Abstract
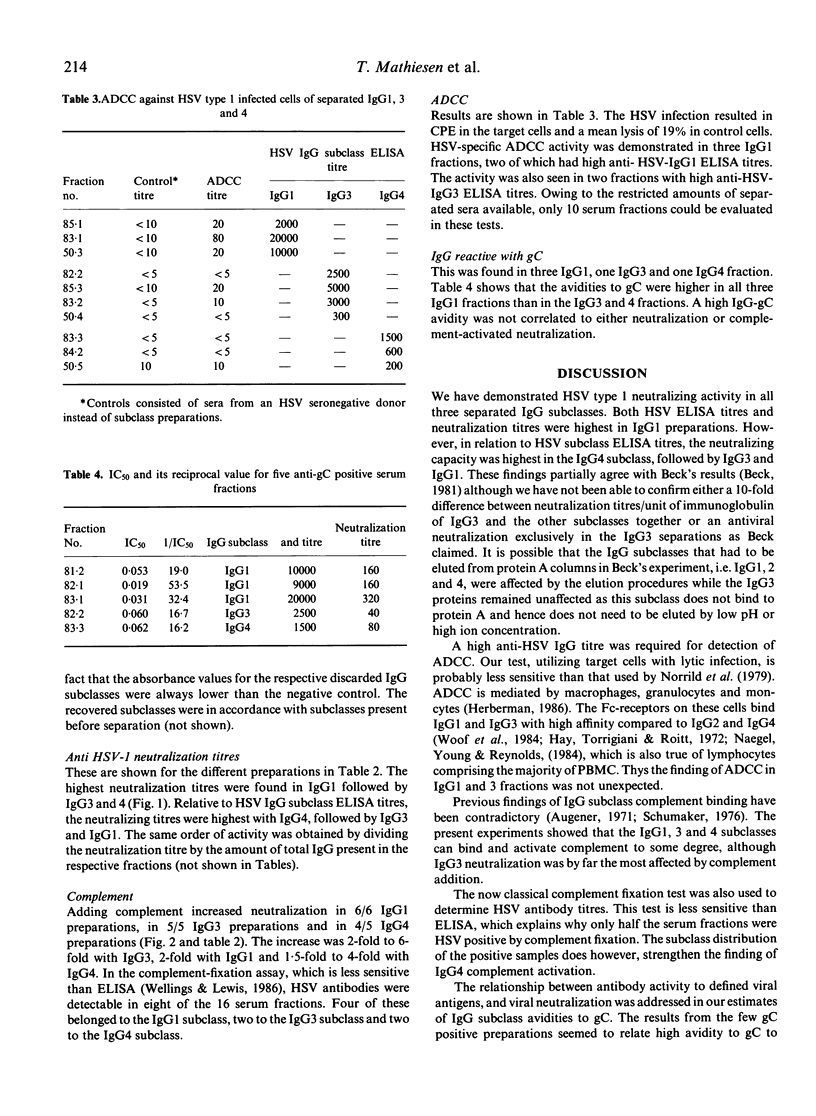
IgG subclasses 1, 3 and 4 in sera from herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) seropositive donors were separated and their functions assayed. The main neutralizing activity to HSV-1 was found in the IgG1 fractions. Both IgG3 and IgG4 possessed higher neutralizing titres than IgG1 in relation to the respective HSV IgG subclass enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) titre. Addition of complement resulted in a strong enhancement of IgG3 neutralizing activity. HSV neutralizations by IgG1 and, surprisingly, IgG4 were also somewhat enhanced by complement. With the addition of complement, the contribution to neutralizing activity of IgG3 was calculated to increase from 31 to 40% of total IgG in HSV neutralization in native sera. The avidities of the IgG fractions to HSV glycoprotein C (gC) were estimated in a few sera but could not be correlated to neutralization results. Antibody dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) was detectable mainly in IgG1 and 3 fractions of sera with high anti-HSV antibody titres.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Augener W., Grey H. M., Cooper N. R., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The reaction of monomeric and aggregated immunoglobulins with C1. Immunochemistry. 1971 Nov;8(11):1011–1020. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90489-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck O. E. Distribution of virus antibody activity among human IgG subclasses. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Mar;43(3):626–632. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird P., Lowe J., Stokes R. P., Bird A. G., Ling N. R., Jefferis R. The separation of human serum IgG into subclass fractions by immunoaffinity chromatography and assessment of specific antibody activity. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Jun 8;71(1):97–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90209-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank S. E., Leslie G. A., Clem L. W. Antibody affinity and valence in viral neutralization. J Immunol. 1972 Mar;108(3):665–673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DRAY S. Three gamma-globulins in normal human serum revealed by monkey precipitins. Science. 1960 Nov 4;132(3436):1313–1314. doi: 10.1126/science.132.3436.1313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrnst A. Separate pathways of C activation by measles virus cytotoxic antibodies: subclass analysis and capacity of F(ab) molecules to activate C via the alternative pathway. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):1206–1212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREY H. M., KUNKEL H. G. H CHAIN SUBGROUPS OF MYELOMA PROTEINS AND NORMAL 7S GAMMA-GLOBULIN. J Exp Med. 1964 Aug 1;120:253–266. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.2.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilljam G., Sundqvist V. A., Linde A., Pihlstedt P., Eklund A. E., Wahren B. Sensitive analytic ELISAs for subclass herpes virus IgG. J Virol Methods. 1985 Mar;10(3):203–214. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(85)90061-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay F. C., Torrigiani G., Roitt I. M. The binding of human IgG subclasses to human monocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1972 Jun;2(3):257–261. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830020312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl S., Starr S. E., oleske J. M., Shore S. L., Ashman R. B., Nahmias A. J. Human monocyte-macrophage-mediated antibody-dependent cytotoxicity to herpes simplex virus-infected cells. J Immunol. 