Abstract
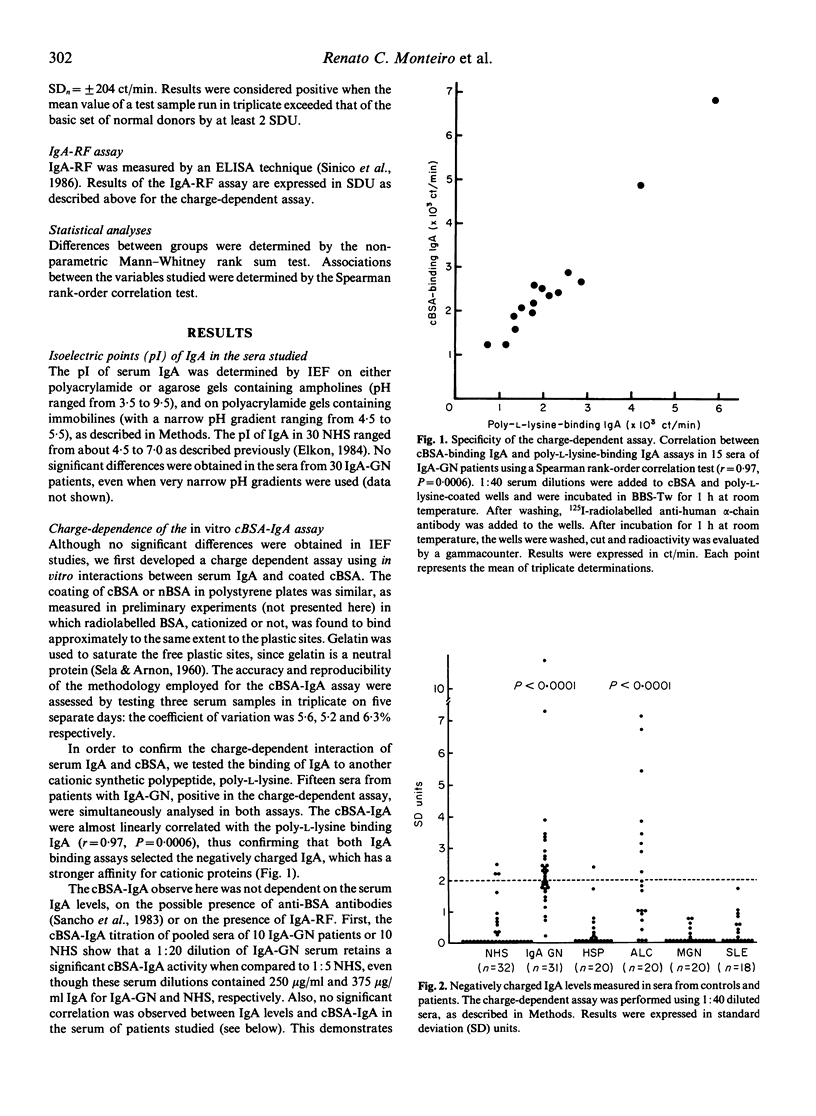
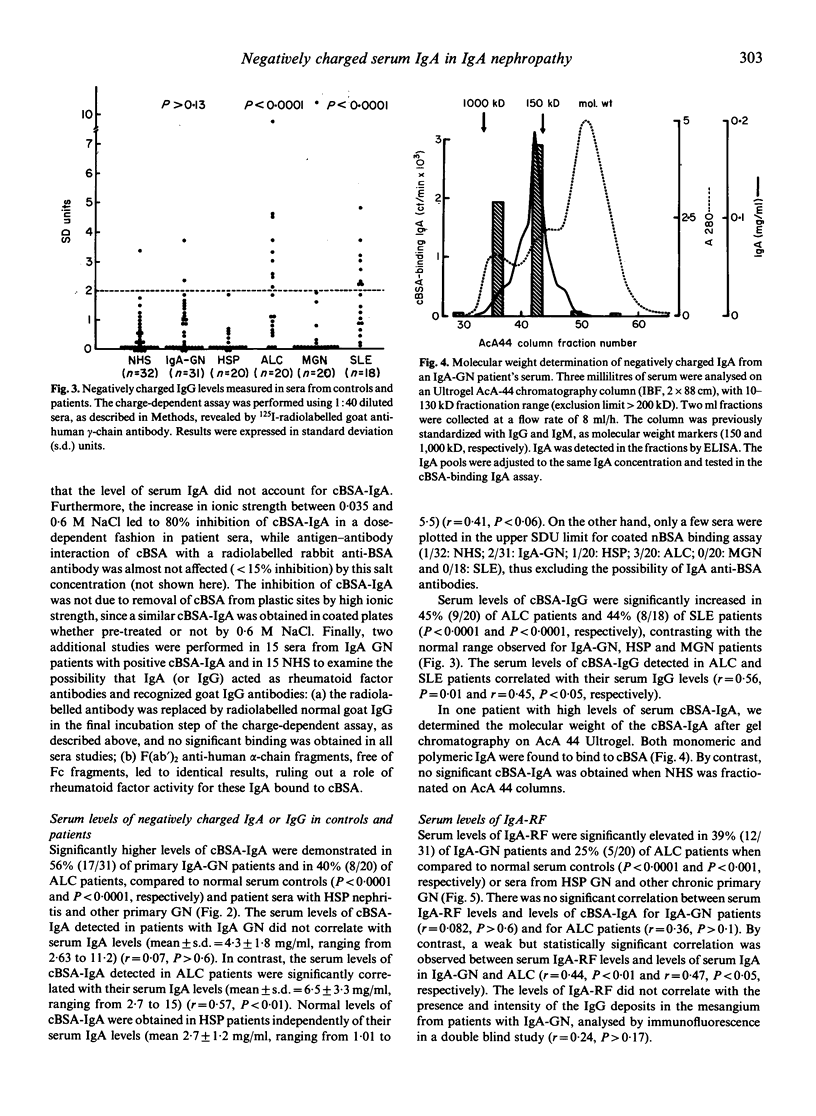
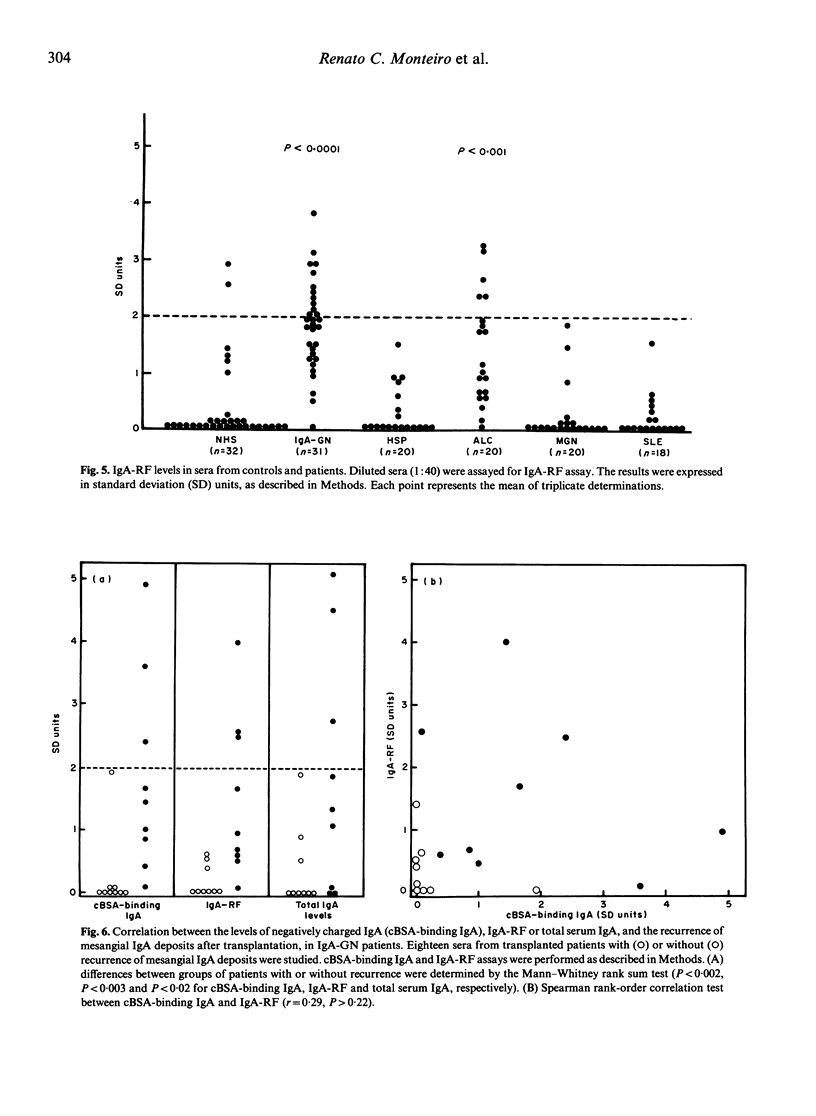
The observation of negatively charged IgA in the mesangium of patients with primary IgA nephropathy (IgA-GN) prompted us to study the charge of serum IgA in IgA-GN, Henoch Schönlein purpura (HSP), alcoholic liver cirrhosis (ALC), membranous nephropathy (MGN) and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Since no abnormal distribution of IgA isoelectric points was detected by isoelectric focusing studies, we developed a sensitive charge-dependent assay using plates coated with either cationized BSA (cBSA) or poly-L-lysine. In 15 IgA-GN sera, the amount of IgA reacting specifically with cBSA (cBSA-IgA) was almost linearly correlated with the poly-L-lysine-binding IgA (r = 0.97, P = 0.0006), suggesting that both assays detect charge-dependent interactions and thus probably measure anionic IgA. Significantly high serum levels of cBSA-IgA were observed in 56% of IgA-GN patients and in 40% of ALC patients. In contrast, normal serum levels of cBSA-IgA were detected in HSP, MGN and SLE. Both, the mono- or polymeric IgA bound to cBSA in a patient's serum studied. Contrasting with the presence of anionic IgA, no increase of cBSA-IgG was observed in IgA-GN. IgA rheumatoid factor (IgA-RF) assay showed high levels in IgA-GN (39%) and in ALC (25%). IgA-RF levels did not correlate with the amount of cBSA-IgA. When 18 patients with IgA-GN were tested after kidney transplantation, increased levels of cBSA-IgA and/or IgA-RF were found to be associated with the recurrence of mesangial IgA deposits in the graft. This suggests that both negatively charged IgA and IgA-RF may play a role in the recurrence of mesangial IgA deposits.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chevailler A., Monteiro R. C., Daëron M., Lesavre P. Induction of Fc receptors for IgA on murine T cell hybridoma by human monoclonal IgA and by high molecular weight IgA in IgA nephropathy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Jan;67(1):114–123. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czerkinsky C., Koopman W. J., Jackson S., Collins J. E., Crago S. S., Schrohenloher R. E., Julian B. A., Galla J. H., Mestecky J. Circulating immune complexes and immunoglobulin A rheumatoid factor in patients with mesangial immunoglobulin A nephropathies. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jun;77(6):1931–1938. doi: 10.1172/JCI112522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danon D., Goldstein L., Marikovsky Y., Skutelsky E. Use of cationized ferritin as a label of negative charges on cell surfaces. J Ultrastruct Res. 1972 Mar;38(5):500–510. doi: 10.1016/0022-5320(72)90087-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkon K. B. Isoelectric focusing of human IgA and secretory proteins using thin layer agarose gels and nitrocellulose capillary blotting. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Feb 10;66(2):313–321. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90343-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo G. R., Caulin-Glaser T., Emancipator S. N., Lamm M. E. Nephritogenicity and differential distribution of glomerular immune complexes related to immunogen charge. Lab Invest. 1983 Mar;48(3):353–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier V. J., Striker G. E., Mannik M. Glomerular localization of preformed immune complexes prepared with anionic antibodies or with cationic antigens. Lab Invest. 1984 Jun;50(6):636–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germuth F. G., Jr, Senterfit L. B., Dreesman G. R. Immune complex disease. V. The nature of the circulating complexes associated with glomerular alterations in the chronic BSA-rabbit system. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1972 Jun;130(6):344–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale G. M., McIntosh S. L., Hiki Y., Clarkson A. R., Woodroffe A. J. Evidence for IgA-specific B cell hyperactivity in patients with IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 1986 Mar;29(3):718–724. doi: 10.1038/ki.1986.