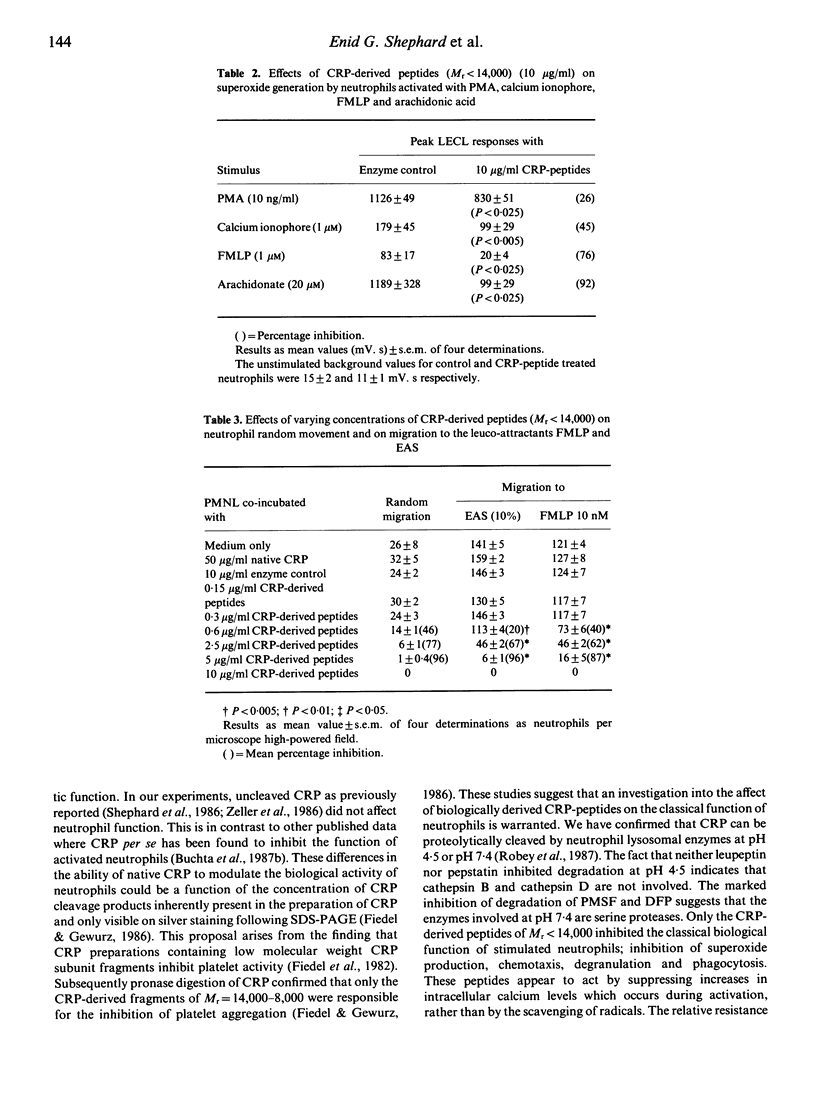
Abstract
Hydrolysis of human C-reactive protein (CRP) at pH 4.5 and pH 7.4 with neutrophil-derived lysosomal enzymes yielded 10% trichloroacetic acid soluble peptides (Mr less than 14,000). These peptides inhibited neutrophil superoxide production, chemotaxis, degranulation and phagocytosis at 2 micrograms/ml. This inhibition was not observed with native CRP or intermediate peptides (Mr greater than 14,000). CRP peptides (Mr less than 14,000) also caused a dose-related inhibition of Quin-2 fluorescence indicating interference with intracellular calcium movements during cell activation. These results point to a potential regulatory role for CRP-derived degradation products on neutrophils during inflammation.
