Abstract
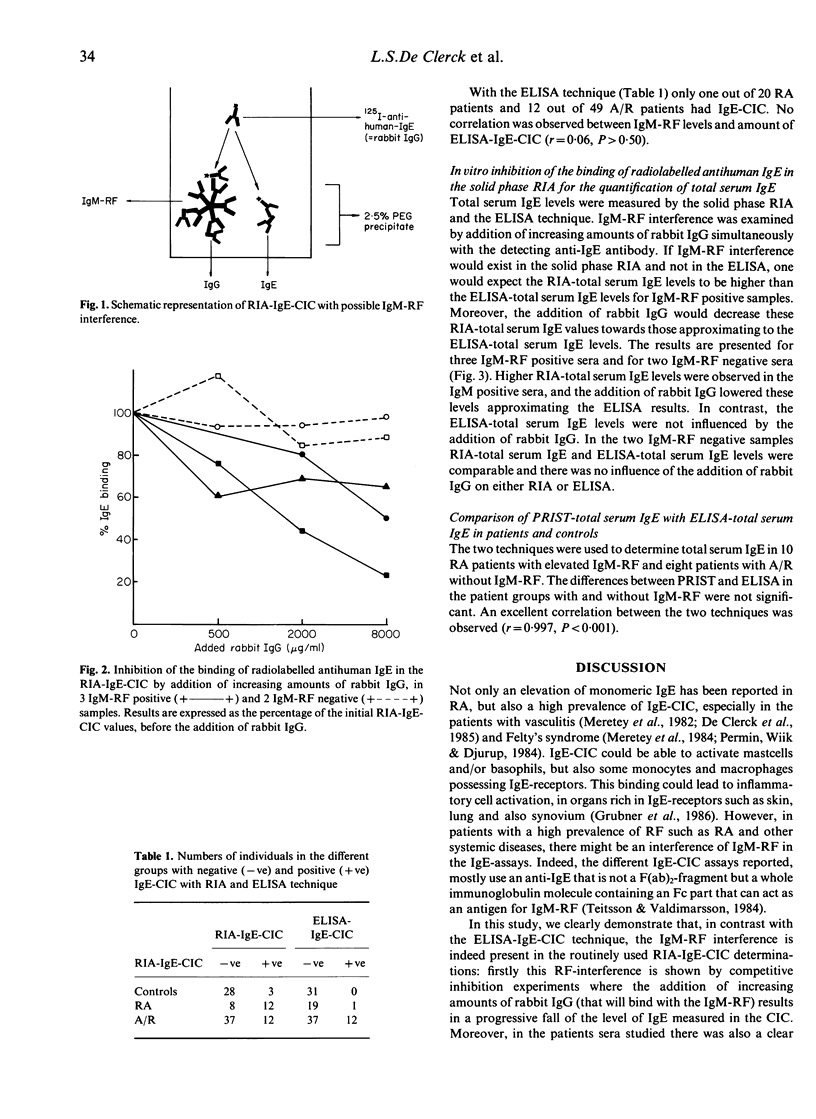
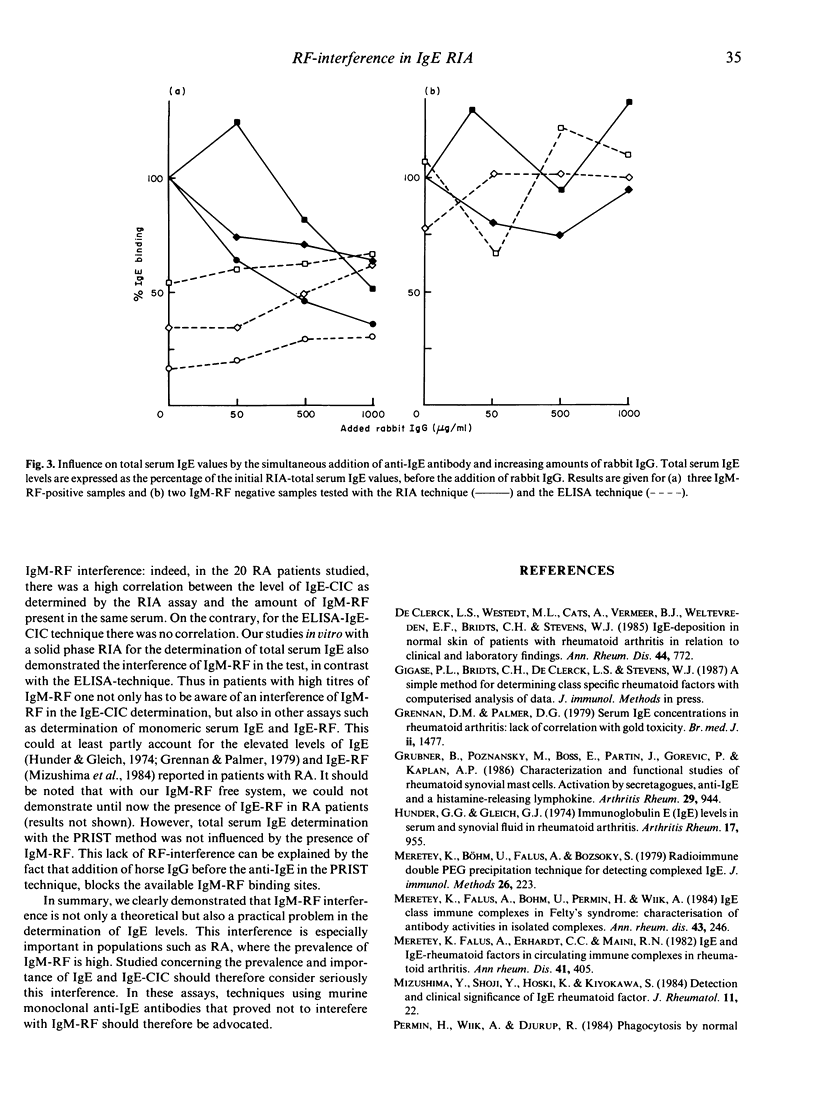
IgM-rheumatoid factor (RF) interference in the determination of total serum IgE and IgE-containing circulating immune complexes (IgE-CIC) was studied by inhibition experiments in vitro comparing a new ELISA technique free of IgM-RF interference with more widely used RIA methods. It was shown that a considerable overestimation of the IgE content in CIC can exist when high levels of IgM-RF are present in the same serum. The clinical part of this study revealed a dramatic fall in prevalence of IgE-CIC in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) with the ELISA technique, compared with the more conventional RIA method (respectively 1/20 compared to 12/20 positive for IgE-CIC). In these patients, there was a good correlation between the level of IgM-RF and the amount of IgE detected in the CIC by the RIA method (r = 0.87) whereas the RF-interference free ELISA method showed no correlation between these two parameters (r = 0.06). Total serum IgE determination with a solid phase RIA was also influenced by IgM-RF interference, whereas the PRIST method was not affected by the presence of IgM-RF. In conclusion, in patients with rheumatic diseases, IgE-assays using polyclonal rabbit or sheep anti-IgE antibodies are not appropriate and monoclonal anti-IgE antibodies that have been proved not to interfere with IgM-RF should be advocated.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- De Clerck L. S., Westedt M. L., Cats A., Vermeer B. J., Weltevreden E. F., Bridts C. H., Stevens W. J. IgE deposition in normal skin of patients with rheumatoid arthritis in relation to clinical and laboratory findings. Ann Rheum Dis. 1985 Nov;44(11):772–777. doi: 10.1136/ard.44.11.772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grennan D. M., Palmer D. G. Serum IgE concentrations in rheumatoid arthritis: lack of correlation with gold toxicity. Br Med J. 1979 Dec 8;2(6203):1477–1478. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6203.1477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruber B., Poznansky M., Boss E., Partin J., Gorevic P., Kaplan A. P. Characterization and functional studies of rheumatoid synovial mast cells. Activation by secretagogues, anti-IgE, and a histamine-releasing lymphokine. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Aug;29(8):944–955. