Abstract
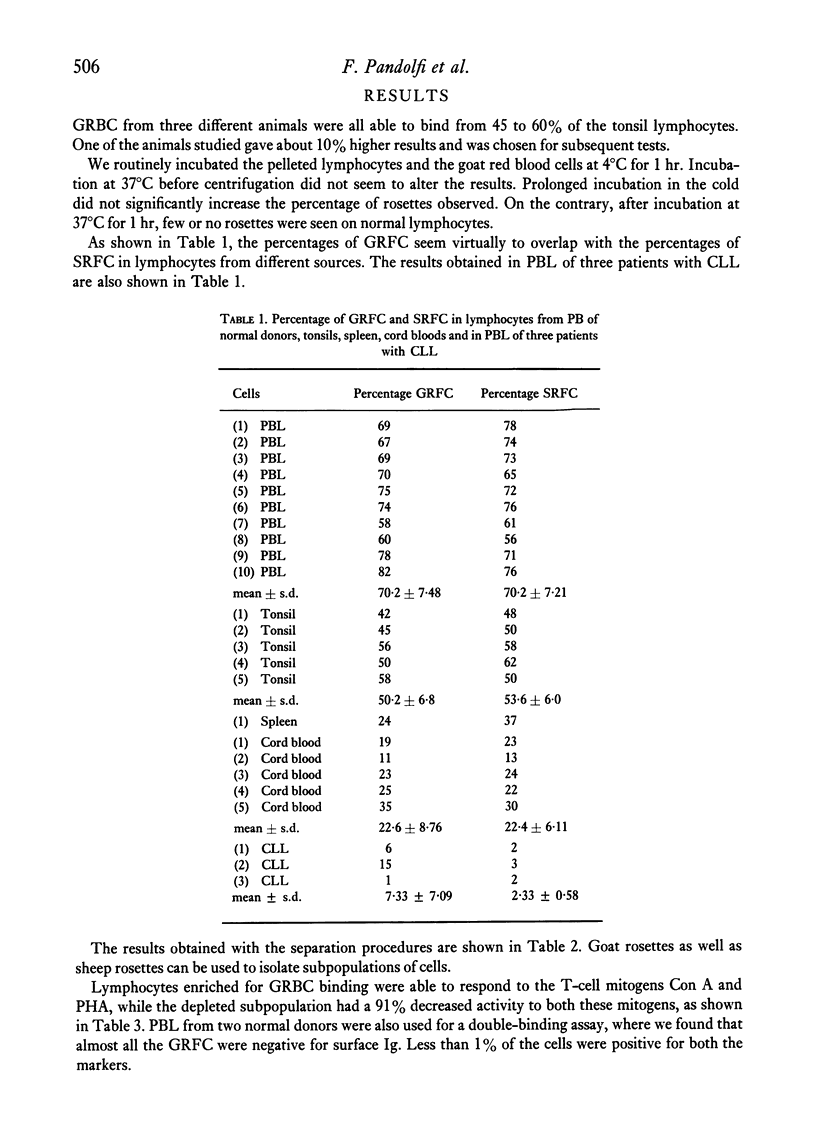
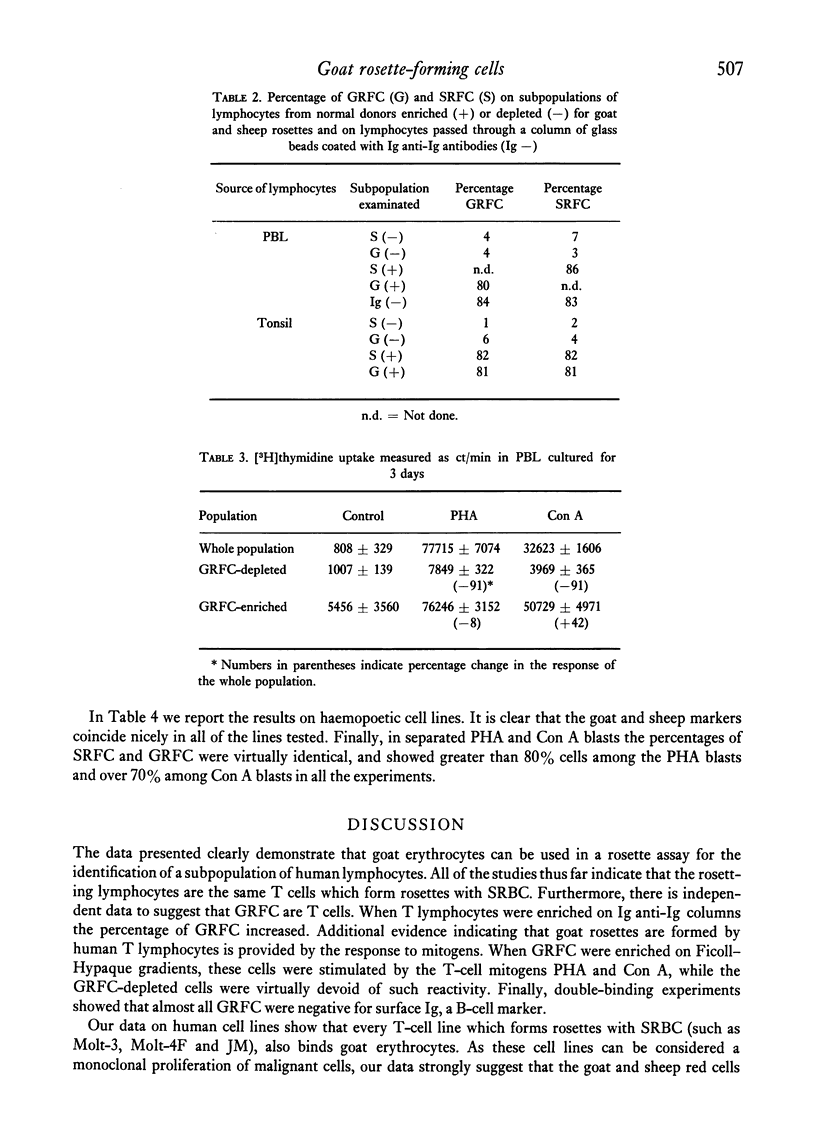
We demonstrate the use of goat erythrocytes in a rosette procedure for the classification of human lymphocytes. The population is almost perfectly overlapping with the lymphocytes which form rosettes with sheep red blood cells. 70·2 ± 7·5% of peripheral lymphocytes form rosettes with goat erythrocytes and less than 1% of these cells have surface immunoglobulins. Enrichment of goat rosette-forming cells results in a population with an increased percentage of both goat and sheep rosettes. This population retains activity to the T-cell mitogens Con A and PHA, while the cells depleted of goat rosettes have greatly diminished responses to these same mitogens. Tonsil and spleen lymphocytes form 50·2 ± 6·8% and 24% of goat rosettes respectively, while peripheral blood lymphocytes from patients with CLL rarely form goat rosettes. Cell lines maintained in vitro rosetted with goat cells in a parallel fashion to sheep cells. Thus T-cell lines, such as Molt-3, which form rosettes with SRBC also rosette with GRBC, while sheep rosette-negative lines, i.e. Molt-4, are negative for both erythrocytes. B-lymphoid cell lines were negative, as were several lymphoma cell lines. There was a slight variation in the binding of goat cells, depending on the source of the goat. Thus, as in sheep rosettes, some animals were better sources than others, although all the animals tested formed rosettes.
Human lymphocytes are capable of binding goat red cells. The cells which bind to the erythrocytes seem identical to those binding sheep red blood cells, and should be considered as a T-cell population. Preliminary inhibition data suggests that the receptor on T cells is the very same structure for both erythrocytes.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiuti F., Wigzell H. Function and distribution pattern of human T lymphocytes. I. Production of anti-T lymphocyte specific sera as estimated by cytotoxicity and elimination of function of lymphocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Feb;13(2):171–181. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borella L., Sen L. E receptors on blasts from untreated acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL): comparison of temperature dependence of E rosettes formed by normal and leukemic lymphoid cells. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 1):187–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brouet J., Toben H. Characterization of a subpopulation of human T lymphocytes reactive with an heteroantiserum to human brain. J Immunol. 1976 Apr;116(4):1041–1044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor H., Boyse E. A. Functional subclasses of T-lymphocytes bearing different Ly antigens. I. The generation of functionally distinct T-cell subclasses is a differentiative process independent of antigen. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1376–1389. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisari F. V., Gealy W. J., Edgington T. S. Recovery of soluble sheep erythrocyte receptor from the T lymphocyte surface by proteolytic cleavage. J Immunol. 