Full text
PDF

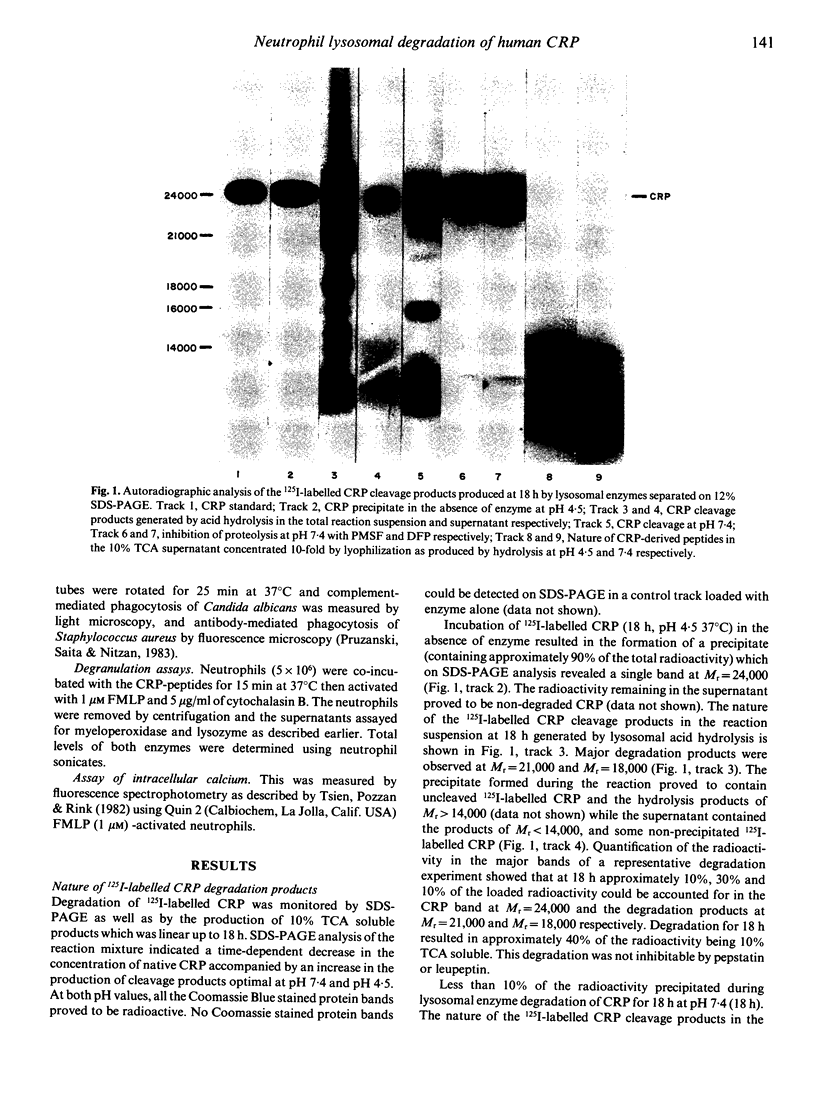
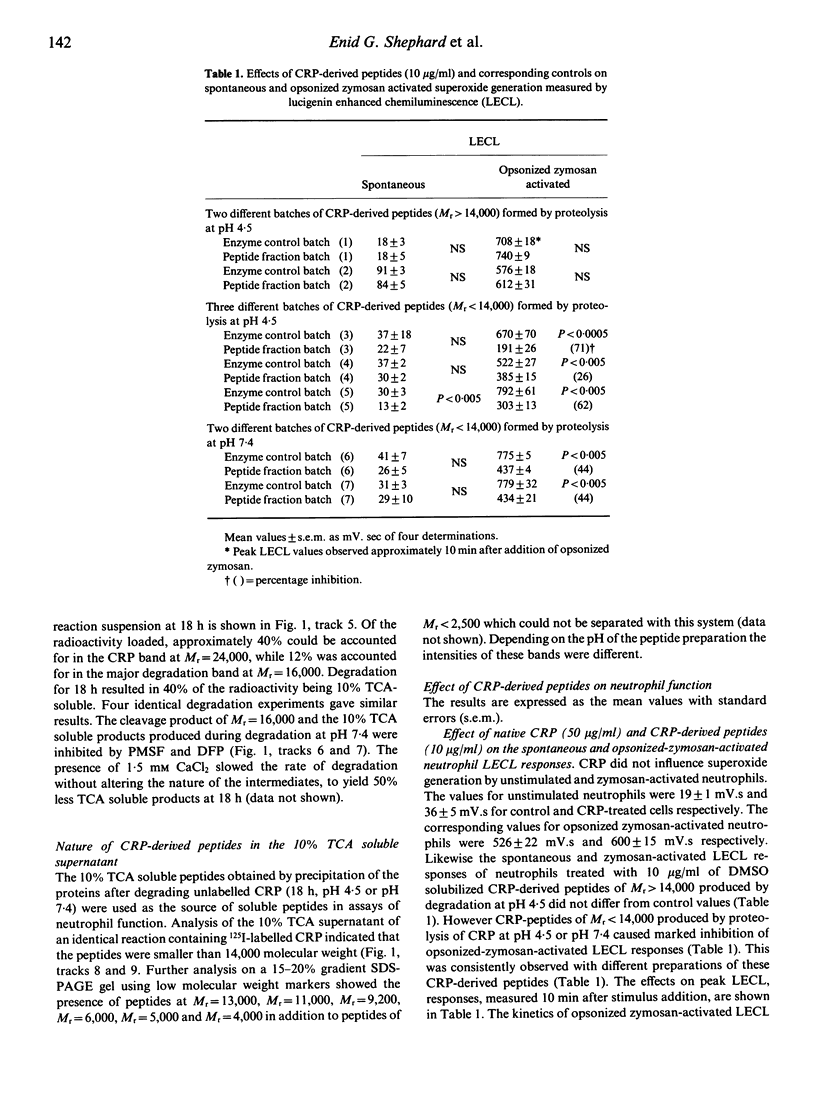
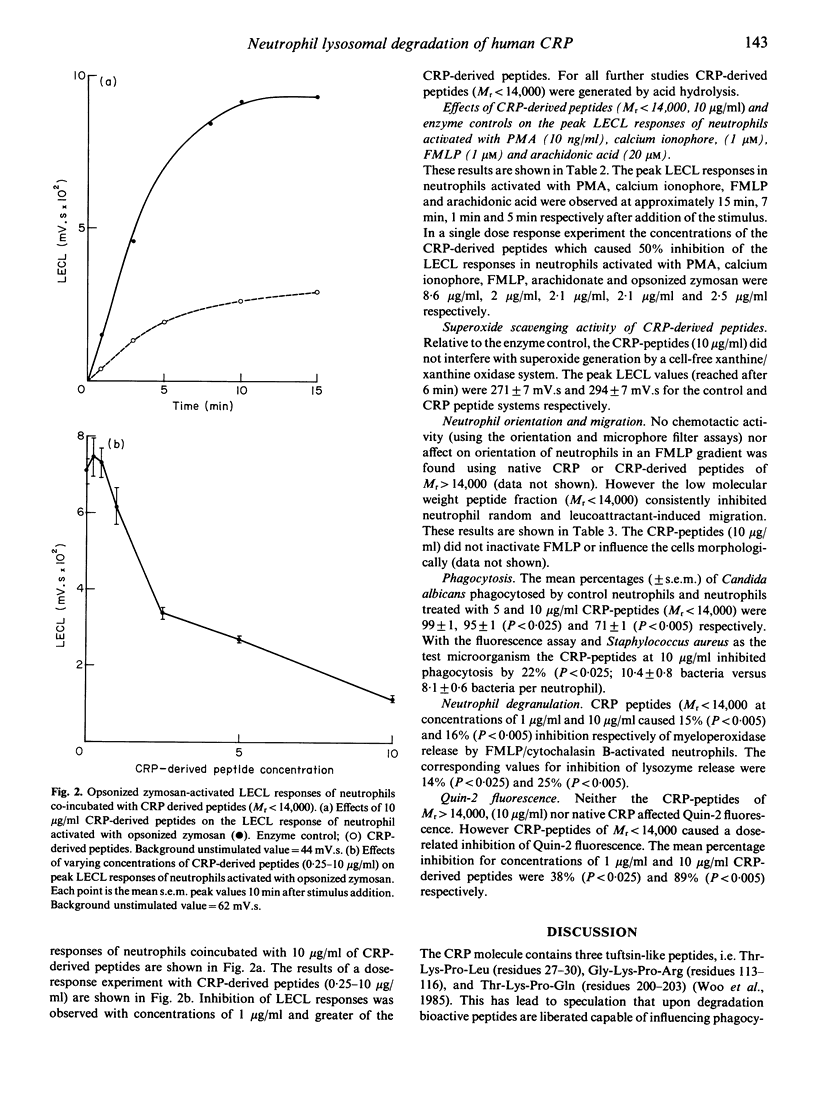

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bentwood B. J., Henson P. M. The sequential release of granule constitutents from human neutrophils. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):855–862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briheim G., Stendahl O., Dahlgren C. Intra- and extracellular events in luminol-dependent chemiluminescence of polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):1–5. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.1-5.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchta R., Fridkin M., Pontet M., Contessi E., Scaggiante B., Romeo D. Modulation of human neutrophil function by C-reactive protein. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Feb 16;163(1):141–146. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb10747.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchta R., Fridkin M., Pontet M., Romeo D. Synthetic peptides from C-reactive protein containing tuftsin-related sequences. Peptides. 1986 Nov-Dec;7(6):961–968. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(86)90121-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Beer F. C., Pepys M. B. Isolation of human C-reactive protein and serum amyloid P component. J Immunol Methods. 1982;50(1):17–31. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90300-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiedel B. A., Gewurz H. Cleaved forms of C-reactive protein are associated with platelet inhibition. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2551–2555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiedel B. A., Potempa L. A., Frenzke M. E., Simpson R. M., Gewurz H. Platelet inhibitory effects of CRP preparations are due to a co-isolating low molecular weight factor. Immunology. 