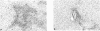Abstract
This report extends our previous study on experimental autoimmune hepatitis in C57BL/6 (B6) mice. Cellular immunity involved in the induction of liver injury in this model was studied by transfer of primed spleen cells from hepatitis donor mice to syngeneic normal recipient mice.
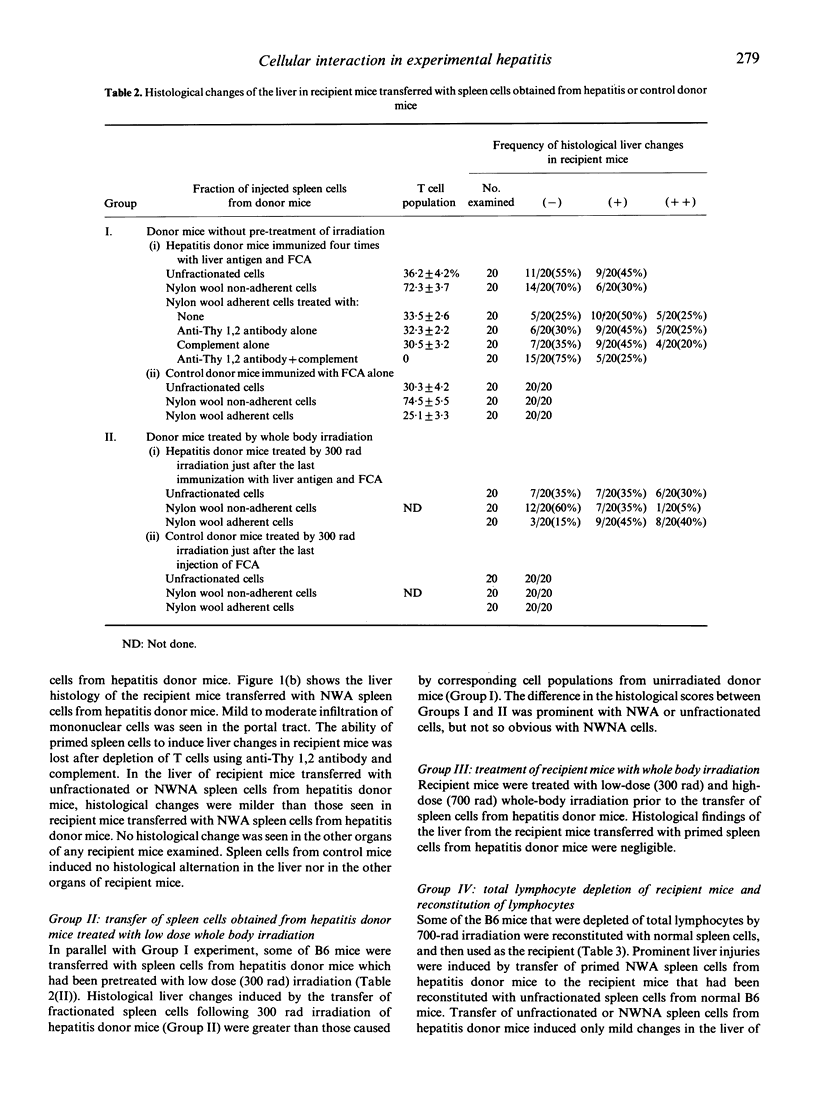
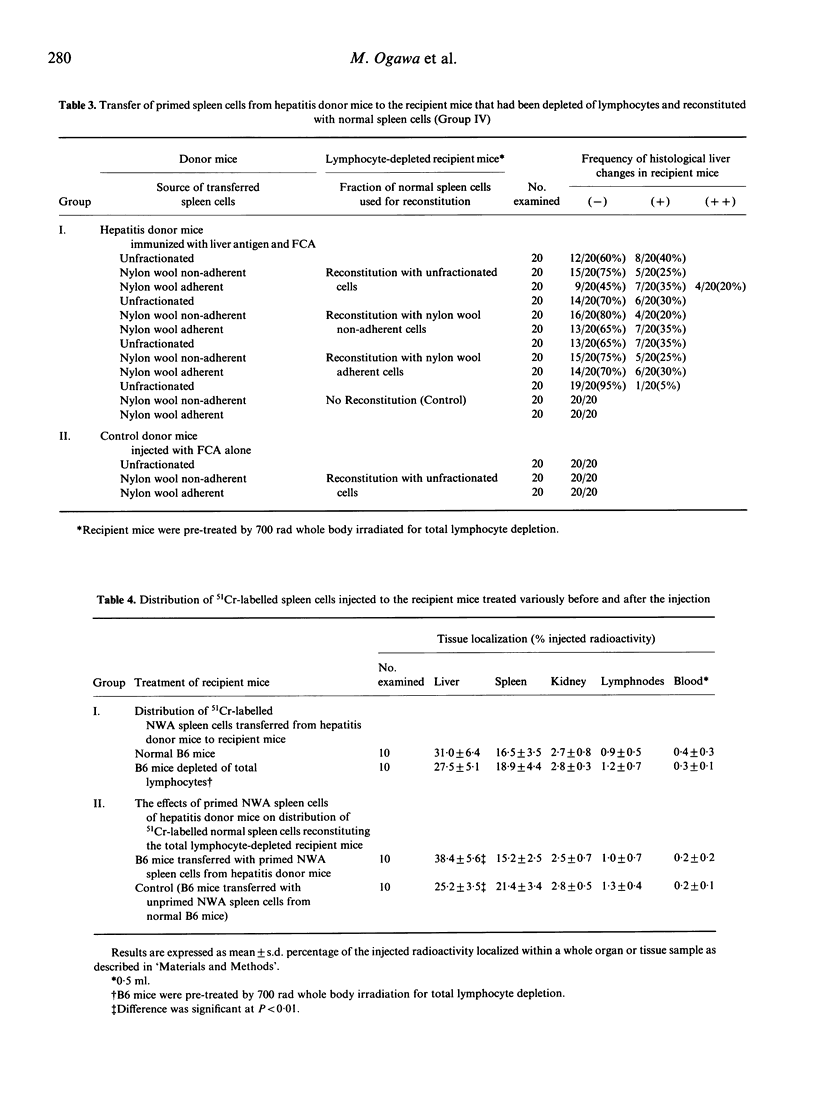
The most prominent liver damage in recipient B6 mice was induced by transfer of nylon wool adherent spleen cells from hepatitis donor mice, and T cells in this fraction were the essential requirement for the liver damage in the recipient mice. Nylon wool adherent spleen cells from hepatitis donor mice after depletion of the suppressor T-cell function by low-dose (300 rad) irradiation induced more severe liver injury compared to the same cells without irradiation. When the recipient mice were depleted of lymphocytes by low or high dose (700 rad) whole body irradiation, transfer of primed spleen cells from hepatitis donor mice did not induce liver lesion in the lymphocyte-depleted mice. This low susceptibility of lymphocyte-depleted recipient mice to primed spleen cells of hepatitis mice was no longer demonstrated after reconstitution with normal spleen cells. In a cell-migration study using 51Cr-labelled spleen cells, it was shown that a considerable number of infiltrating cells in the liver of recipient mice were derived from recipient mice themselves. These results seem to indicate that cell-to-cell interaction between radiosensitive precursor cells of recipient mice and liver-antigen-primed T cells from hepatitis donor mice play an essential role in the induction of liver injury in the recipient mice.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. E., Warner N. L. Ionizing radiation and the immune response. Adv Immunol. 1976;24:215–335. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60331-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnaba V., Levrero M., Franco A., Ruberti G., Musca A., Bonavita M. S., Balsano F. Characterization of effector cells in lymphocytotoxicity to autologous hepatocytes in HBsAg-positive and autoimmune chronic active hepatitis (CAH). Liver. 1986 Feb;6(1):45–52. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0676.1986.tb00267.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartholomaeus W. N., Reed W. D., Joske R. A. Autoantibody to liver-specific lipoprotein in the mouse: regulation by naturally occurring autoantigen specific suppressor cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Nov;58(2):307–316. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard C. C., Leydon J., Mackay I. R. T cell necessity in the pathogenesis of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Sep;6(9):655–660. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor H., Boyse E. A. Functional subclasses of T lymphocytes bearing different Ly antigens. II. Cooperation between subclasses of Ly+ cells in the generation of killer activity. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1390–1399. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll A. M., de Sousa M. Lyt phenotype, lymphocyte migration and the selective tissue positioning of mouse T cell sets. Immunology. 1984 Jun;52(2):331–339. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane A. M., Moussouros A., Thomsom A. D., Eddleston A. L., Wiiliams R. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated (K cell) cytotoxicity against isolated hepatocytes in chronic active hepatitis. Lancet. 1976 Feb 28;1(7957):441–444. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91472-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colucci G., Colombo M., Del Ninno E., Paronetto F. In situ characterization by monoclonal antibodies of the mononuclear cell infiltrate in chronic active hepatitis. Gastroenterology. 1983 Nov;85(5):1138–1145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doria G., Agarossi G., Adorini L. Selective effects of ionizing radiations on immunoregulatory cells. Immunol Rev. 1982;65:23–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00426.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glasser M., Law L. W. T-T cell collaboration in rejection of a syngeneic SV40-induced sarcoma in mice. Nature. 1978 Jun 1;273(5661):385–387. doi: 10.1038/273385a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holda J. H., Silberg D., Swanborg R. H. Autoimmune effector cells. IV. Induction of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in Lewis rats without adjuvant. J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):732–734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuriki J., Murakami H., Kakumu S., Sakamoto N., Yokochi T., Nakashima I., Kato N. Experimental autoimmune hepatitis in mice after immunization with syngeneic liver proteins together with the polysaccharide of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Gastroenterology. 1983 Mar;84(3):596–603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H., Hopf U. Studies on the pathogenesis of experimental chronic active hepatitis in rabbits. I. Induction of the disease and protective effect of allogeneic liver specific proteins. Br J Exp Pathol. 1974 Oct;55(5):498–508. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori T., Mori Y., Yoshida H., Ueda S., Ogawa M., Iesato K., Wakashin Y., Wakashin M., Okuda K. Cell-mediated cytotoxicity of sensitized spleen cells against target liver cells--in vivo and in vitro study with a mouse model of experimental autoimmune hepatitis. Hepatology. 1985 Sep-Oct;5(5):770–777. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840050511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori Y., Mori T., Ueda S., Yoshida H., Iesato K., Wakashin Y., Wakashin M., Okuda K. Study of cellular immunity in experimental autoimmune hepatitis in mice: transfer of spleen cells sensitized with liver proteins. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Sep;61(3):577–584. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori Y., Mori T., Yoshida H., Ueda S., Iesato K., Wakashin Y., Wakashin M., Okuda K. Study of cellular immunity in experimental autoimmune hepatitis in mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Jul;57(1):85–92. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheiffarth F., Warnatz H., Mayer K. Studies concerning the importance of mononuclear cells in the development of experimental hepatitis. J Immunol. 1967 Feb;98(2):396–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson A. D., Cochrane M. A., McFarlane I. G., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Lymphocyte cytotoxicity to isolated hepatocytes in chronic active hepatitis. Nature. 1974 Dec 20;252(5485):721–722. doi: 10.1038/252721a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uibo R. M., Helin H. J., Krohn K. J. Immunological reactions to liver-specific membrane lipoprotein (LSP) in experimental autoimmune liver disease in rabbits. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 May;48(2):505–512. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vento S., Eddleston A. L. Immunological aspects of chronic active hepatitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 May;68(2):225–232. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vergani G. M., Vergani D., Jenkins P. J., Portmann B., Mowat A. P., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Lymphocyte cytotoxicity to autologous hepatocytes in HBsAg-negative chronic active hepatitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Oct;38(1):16–21. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warnatz H., Scheiffarth F., Wolf F., Schmidt H. J. Autoradiographic experiments concerning the importance of mononuclear cells in experimental hepatitis. J Immunol. 1967 Feb;98(2):402–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]