1977 Mar;118(3):729–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe J., Bird P., Hardie D., Jefferis R., Ling N. R. Monoclonal antibodies (McAbs) to determinants on human gamma chains: properties of antibodies showing subclass restriction or subclass specificity. Immunology. 1982 Oct;47(2):329–336. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naegel G. P., Young K. R., Jr, Reynolds H. Y. Receptors for human IgG subclasses on human alveolar macrophages. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Mar;129(3):413–418. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.129.3.413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrild B., Shore S. L., Nahmias A. J. Herpes simplex virus glycoproteins: participation of individual herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein antigens in immunocytolysis and their correlation with previously identified glycopolypeptides. J Virol. 1979 Dec;32(3):741–748. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.3.741-748.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson M. A. Preparation of human sera containing one single IgG subclass using affinity chromatography. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Apr 2;98(1):91–98. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90440-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratner J. J., Sanford B. A., Smith K. O. Use of protein A-treated sera in unmasking herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) immunoglobulin A and identifying HSV-1 immunoglobulin G as the predominant neutralizing antibody. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Oct;10(4):415–418. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.4.415-418.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimer C. B., Phillips D. J., Aloisio C. H., Moore D. D., Galland G. G., Wells T. W., Black C. M., McDougal J. S. Evaluation of thirty-one mouse monoclonal antibodies to human IgG epitopes. Hybridoma. 1984 Fall;3(3):263–275. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1984.3.263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumaker V. N., Calcott M. A., Spiegelberg H. L., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Ultracentifuge studies of the binding of IgG of different subclasses to the Clq subunit of the first component of complement. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 16;15(23):5175–5181. doi: 10.1021/bi00668a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore S. L., Black C. M., Melewicz F. M., Wood P. A., Nahmias A. J. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity to target cells infected with type 1 and type 2 herpes simplex virus. J Immunol. 1976 Jan;116(1):194–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian T., Rawls W. E. Comparison of antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity and complement-dependent antibody lysis of herpes simplex virus-infected cells as methods of detecting antiviral antibodies in human sera. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jun;5(6):551–558. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.6.551-558.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundqvist V. A., Linde A., Wahren B. Virus-specific immunoglobulin G subclasses in herpes simplex and varicella-zoster virus infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jul;20(1):94–98. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.1.94-98.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERRY W. D., FAHEY J. L. SUBCLASSES OF HUMAN GAMMA-2-GLOBULIN BASED ON DIFFERENCES IN THE HEAVY POLYPEPTIDE CHAINS. Science. 1964 Oct 16;146(3642):400–401. doi: 10.1126/science.146.3642.400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woof J. M., Nik Jaafar M. I., Jefferis R., Burton D. R. The monocyte binding domain(s) on human immunoglobulin G. Mol Immunol. 1984 Jun;21(6):523–527. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(84)90068-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


