Abstract
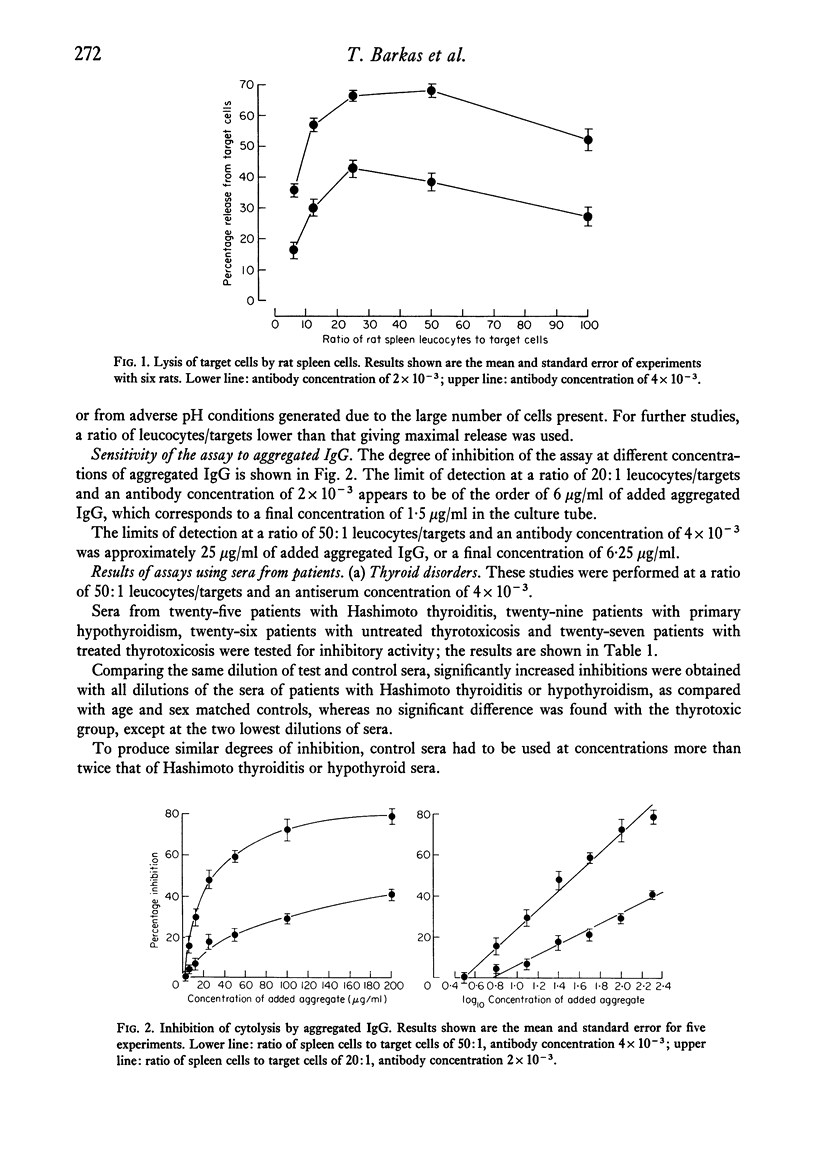
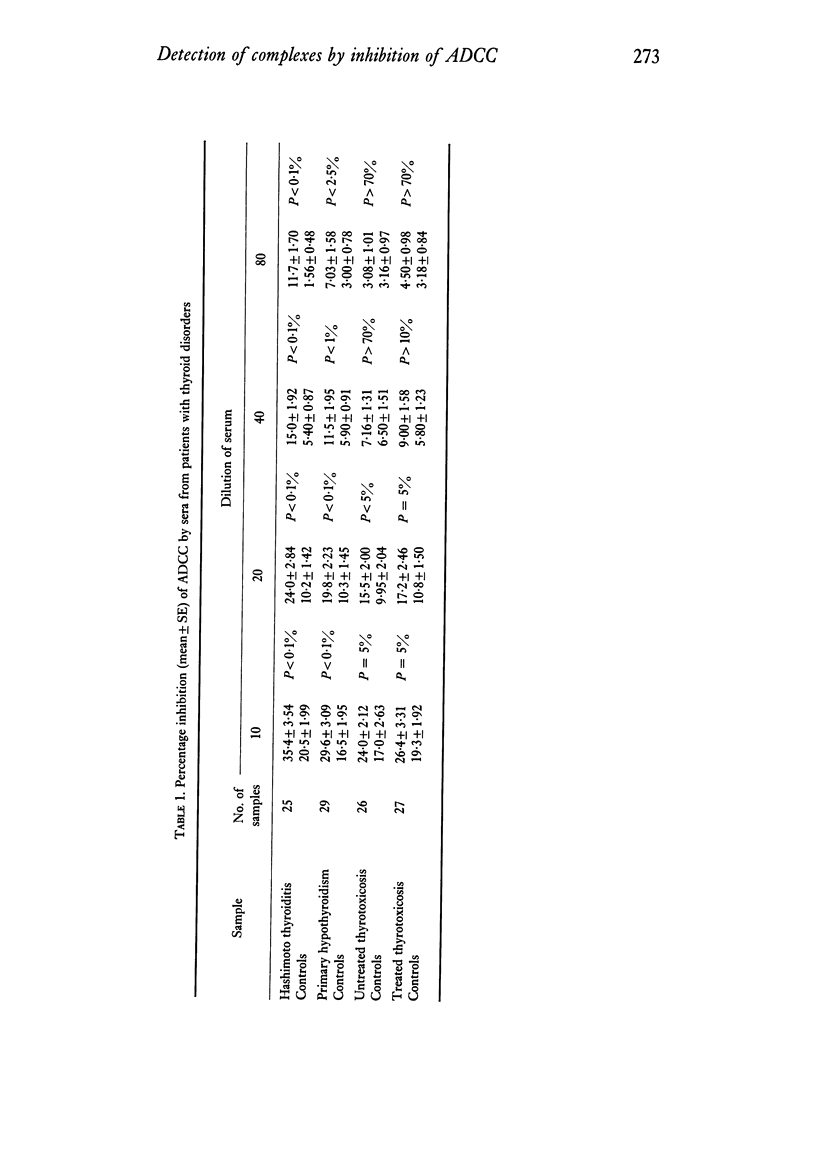
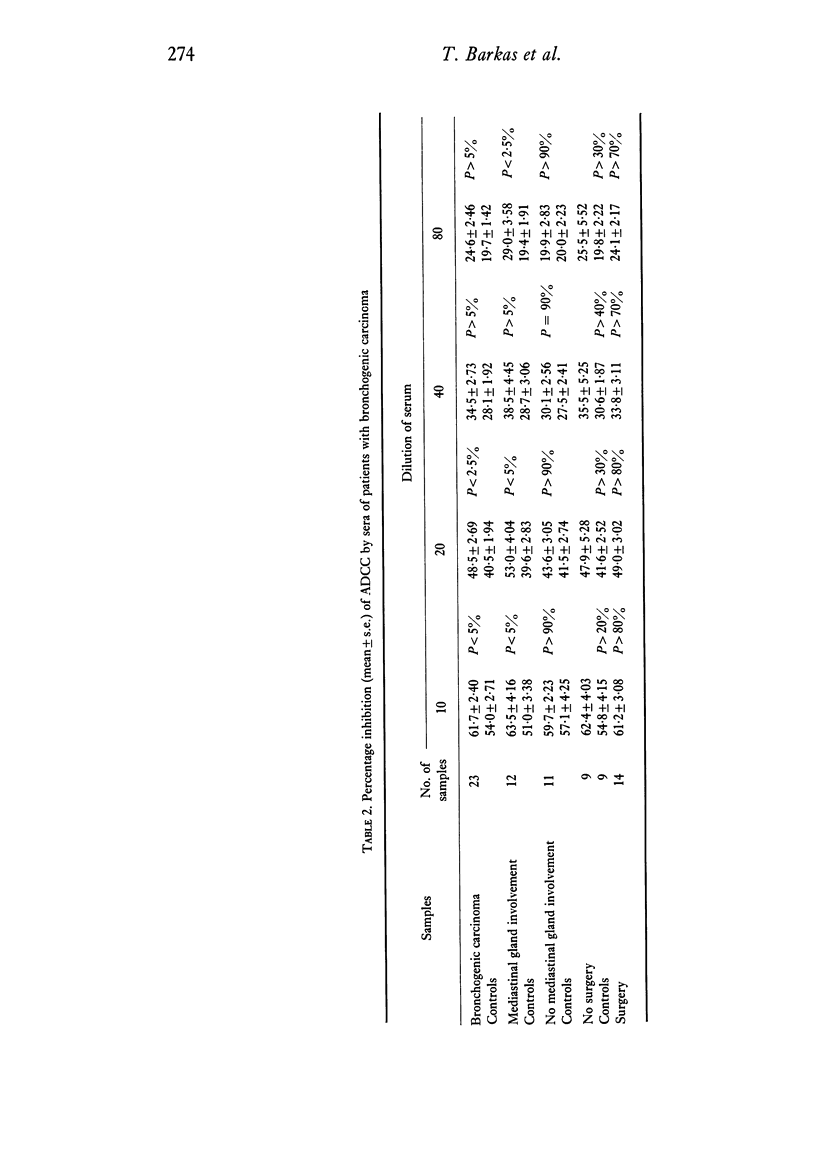
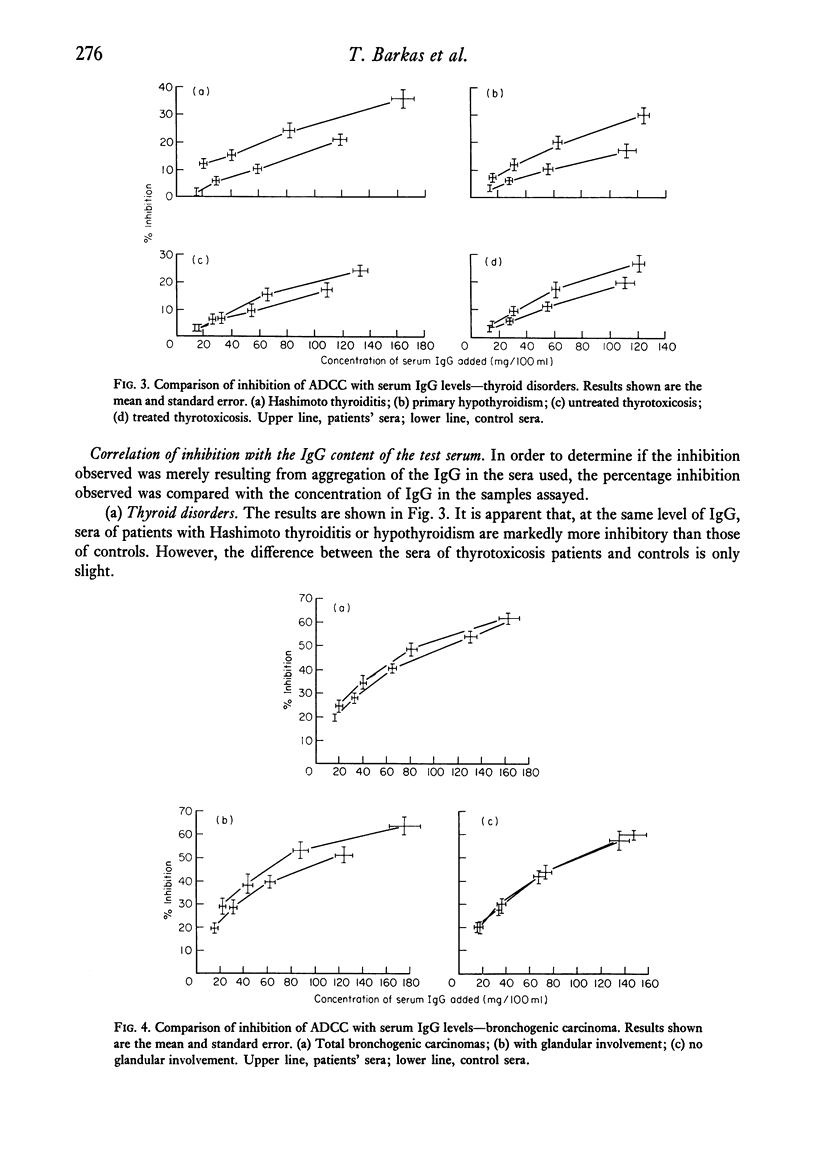
Circulating immune complexes in the sera of patients with thyroid disorders or bronchogenic carcinoma were investigated using an assay system based on the inhibition of the ADCC activity of rat spleen cells. Increased inhibition, as compared with that of the sera of age and sex matched controls, was found in patients with thashimoto thyroiditis, primary hypothyroidism and bronchogenic carcinoma. The degree of inhibition in the first two groups was markedly increased compared with control sera of the same IgG content. However, the results in the lung cancer group were slightly but not significantly greater than in controls with the same level of IgG. Increased IgG levels were found in patients with thashimoto thyroiditis and thyrotoxicosis, and also in patients with bronchogenic carcinoma who had mediastinal gland involvement. The lower level of sensitivity of the assay system was approximately 600 ng added aggregated IgG, corresponding to a concentration of 6mu g/ml in the sample assayed. It is possible that circulating immune complexes may exist in lung cancer, but at a level below that of the present assay system.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHRISTIAN C. L. Studies of aggregated gamma-globulin. I. Sedimentation, electrophoretic and anticomplementary properties. J Immunol. 1960 Jan;84:112–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calder E. A., McLeman D., Irvine W. J. Lymphocyte cytotoxicity induced by pre-incubation with serum from patients with Hashimoto thyroiditis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Nov;15(3):467–470. