Abstract
There is an association between the clinical stage of HIV-1 infection and the presence of antibodies against viral gag proteins (p17 and p24). The IgG subclass (G1 and G3) pattern against these antigens was analysed in stable patients and HIV patients progressing to AIDS. Antibodies were analysed with whole viral or peptide ELISA (using sequentially overlapping peptides) and Western Blots. IgG1 was found to be the dominant anti-HIV-1 IgG subclass and IgG1 antibodies declined in progressing patients against all HIV antigens evaluated in Western blot, including p17, p24, p31, gp41, p64, gp120 and gp160. In contrast IgG3 antibodies, which were found to be predominantly directed against gag proteins, and which could be detected in almost all patients, remained in the circulation during disease progression. By peptide assays distinct immunogenic regions were found in p17 in contrast to more evenly distributed epitopes in p24. A decreased divergence of antibody reactivity to both p17 and p24 peptides in the group of patients who developed AIDS was seen. No reaction to any single gag epitope related to disease progression. The difference between IgG1 and IgG3 anti-gag antibodies in relation to clearance during disease progression may depend on different properties of immune complexes formed by these two IgG subclasses.
Full text
PDF
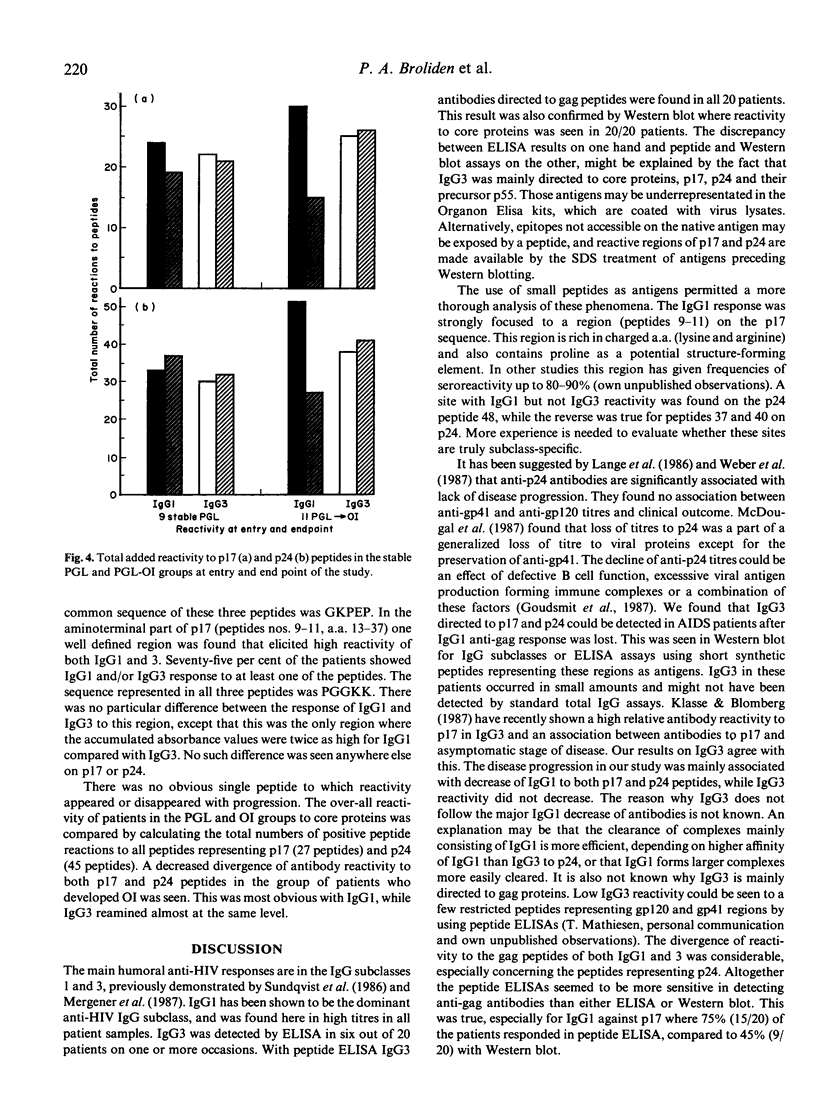

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barré-Sinoussi F., Chermann J. C., Rey F., Nugeyre M. T., Chamaret S., Gruest J., Dauguet C., Axler-Blin C., Vézinet-Brun F., Rouzioux C. Isolation of a T-lymphotropic retrovirus from a patient at risk for acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Science. 1983 May 20;220(4599):868–871. doi: 10.1126/science.6189183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaines H., von Sydow M., Sönnerborg A., Albert J., Czajkowski J., Pehrson P. O., Chiodi F., Moberg L., Fenyö E. M., Asjö B. Antibody response in primary human immunodeficiency virus infection. Lancet. 1987 May 30;1(8544):1249–1253. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92696-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo R. C., Salahuddin S. Z., Popovic M., Shearer G. M., Kaplan M., Haynes B. F., Palker T. J., Redfield R., Oleske J., Safai B. Frequent detection and isolation of cytopathic retroviruses (HTLV-III) from patients with AIDS and at risk for AIDS. Science. 1984 May 4;224(4648):500–503. doi: 10.1126/science.6200936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goudsmit J., Lange J. M., Paul D. A., Dawson G. J. Antigenemia and antibody titers to core and envelope antigens in AIDS, AIDS-related complex, and subclinical human immunodeficiency virus infection. J Infect Dis. 1987 Mar;155(3):558–560. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.3.558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferis R. Polyclonal and monoclonal antibody reagents specific for IgG subclasses. Monogr Allergy. 1986;19:71–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khalife J., Guy B., Capron M., Kieny M. P., Ameisen J. C., Montagnier L., Lecocq J. P., Capron A. Isotypic restriction of the antibody response to human immunodeficiency virus. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1988 Feb;4(1):3–9. doi: 10.1089/aid.1988.4.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klasse J., Blomberg J. Patterns of antibodies to human immunodeficiency virus proteins in different subclasses of IgG. J Infect Dis. 1987 Dec;156(6):1026–1030. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.6.1026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange J. M., Coutinho R. A., Krone W. J., Verdonck L. F., Danner S. A., van der Noordaa J., Goudsmit J. Distinct IgG recognition patterns during progression of subclinical and clinical infection with lymphadenopathy associated virus/human T lymphotropic virus. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Jan 25;292(6515):228–230. doi: 10.1136/bmj.292.6515.228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linde G. A., Hammarström L., Persson M. A., Smith C. I., Sundqvist V. A., Wahren B. Virus-specific antibody activity of different subclasses of immunoglobulins G and A in cytomegalovirus infections. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):237–244. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.237-244.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljunggren K., Broliden P. A., Morfeldt-Månson L., Jondal M., Wahren B. IgG subclass response to HIV in relation to antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity at different clinical stages. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Sep;73(3):343–347. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljunggren K., Fenyö E. M., Biberfeld G., Jondal M. Detection of antibodies which mediate human immunodeficiency virus-specific cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) in vitro. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Nov 23;104(1-2):7–14. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90481-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougal J. S., Kennedy M. S., Nicholson J. K., Spira T. J., Jaffe H. W., Kaplan J. E., Fishbein D. B., O'Malley P., Aloisio C. H., Black C. M. Antibody response to human immunodeficiency virus in homosexual men. Relation of antibody specificity, titer, and isotype to clinical status, severity of immunodeficiency, and disease progression. J Clin Invest. 1987 Aug;80(2):316–324. doi: 10.1172/JCI113075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mergener K., Enzensberger W., Rübsamen-Waigmann H., von Briesen H., Doerr H. W. Immunoglobulin class- and subclass-specific HIV antibody detection in serum and CSF specimens by ELISA and Western blot. Infection. 1987;15(5):317–322. doi: 10.1007/BF01647729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüpbach J., Popovic M., Gilden R. V., Gonda M. A., Sarngadharan M. G., Gallo R. C. Serological analysis of a subgroup of human T-lymphotropic retroviruses (HTLV-III) associated with AIDS. Science. 1984 May 4;224(4648):503–505. doi: 10.1126/science.6200937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundqvist V. A., Linde A., Kurth R., Werner A., Helm E. B., Popovic M., Gallo R. C., Wahren B. Restricted IgG subclass responses to HTLV-III/LAV and to cytomegalovirus in patients with AIDS and lymphadenopathy syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1986 May;153(5):970–973. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.5.970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundqvist V. A., Linde A., Wahren B. Virus-specific immunoglobulin G subclasses in herpes simplex and varicella-zoster virus infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jul;20(1):94–98. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.1.94-98.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vento S., Rondanelli E. G., Ranieri S., O'Brien C. J., Williams R., Eddleston A. L. Prospective study of cellular immunity to hepatitis-B-virus antigens from the early incubation phase of acute hepatitis B. Lancet. 1987 Jul 18;2(8551):119–122. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92329-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]