Abstract
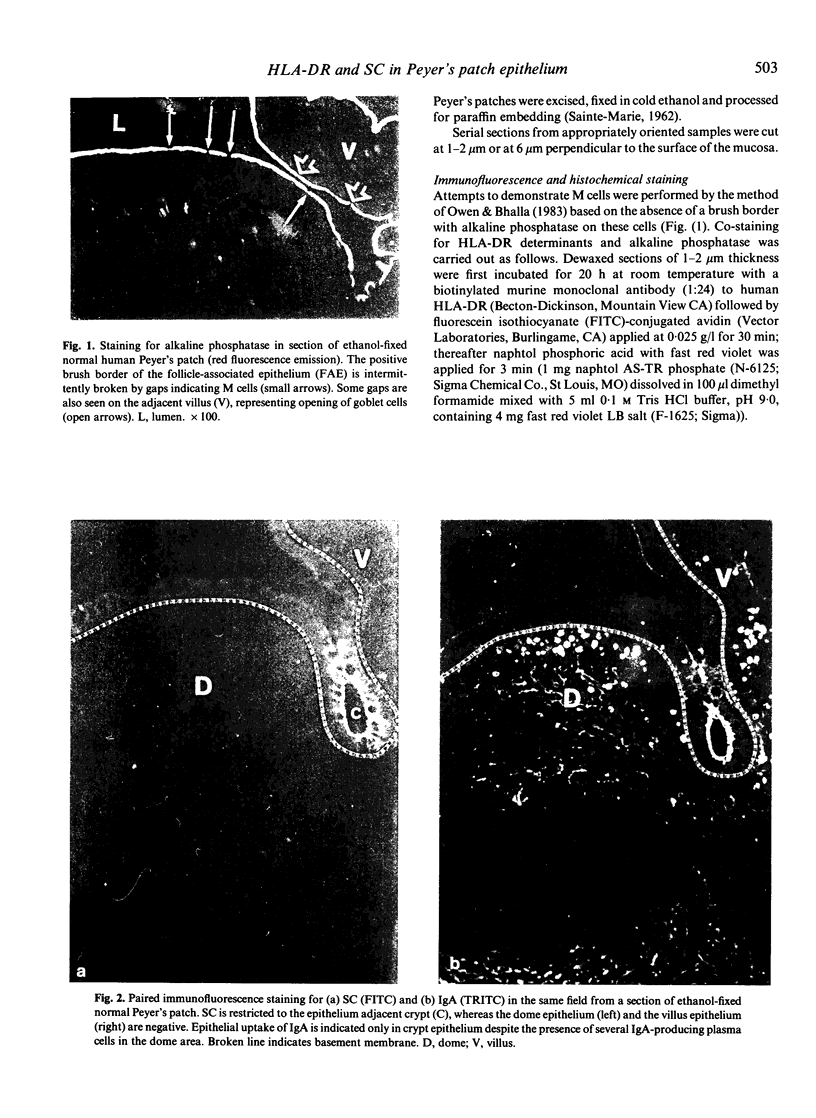
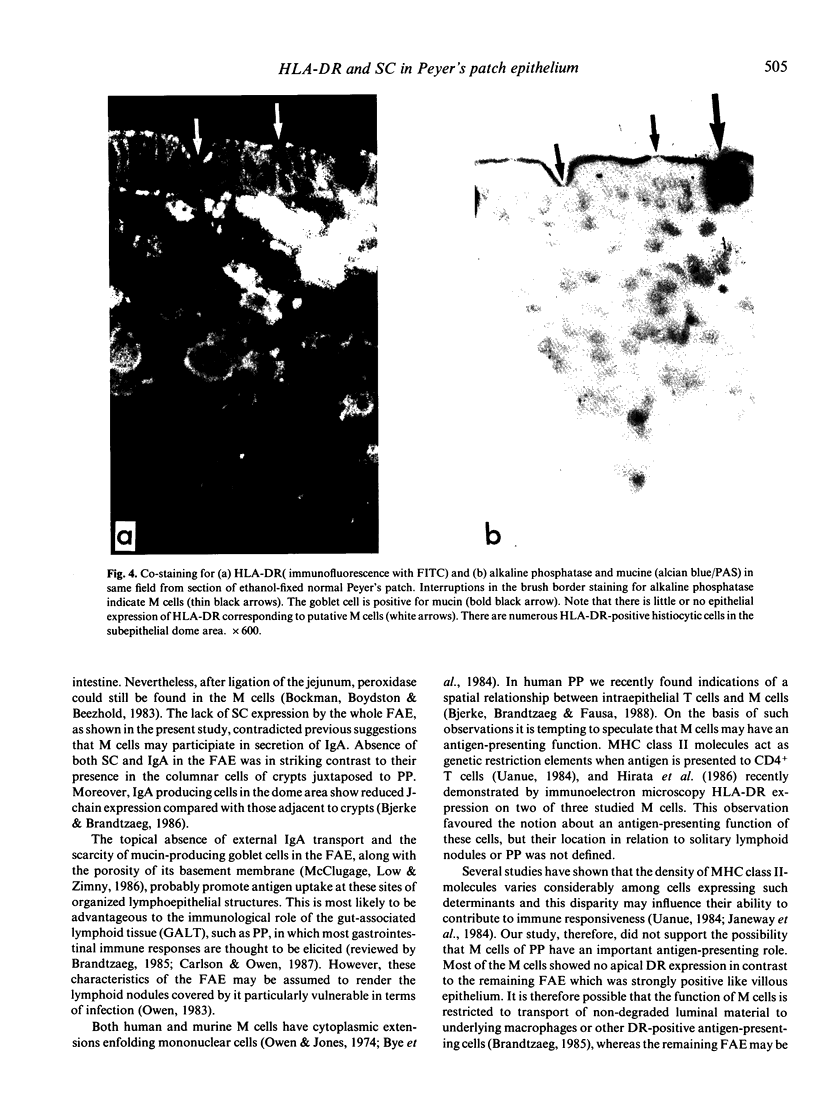
Follicle-associated epithelium (FAE) of normal human Peyer's patches (PP) was studied with regard to expression of HLA-DR determinants and secretory component (SC); the latter acts as a receptor for polymeric immunoglobulins (pIg). Putative M cells were identified in FAE by lack of a brush border with alkaline phosphatase. These cells were virtually negative for HLA-DR whereas the remaining FAE was strongly positive like villous epithelium. Conversely, the complete FAE showed no SC expression and was negative for IgA. These findings suggested that the FAE (including the M cells) does not participate in SC-mediated transport of pIgA, which in the gut mainly takes place through columnar crypt cells. The FAE (excepting the M cells) may be involved in an MHC class II-restricted antigen-presenting function as recently suggested for villous epithelium. The role of M cells may hence be limited to uptake and transport of luminal antigens.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benacerraf B. Role of MHC gene products in immune regulation. Science. 1981 Jun 12;212(4500):1229–1238. doi: 10.1126/science.6165083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjerke K., Brandtzaeg P. Immunoglobulin- and J chain-producing cells associated with lymphoid follicles in the human appendix, colon and ileum, including Peyer's patches. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 May;64(2):432–441. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bland P. W., Warren L. G. Antigen presentation by epithelial cells of the rat small intestine. I. Kinetics, antigen specificity and blocking by anti-Ia antisera. Immunology. 1986 May;58(1):1–7. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockman D. E., Boydston W. R., Beezhold D. H. The role of epithelial cells in gut-associated immune reactivity. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1983 Jun 30;409:129–144. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1983.tb26864.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockman D. E., Cooper M. D. Pinocytosis by epithelium associated with lymphoid follicles in the bursa of Fabricius, appendix, and Peyer's patches. An electron microscopic study. Am J Anat. 1973 Apr;136(4):455–477. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001360406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockman D. E. Functional histology of appendix. Arch Histol Jpn. 1983 Jun;46(3):271–292. doi: 10.1679/aohc.46.271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockman D. E., Stevens W. Gut-associated lymphoepithelial tissue: bidirectional transport of tracer by specialized epithelial cells associated with lymphoid follicles. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1977 Apr;21(4):245–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P. Prolonged incubation time in immunohistochemistry: effects on fluorescence staining of immunoglobulins and epithelial components in ethanol- and formaldehyde-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Nov;29(11):1302–1315. doi: 10.1177/29.11.7033362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P., Prydz H. Direct evidence for an integrated function of J chain and secretory component in epithelial transport of immunoglobulins. Nature. 