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calder E. A., Penhale W. J., McLeman D., Barnes E. W., Irvine W. J. Lymphocyte-dependent antibody-mediated cytotoxicity in Hashimoto thyroiditis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Jun;14(2):153–158. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowdery J. S., Jr, Treadwell P. E., Fritz R. B. A radioimmunoassay for human antigen-antibody complexes in clinical material. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 1):5–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eden A., Bianco C., Nussenzweig Mechanism of binding of soluble immune complexes to lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1973 Jun;7(3):459–473. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(73)90210-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand E. W., Morris S. A., Resch K. Antibody-dependent cytotoxicity: modulation by the cytochalasins and microtubule-disruptive agents. J Immunol. 1975 Mar;114(3):919–924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynne A., Thomson J. A. Serum immunoglobulin levels in thyroid disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Sep;12(1):71–78. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes N. R. Serum concentrations of G, A, and M immunoglobulins in patients with carcinoma, melanoma, and sarcoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1971 May;46(5):1015–1028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jewell D. P., MacLennan I. C. Circulating immune complexes in inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Jun;14(2):219–226. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon A. E., Bogaars H. A., Diamond I. Ultrastructural alterations of the follicular basement membrane in Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Report of eight cases with basement deposits. Am J Med. 1973 Oct;55(3):485–491. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(73)90205-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUXTON R. W., COOKE R. T. Hashimoto's struma lymphomatosa; diagnostic value and significance of serum-flocculation reactions. Lancet. 1956 Jul 21;271(6934):105–109. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(56)90860-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lustig H. J., Bianco C. Antibody-mediated cell cytotoxicity in a defined system: regulation by antigen, antibody, and complement. J Immunol. 1976 Jan;116(1):253–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luthra H. S., McDuffie F. C., Hunder G. G., Samayoa E. A. Immune complexes in sera and synovial fluids of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Radioimmunoassay with monocylonal rheumatoid factor. J Clin Invest. 1975 Aug;56(2):458–466. doi: 10.1172/JCI108112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan I. C. Competition for receptors for immunoglobulin on cytotoxic lymphocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Feb;10(2):275–283. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michael A. F., Jr, Drummond K. N., Good R. A., Vernier R. L. Acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis: immune deposit disease. J Clin Invest. 1966 Feb;45(2):237–248. doi: 10.1172/JCI105336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nydegger U. E., Lambert P. H., Gerber H., Miescher P. A. Circulating immune complexes in the serum in systemic lupus erythematosus and in carriers of hepatitis B antigen. Quantitation by binding to radiolabeled C1q. J Clin Invest. 1974 Aug;54(2):297–309. doi: 10.1172/JCI107765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill P., Mackler B. F., Wyde P. Complement (C3) receptor-bearing lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity and lymphotoxin responses. Cell Immunol. 1975 Nov;20(1):33–41. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(75)90081-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada H., Baba T. Rosette formation of human erythrocytes on cultured cells of tumour origin and activation of complement by cell membrane. Nature. 1974 Apr 5;248(448):521–522. doi: 10.1038/248521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onyewotu I. I., Holborow E. J., Johnson G. D. Detection and radioassay of soluble circulating immune complexes using guinea pig peritoneal exudate cells. Nature. 1974 Mar 8;248(5444):156–159. doi: 10.1038/248156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B. Complement-mediated mixed aggregation of murine spleen cells. Nature. 1974 May 3;249(452):51–53. doi: 10.1038/249051a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann P., Perlmann H., Müller-Eberhard H. J., Manni J. A. Cytotoxic effects of leukocyres triggered by complement bound to target cells. Science. 1969 Feb 28;163(3870):937–939. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3870.937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platts-Mills T. A., Ishizaka K. Activation of the alternate pathway of human complements by rabbit cells. J Immunol. 1974 Jul;113(1):348–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKILLERN P. G., CRILE G., Jr, MCCULLAGH E. P., HAZARD J. B., LEWIS L. A., BROWN H. Struma lymphomatosa: primary thyroid failure with compensatory thyroid enlargement. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1956 Jan;16(1):35–54. doi: 10.1210/jcem-16-1-35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scornik J. C., Drewinko B. Receptors for IgG and complement in human spleen lymphoid cells. Preferential binding of particulate immune complexes through complement receptors. J Immunol. 1975 Nov;115(5):1223–1226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Schur P. H., Carr R. I., Kunkel H. G. Deoxybonucleic acid (DNA) and antibodies to DNA in the serum of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1966 Nov;45(11):1732–1740. doi: 10.1172/JCI105479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theofilopoulos A. N., Wilson C. B., Bokisch V. A., Dixon F. J. Binding of soluble immune complexes to human lymphoblastoid cells. II. Use of Raji cells to detect circulating immune complexes in animal and human sera. J Exp Med. 1974 Nov 1;140(5):1230–1244. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.5.1230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theofilopoulos A. N., Wilson C. B., Dixon F. J. The Raji cell radioimmune assay for detecting immune complexes in human sera. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jan;57(1):169–182. doi: 10.1172/JCI108257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedermann G., Denk H., Stemberger H., Eckerstorfer R., Tappeiner G. Influence of the antigenicity of target cells on the antibody-mediated cytotoxicity of nonsensitized lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1975 Jun;17(2):440–446. doi: 10.1016/s0008-8749(75)80048-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman T. S., Kolb W. P. Human platelet-initiated formation and uptake of the C5-9 complex of human complement. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jan;57(1):203–211. doi: 10.1172/JCI108261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