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs K. L., Miller F. Antigen size and charge in immune complex glomerulonephritis. II. Passive induction of immune deposits with dextran-anti-dextran immune complexes. Am J Pathol. 1983 Jun;111(3):298–306. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs K. L., Miller F. Role of antigen size and charge in immune complex glomerulonephritis. Lab Invest. 1982 Aug;47(2):198–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffmann R. H., Herrmann W. A., Meÿer C. J., Daha M. R., Van Es L. A. Circulating IgA-immune complexes in Henoch-Schönlein purpura. A longitudinal study of their relationship to disease activity and vascular deposition of IgA. Am J Med. 1980 Dec;69(6):859–866. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(80)80011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffmann R. H., Van Es L. A., Daha M. R. The specific detection of IgA in immune complexes. J Immunol Methods. 1981;40(2):117–129. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90058-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesavre P., Digeon M., Bach J. F. Analysis of circulating IgA and detection of immune complexes in primary IgA nephropathy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Apr;48(1):61–69. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monteiro R. C., Halbwachs-Mecarelli L., Roque-Barreira M. C., Noel L. H., Berger J., Lesavre P. Charge and size of mesangial IgA in IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 1985 Oct;28(4):666–671. doi: 10.1038/ki.1985.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifai A., Small P. A., Jr, Teague P. O., Ayoub E. M. Experimental IgA nephropathy. J Exp Med. 1979 Nov 1;150(5):1161–1173. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.5.1161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SELA M., ARNON R. Studies on the chemical basis of the antigenicity of proteins. 