1977 Apr;118(4):1138–1142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M., Holm G., Wigzell H. Surface markers on human T and B lymphocytes. I. A large population of lymphocytes forming nonimmune rosettes with sheep red blood cells. J Exp Med. 1972 Aug 1;136(2):207–215. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M., Klein G. Surface markers on human B and T lymphocytes. II. Presence of Epstein-Barr virus receptors on B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1973 Dec 1;138(6):1365–1378. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.6.1365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lay W. H., Mendes N. F., Bianco C., Nussenzweig V. Binding of sheep red blood cells to a large population of human lymphocytes. Nature. 1971 Apr 23;230(5295):531–532. doi: 10.1038/230531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minowada J., Onuma T., Moore G. E. Rosette-forming human lymphoid cell lines. I. Establishment and evidence for origin of thymus-derived lymphocytes. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 Sep;49(3):891–895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta L., Ferrarini M., Durante M. L., Mingari M. C. Expression of a receptor for IgM by human T cells in vitro. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Aug;5(8):565–569. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson K., Pontén J. Classification and biological nature of established human hematopoietic cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1975 Feb 15;15(2):321–341. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910150217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrino M. A., Ferrone S., Theofilopoulos A. N. Rosette formation of human lymphoid cells with monkey red blood cells. J Immunol. 1975 Oct;115(4):1065–1071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pernis B., Forni L., Amante L. Immunoglobulin spots on the surface of rabbit lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1970 Nov;132(5):1001–1018. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.5.1001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyke K. W., Rawlings G. A., Gelfand E. W. Isolation and characterization of the sheep erythrocyte receptor in man. J Immunol. 1975 Jul;115(1):211–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C. Surface antigenic markers for distinguishing T and B lymphocytes in mice. Transplant Rev. 1971;6:52–80. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1971.tb00459.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stathopoulos G., Elliott E. V. Formation of mouse or sheep red-blood-cell rosettes by lymphocytes from normal and leukaemic individuals. Lancet. 1974 Apr 6;1(7858):600–601. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92655-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigzell H., Sundqvist K. G., Yoshida T. O. Separation of cells according to surface antigens by the use of antibody-coated columns. Fractionation of cells carrying immunoglobulins and blood group antigen. Scand J Immunol. 1972;1(1):75–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1972.tb03737.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