1984 Sep 6;311(5981):71–73. doi: 10.1038/311071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P. Research in gastrointestinal immunology. State of the art. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1985;114:137–156. doi: 10.3109/00365528509093774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bye W. A., Allan C. H., Trier J. S. Structure, distribution, and origin of M cells in Peyer's patches of mouse ileum. Gastroenterology. 1984 May;86(5 Pt 1):789–801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson C. O., Ealding W. Generalized systemic and mucosal immunity in mice after mucosal stimulation with cholera toxin. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):2736–2741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata I., Austin L. L., Blackwell W. H., Weber J. R., Dobbins W. O., 3rd Immunoelectron microscopic localization of HLA-DR antigen in control small intestine and colon and in inflammatory bowel disease. Dig Dis Sci. 1986 Dec;31(12):1317–1330. doi: 10.1007/BF01299810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inman L. R., Cantey J. R. Specific adherence of Escherichia coli (strain RDEC-1) to membranous (M) cells of the Peyer's patch in Escherichia coli diarrhea in the rabbit. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jan;71(1):1–8. doi: 10.1172/JCI110737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landsverk T. The epithelium covering Peyer's patches in young milk-fed calves. An ultrastructural and enzyme histochemical investigation. Acta Vet Scand. 1981;22(2):198–210. doi: 10.1186/BF03547509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupetti M., Dolfi A. Concerning bidirectional transport by the lymphoid follicle-associated epithelial cells. Cell Mol Biol Incl Cyto Enzymol. 1980;26(6):609–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayrhofer G., Pugh C. W., Barclay A. N. The distribution, ontogeny and origin in the rat of Ia-positive cells with dendritic morphology and of Ia antigen in epithelia, with special reference to the intestine. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Feb;13(2):112–122. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830130206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClugage S. G., Low F. N., Zimny M. L. Porosity of the basement membrane overlying Peyer's patches in rats and monkeys. Gastroenterology. 1986 Nov;91(5):1128–1133. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(86)80007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natali P. G., De Martino C., Quaranta V., Nicotra M. R., Frezza F., Pellegrino M. A., Ferrone S. Expression of Ia-like antigens in normal human nonlymphoid tissues. Transplantation. 1981 Jan;31(1):75–78. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198101000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen R. L. And now pathophysiology of M cells--good news and bad news from Peyer's patches. Gastroenterology. 1983 Aug;85(2):468–470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen R. L., Bhalla D. K. Cytochemical analysis of alkaline phosphatase and esterase activities and of lectin-binding and anionic sites in rat and mouse Peyer's patch M cells. Am J Anat. 1983 Oct;168(2):199–212. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001680207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen R. L., Jones A. L. Epithelial cell specialization within human Peyer's patches: an ultrastructural study of intestinal lymphoid follicles. Gastroenterology. 