Abstract
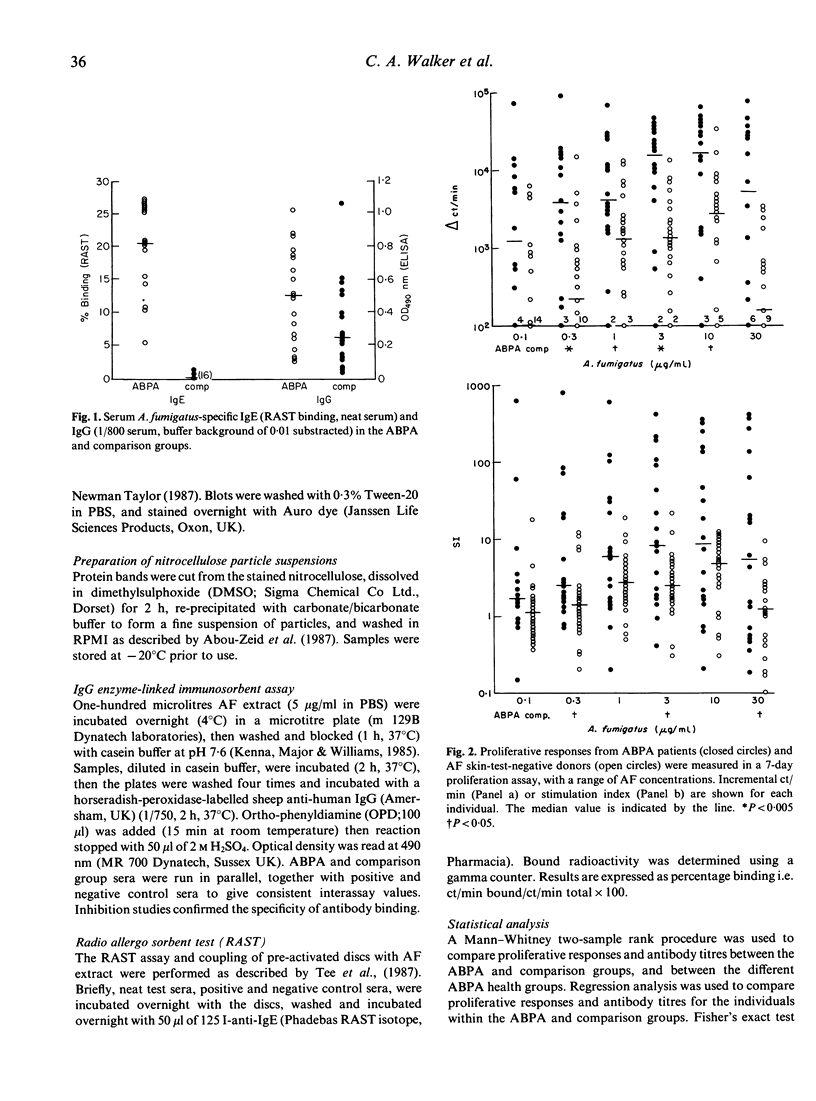
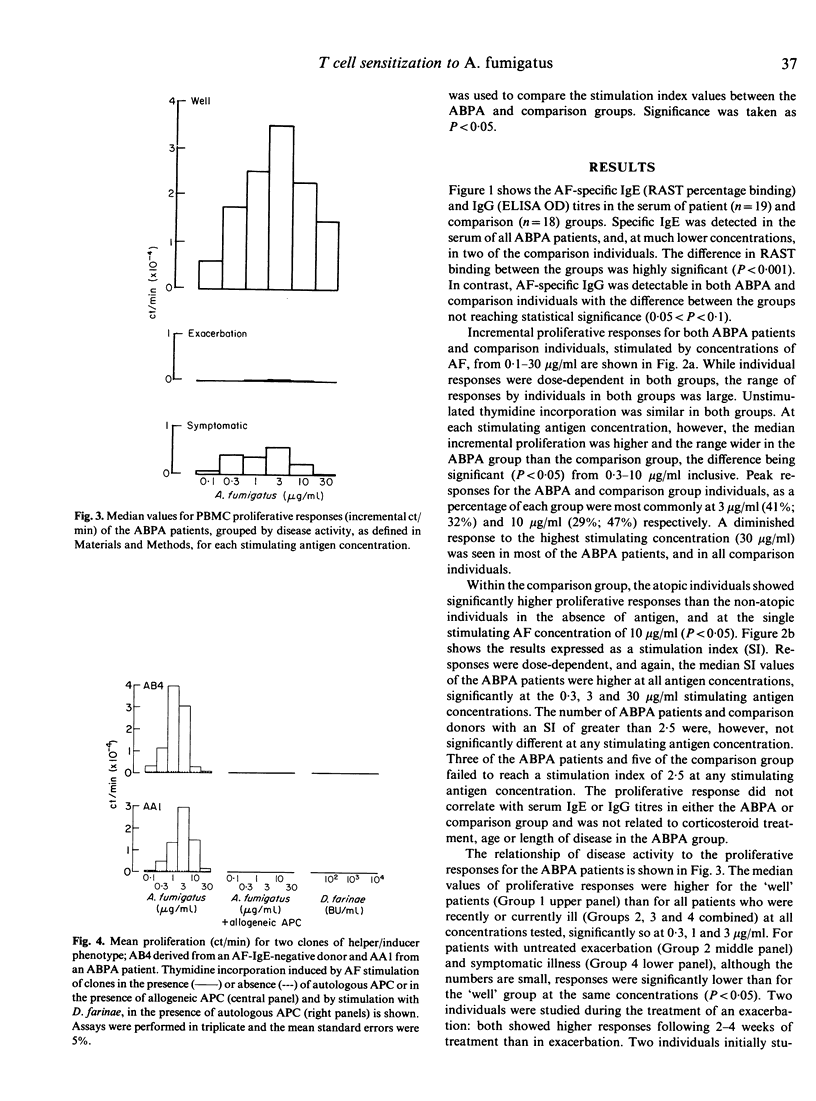
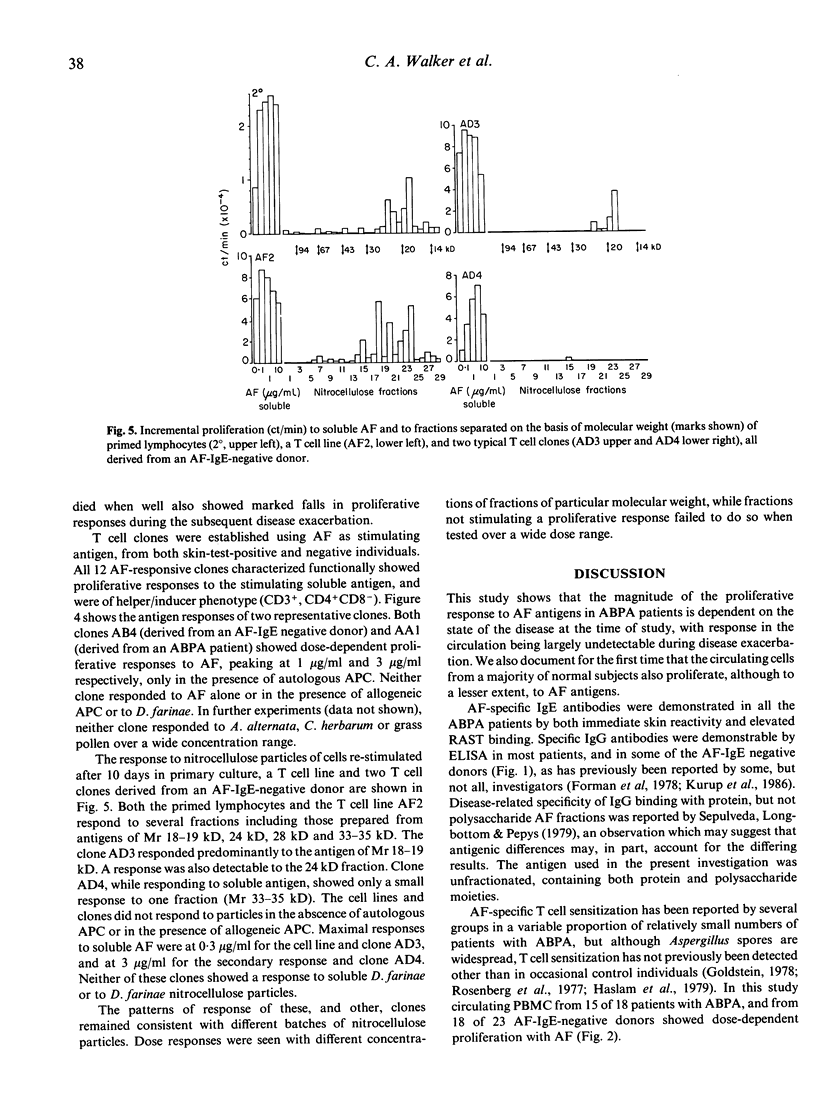
Peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) proliferation induced by an extract of Aspergillus fumigatus (AF) was examined in patients with allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA), all of whom had an immediate skin prick test reaction (SPT) and increased RAST binding to AF, and, for comparison, in individuals without immediate SPT reactivity or increased RAST binding to AF. The proliferative responses of PBMC from the ABPA patients were greater than those from the comparison donors. A substantial proportion of the comparison group, however, showed evidence of a specific immune response to AF, with AF-specific IgG measured by ELISA and specific lymphoproliferative responses. AF-responsive T cell lines and T cell clones were established from both ABPA patients and IgE-negative individuals. These clones, of helper/inducer (CD4+) phenotype, showed antigenic specificity and MHC restriction. The stimulating antigen was determined for four of six clones derived from a skin-prick-test-negative individual, and found to be of Mr 18 kD, possibly the major allergen, 'Ag 3'. ABPA patients showed a marked diminution of the proliferative response during disease exacerbation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abou-Zeid C., Filley E., Steele J., Rook G. A. A simple new method for using antigens separated by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis to stimulate lymphocytes in vitro after converting bands cut from Western blots into antigen-bearing particles. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Apr 2;98(1):5–10. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90429-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley R. H., Seymour F., Sanal S. O., Ownby D. R., Becker W. G. Lymphocyte responses to purified ragweed allergens in vitro. I. Proliferative responses in normal, newborn, agammaglobulinemic, and atopic subjects. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1977 Jan;59(1):70–78. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(77)90180-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cromwell O., Moqbel R., Fitzharris P., Kurlak L., Harvey C., Walsh G. M., Shaw R. J., Kay A. B. Leukotriene C4 generation from human eosinophils stimulated with IgG-Aspergillus fumigatus antigen immune complexes. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1988 Oct;82(4):535–543. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(88)90962-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman S. R., Fink J. N., Moore V. L., Wang J., Patterson R. Humoral and cellular immune responses in Aspergillus fumigatus pulmonary disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1978 Sep;62(3):131–136. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(78)90096-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein R. A. Cellular immune responses in aspergillosis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1978 Apr;61(4):229–230. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(78)90190-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberger P. A. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1984 Nov;74(5):645–653. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(84)90223-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halvorsen R., Bosnes V., Thorsby E. T cell responses to a Dermatophagoides farinae allergen preparation in allergics and healthy controls. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1986;80(1):62–69. doi: 10.1159/000234027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam P., Lukoszek A., Longbottom J. L., Turner-Warwick M. Lymphocyte sensitization to Aspergillus fumigatus antigens in pulmonary diseases in man. Clin Allergy. 1976 May;6(3):277–291. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1976.tb01908.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenna J. G., Major G. N., Williams R. S. Methods for reducing non-specific antibody binding in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Dec 27;85(2):409–419. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90150-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurup V. P., Resnick A., Scribner G. H., Gunasekaran M., Fink J. N. Enzyme profile and immunochemical characterization of Aspergillus fumigatus antigens. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1986 Dec;78(6):1166–1173. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(86)90267-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb J. R., Eckels D. D., Lake P., Johnson A. H., Hartzman R. J., Woody J. N. Antigen-specific human T lymphocyte clones: induction, antigen specificity, and MHC restriction of influenza virus-immune clones. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):233–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb J. R., Zanders E. D., Sewell W., Crumpton M. J., Feldmann M., Owen M. J. Antigen-specific T cell unresponsiveness in cloned helper T cells mediated via the CD2 or CD3/Ti receptor pathways. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Nov;17(11):1641–1644. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830171118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longbottom J. L. Antigens and allergens of Aspergillus fumigatus. II. Their further identification and partial characterization of a major allergen (Ag 3). J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1986 Jul;78(1 Pt 1):18–24. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(86)90109-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longbottom J. L., Austwick P. K. Antigens and allergens of Aspergillus fumigatus. I. Characterization by quantitative immunoelectrophoretic techniques. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1986 Jul;78(1 Pt 1):9–17. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(86)90108-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez A. F., Sanderson C. J., Gamble J. R., Campbell H. D., Young I. G., Vadas M. A. Recombinant human interleukin 5 is a selective activator of human eosinophil function. J Exp Med. 1988 Jan 1;167(1):219–224. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.1.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hehir R. E., Young D. B., Kay A. B., Lamb J. R. Cloned human T lymphocytes reactive with Dermatophagoides farinae (house dust mite): a comparison of T- and B-cell antigen recognition. Immunology. 1987 Dec;62(4):635–640. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips L., Chambers C., Underdown B. J., Zimmerman B. Lymphocyte proliferation to antigen E: demonstration of the restriction of antigen E-specific T cells to ragweed-allergic donors. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1987 Jun;79(6):933–940. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(87)90243-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawle F. C., Mitchell E. B., Platts-Mills T. A. T cell responses to the major allergen from the house dust mite Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus, Antigen P1: comparison of patients with asthma, atopic dermatitis, and perennial rhinitis. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):195–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocklin R. E. Lymphocyte responses to ragweed antigens from different sources. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1979 Jan;63(1):68–69. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(79)90170-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Patterson R., Mintzer R., Cooper B. J., Roberts M., Harris K. E. Clinical and immunologic criteria for the diagnosis of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Apr;86(4):405–414. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-86-4-405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi G. A., Balbi B., Manca F. Tuberculous pleural effusions. Evidence for selective presence of PPD-specific T-lymphocytes at site of inflammation in the early phase of the infection. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Sep;136(3):575–579. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/136.3.575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sepulveda R., Longbottom J. L., Pepys J. Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for IgG and IgE antibodies to protein and polysaccharide antigens of Aspergillus fumigatus. Clin Allergy. 1979 Jul;9(4):359–371. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1979.tb02494.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tee R. D., Gordon D. J., Taylor A. J. Cross-reactivity between antigens of fungal extracts studied by RAST inhibition and immunoblot technique. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1987 Apr;79(4):627–633. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(87)80159-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