1982 Jan;45(1):15–22. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridkin M., Gottlieb P. Tuftsin, Thr-Lys-Pro-Arg. Anatomy of an immunologically active peptide. Mol Cell Biochem. 1981 Dec 4;41:73–97. doi: 10.1007/BF00225299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman N. D., Liu T. Y. Biosynthesis of human C-reactive protein in cultured hepatoma cells is induced by a monocyte factor(s) other than interleukin-1. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2363–2368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARRY R. M., Jr, CHANDAN R. C., SHAHANI K. M. A RAPID AND SENSITIVE ASSAY OF MURAMIDASE. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Jun;119:384–386. doi: 10.3181/00379727-119-30188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul B. B., Selvaraj R. J., Sbarra A. J. A sensitive assay method for peroxidases from various sources. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1978 May;23(5):407–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B., Butler P. J. Serum amyloid P component is the major calcium-dependent specific DNA binding protein of the serum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Oct 14;148(1):308–313. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91111-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruzanski W., Saito S., Nitzan D. W. The influence of lysostaphin on phagocytosis, intracellular bactericidal activity, and chemotaxis of human polymorphonuclear cells. J Lab Clin Med. 1983 Aug;102(2):298–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robey F. A., Ohura K., Futaki S., Fujii N., Yajima H., Goldman N., Jones K. D., Wahl S. Proteolysis of human C-reactive protein produces peptides with potent immunomodulating activity. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):7053–7057. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shephard E. G., Anderson R., Strachan A. F., Kühn S. H., De Beer F. C. CRP and neutrophils: functional effects and complex uptake. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Mar;63(3):718–727. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y., Pozzan T., Rink T. J. Calcium homeostasis in intact lymphocytes: cytoplasmic free calcium monitored with a new, intracellularly trapped fluorescent indicator. J Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;94(2):325–334. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.2.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson P. C. The measurement of leucocyte chemotaxis. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Jun 11;51(2):133–148. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90253-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woo P., Korenberg J. R., Whitehead A. S. Characterization of genomic and complementary DNA sequence of human C-reactive protein, and comparison with the complementary DNA sequence of serum amyloid P component. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 25;260(24):13384–13388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeller J. M., Landay A. L., Lint T. F., Gewurz H. Aggregated C-reactive protein binds to human polymorphonuclear leukocytes and potentiates Fc receptor-mediated chemiluminescence. J Lab Clin Med. 1986 Dec;108(6):567–576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigmond S. H. Ability of polymorphonuclear leukocytes to orient in gradients of chemotactic factors. J Cell Biol. 1977 Nov;75(2 Pt 1):606–616. doi: 10.1083/jcb.75.2.606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]