1974 Feb;66(2):189–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen R. L. Sequential uptake of horseradish peroxidase by lymphoid follicle epithelium of Peyer's patches in the normal unobstructed mouse intestine: an ultrastructural study. Gastroenterology. 1977 Mar;72(3):440–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott H., Solheim B. G., Brandtzaeg P., Thorsby E. HLA-DR-like antigens in the epithelium of the human small intestine. Scand J Immunol. 1980;12(1):77–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1980.tb00043.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby W. S., Janossy G., Goldstein G., Jewell D. P. T lymphocyte subsets in human intestinal mucosa: the distribution and relationship to MHC-derived antigens. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Jun;44(3):453–458. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simecka J. W., Davis J. K., Cassell G. H. Distribution of Ia antigens and T lymphocyte subpopulations in rat lungs. Immunology. 1986 Jan;57(1):93–98. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer J., Finn T., Isaacson P. G. Expression of HLA-DR antigens on epithelium associated with lymphoid tissue in the human gastrointestinal tract. Gut. 1986 Feb;27(2):153–157. doi: 10.1136/gut.27.2.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Allen P. M. Comment on the finding of Ia expression in nonlymphoid cells. Lab Invest. 1986 Aug;55(2):123–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R. Antigen-presenting function of the macrophage. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:395–428. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.002143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilders M. M., Sminia T., Janse E. M. Ontogeny of non-lymphoid and lymphoid cells in the rat gut with special reference to large mononuclear Ia-positive dendritic cells. Immunology. 1983 Oct;50(2):303–314. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. F. The immunoglobulin superfamily takes shape. Nature. 1984 Mar 1;308(5954):12–13. doi: 10.1038/308012a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiman K., Curman B., Forsum U., Klareskog L., Malmnäs-Tjernlund U., Rask L., Trägårdh L., Peterson P. A. Occurrence of Ia antigens on tissues on non-lymphoid origin. Nature. 1978 Dec 14;276(5689):711–713. doi: 10.1038/276711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf J. L., Kauffman R. S., Finberg R., Dambrauskas R., Fields B. N., Trier J. S. Determinants of reovirus interaction with the intestinal M cells and absorptive cells of murine intestine. Gastroenterology. 1983 Aug;85(2):291–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf J. L., Rubin D. H., Finberg R., Kauffman R. S., Sharpe A. H., Trier J. S., Fields B. N. Intestinal M cells: a pathway for entry of reovirus into the host. Science. 1981 Apr 24;212(4493):471–472. doi: 10.1126/science.6259737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Rosen L., Podjaski B., Bettmann I., Otto H. F. Observations on the ultrastructure and function of the so-called "microfold" or "membraneous" cells (M cells) by means of peroxidase as a tracer. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol. 1981;390(3):289–312. doi: 10.1007/BF00496560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]