Abstract
Cultures of human thymic epithelial (TE) cells are able to produce a interleukin 1 (IL-1) like activity. This IL-1 activity can be detected either using mouse thymocytes in a traditional IL-1 assay, or using thymic lymphocytes obtained from cases of pediatric cardio-vascular surgery. Production of IL-1 activity by TE cells was found to be maximal between 3 and 4 weeks after culture initiation. Human thymocytes worked best as targets in an IL-1 assay, when these cells were derived from donors younger than 1 year of age. Infection of human TE cells by any of human cytomegalovirus, herpes simplex virus type 2, adenovirus 7, Coxsackie B1, and respiratory syncytial virus led to marked reductions in the ability of these cells to secrete measurable IL-1 activity. In the case of TE cells infected by cytomegalovirus, respiratory syncytial virus, and Coxsackie B1, this abrogation of production of IL-1 activity occurred in the absence of any obvious virus-induced cytopathic effect.
Full text
PDF


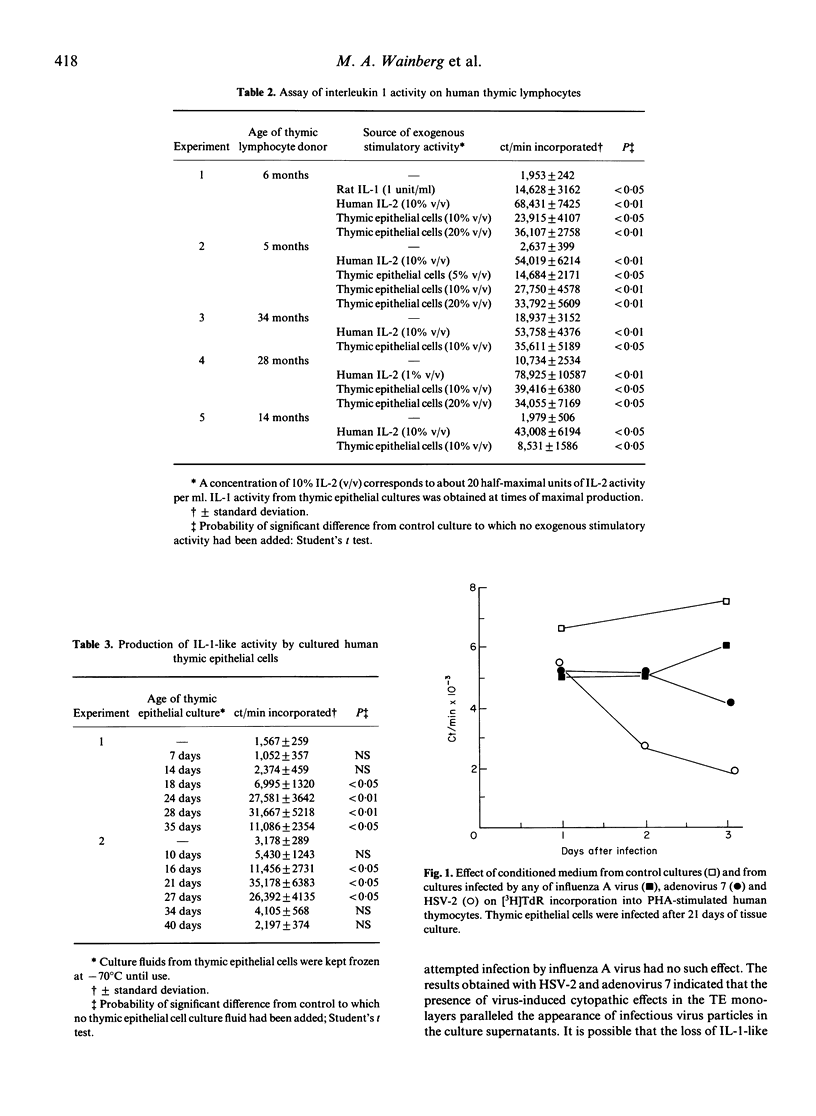
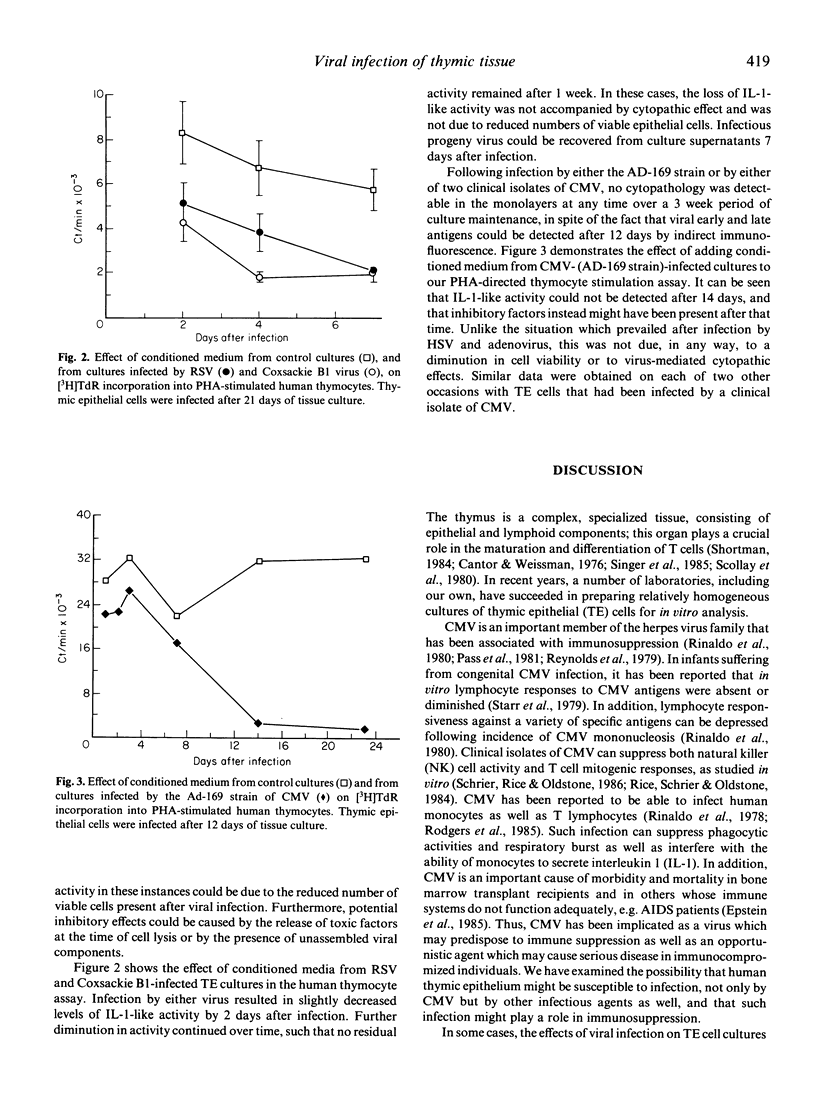


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cantor H., Weissman I. Development and function of subpopulations of thymocytes and T lymphocytes. Prog Allergy. 1976;20:1–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copelan E. A., Rinehart J. J., Lewis M., Mathes L., Olsen R., Sagone A. The mechanism of retrovirus suppression of human T cell proliferation in vitro. J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):2017–2020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Jan-Feb;6(1):51–95. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein J. S., Frederick W. R., Rook A. H., Jackson L., Manischewitz J. F., Mayner R. E., Masur H., Enterline J. C., Djeu J. Y., Quinnan G. V., Jr Selective defects in cytomegalovirus- and mitogen-induced lymphocyte proliferation and interferon release in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1985 Oct;152(4):727–733. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.4.727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gery I., Gershon R. K., Waksman B. H. Potentiation of cultured mouse thymocyte responses by factors released by peripheral leucocytes. J Immunol. 1971 Dec;107(6):1778–1780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes B. F., Harden E. A., Telen M. J., Hemler M. E., Strominger J. L., Palker T. J., Scearce R. M., Eisenbarth G. S. Differentiation of human T lymphocytes. I. Acquisition of a novel human cell surface protein (p80) during normal intrathymic T cell maturation. J Immunol. 1983 Sep;131(3):1195–1200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. D., Rota T. R., Andrews C. A., Hirsch M. S. Replication of human cytomegalovirus in endothelial cells. J Infect Dis. 1984 Dec;150(6):956–957. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.6.956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miossec P., Cavender D., Ziff M. Production of interleukin 1 by human endothelial cells. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2486–2491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oosterom R., Kater L., Oosterom J. Effects of human thymic epithelial-conditioned medium on mitogen responsiveness of human and mouse lymphocytes. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1979 Apr;12(4):460–470. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(79)90051-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oosterom R., Kater L. Target cell subpopulations for human thymic epithelial conditioned medium in the mouse thymus. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1980 Oct;17(2):183–195. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(80)90086-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pass R. F., Dworsky M. E., Whitley R. J., August A. M., Stagno S., Alford C. A., Jr Specific lymphocyte blastogenic responses in children with cytomegalovirus and herpes simplex virus infections acquired early in infancy. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):166–170. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.166-170.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds D. W., Dean P. H., Pass R. F., Alford C. A. Specific cell-mediated immunity in children with congenital and neonatal cytomegalovirus infection and their mothers. J Infect Dis. 1979 Oct;140(4):493–499. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.4.493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice G. P., Schrier R. D., Oldstone M. B. Cytomegalovirus infects human lymphocytes and monocytes: virus expression is restricted to immediate-early gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6134–6138. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldo C. R., Jr, Carney W. P., Richter B. S., Black P. H., Hirsch M. S. Mechanisms of immunosuppression in cytomegaloviral mononucleosis. J Infect Dis. 1980 Apr;141(4):488–495. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.4.488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldo C. R., Jr, Richter B. S., Black P. H., Callery R., Chess L., Hirsch M. S. Replication of herpes simplex virus and cytomegalovirus in human leukocytes. J Immunol. 1978 Jan;120(1):130–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers B. C., Scott D. M., Mundin J., Sissons J. G. Monocyte-derived inhibitor of interleukin 1 induced by human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):527–532. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.527-532.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier R. D., Rice G. P., Oldstone M. B. Suppression of natural killer cell activity and T cell proliferation by fresh isolates of human cytomegalovirus. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jun;153(6):1084–1091. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.6.1084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scollay R., Jacobs S., Jerabek L., Butcher E., Weissman I. T cell maturation: thymocyte and thymus migrant subpopulations defined with monoclonal antibodies to MHC region antigens. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2845–2853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortman K. T-cell development in the thymus. Nature. 1984 Jun 14;309(5969):583–584. doi: 10.1038/309583b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer K. H., Harden E. A., Robertson A. L., Lobach D. F., Haynes B. F. In vitro growth and phenotypic characterization of mesodermal-derived and epithelial components of normal and abnormal human thymus. Hum Immunol. 1985 Jul;13(3):161–176. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(85)90009-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer K. H., Wolf L. S., Lobach D. F., Denning S. M., Tuck D. T., Robertson A. L., Haynes B. F. Human thymocytes bind to autologous and allogeneic thymic epithelial cells in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6588–6592. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A., Gilbride K. J., Favata M. F. Lymphocyte activating factor promotes T-cell growth factor production by cloned murine lymphoma cells. Nature. 1980 Oct 30;287(5785):853–855. doi: 10.1038/287853a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr S. E., Tolpin M. D., Friedman H. M., Paucker K., Plotkin S. A. Impaired cellular immunity to cytomegalovirus in congenitally infected children and their mothers. J Infect Dis. 1979 Oct;140(4):500–505. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.4.500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutman O. Intrathymic and extrathymic T cell maturation. Immunol Rev. 1978;42:138–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1978.tb00261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tormey D. C., Simon R., Falkson G., Bull J., Band P., Perlin E., Blom J. Evaluation of adriamycin and dibromodulcitol in metastatic breast carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1977 Feb;37(2):529–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wainberg M. A., Spira B., Boushira M., Margolese R. G. Inhibition by human T-lymphotropic virus (HTLV-I) of T-lymphocyte mitogenesis: failure of exogenous T-cell growth factor to restore responsiveness to lectin. Immunology. 1985 Jan;54(1):1–7. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wainberg M. A., Vydelingum S., Margolese R. G. Viral inhibition of lymphocyte mitogenesis: interference with the synthesis of functionally active T cell growth factor (TCGF) activity and reversal of inhibition by the addition of same. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2372–2378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wentworth B. B., French L. Plaque assay of cytomegalovirus strains of human origin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Nov;135(2):253–258. doi: 10.3181/00379727-135-35031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. G., Boyd J. F. The effect of measles on the thymus and other lymphoid tissues. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Mar;13(3):343–357. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