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunder G. G., Gleich G. J. Immunoglobulin E (IgE) levels in serum and synovial fluid in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1974 Nov-Dec;17(6):955–963. doi: 10.1002/art.1780170606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meretey K., Böhm U., Falus A., Bozsoky S. Radioimmune double PEG precipitation technique for detecting complexed IgE. J Immunol Methods. 1979;26(3):223–228. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90247-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meretey K., Falus A., Erhardt C. C., Maini R. N. IgE and IgE-rheumatoid factors in circulating immune complexes in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1982 Aug;41(4):405–408. doi: 10.1136/ard.41.4.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merétey K., Falus A., Böhm U., Permin H., Wiik A. IgE class immune complexes in Felty's syndrome: characterisation of antibody activities in isolated complexes. Ann Rheum Dis. 1984 Apr;43(2):246–250. doi: 10.1136/ard.43.2.246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizushima Y., Shoji Y., Hoshi K., Kiyokawa S. Detection and clinical significance of IgE rheumatoid factor. J Rheumatol. 1984 Feb;11(1):22–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Permin H., Wiik A., Djurup R. Phagocytosis by normal polymorphonuclear leukocytes of immune complexes from serum of patients with Felty's syndrome and rheumatoid arthritis with special reference to IgE immune complexes. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand C. 1984 Feb;92(1):37–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1984.tb00049.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROPES M. W., BENNETT G. A., COBB S., JACOX R., JESSAR R. A. 1958 Revision of diagnostic criteria for rheumatoid arthritis. Bull Rheum Dis. 1958 Dec;9(4):175–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens W. J., Bridts C. H. IgG-containing and IgE-containing circulating immune complexes in patients with asthma and rhinitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1984 Feb;73(2):276–282. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(84)80020-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teitsson I., Valdimarsson H. Use of monoclonal antibodies and F(ab')2 enzyme conjugates in ELISA for IgM, IgA and IgG rheumatoid factors. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Jul 6;71(2):149–161. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90061-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