1. Antigenicity of polypeptidyl gelatins. Biochem J. 1960 Apr;75:91–102. doi: 10.1042/bj0750091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancho J., Egido J., Rivera F., Hernando L. Immune complexes in IgA nephropathy: presence of antibodies against diet antigens and delayed clearance of specific polymeric IgA immune complexes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Oct;54(1):194–202. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saulsbury F. T. IgA rheumatoid factor in Henoch-Schönlein purpura. J Pediatr. 1986 Jan;108(1):71–76. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80771-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinico R. A., Fornasieri A., Oreni N., Benuzzi S., D'Amico G. Polymeric IgA rheumatoid factor in idiopathic IgA mesangial nephropathy (Berger's disease). J Immunol. 1986 Jul 15;137(2):536–541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trascasa M. L., Egido J., Sancho J., Hernando L. IgA glomerulonephritis (Berger's disease): evidence of high serum levels of polymeric IgA. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Nov;42(2):247–254. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Wiel A., Seifert W. F., Van der Linden J. A., Gmelig-Meyling F. H., Kater L., Schuurman H. J. Spontaneous IgA synthesis by blood mononuclear cells in alcoholic liver disease. Scand J Immunol. 1987 Feb;25(2):181–187. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1987.tb01062.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J. H., Bhathena D. B., Curtis J. J., Lucas B. A., Luke R. G. A possible relationship between Henoch-Schonlein syndrome and IgA nephropathy (Berger's disease). An illustrative case. Nephron. 1978;22(4-6):582–591. doi: 10.1159/000181539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodroffe A. J., Gormly A. A., McKenzie P. E., Wootton A. M., Thompson A. J., Seymour A. E., Clarkson A. R. Immunologic studies in IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 1980 Sep;18(3):366–374. doi: 10.1038/ki.1980.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


