. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terasaki P. I., Mottironi V. D., Barnett E. V. Cytotoxins in disease. Autocytotoxins in lupus. N Engl J Med. 1970 Oct 1;283(14):724–728. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197010012831403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toh B. H., Roberts-Thomson I. C., Mathews J. D., Whittingham S., Mackay I. R. Depression of cell-mediated immunity in old age and the immunopathic diseases, lupus erythematosus, chronic hepatitis and rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Jun;14(2):193–202. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utsinger P. D. Lymphocyte responsiveness in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1976 Jan-Feb;19(1):88–92. doi: 10.1002/art.1780190115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wernet P., Kunkel H. G. Antibodies to a specific surface antigen of T cells in human sera inhibiting mixed leukocyte culture reactions. J Exp Med. 1973 Oct 1;138(4):1021–1026. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.4.1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winchester R. J., Winfield J. B., Siegal F., Wernet P., Bentwich Z., Kunkel H. G. Analyses of lymphocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Occurrence of interfering cold-reactive antilymphocyte antibodies. J Clin Invest. 1974 Nov;54(5):1082–1092. doi: 10.1172/JCI107852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


