Abstract
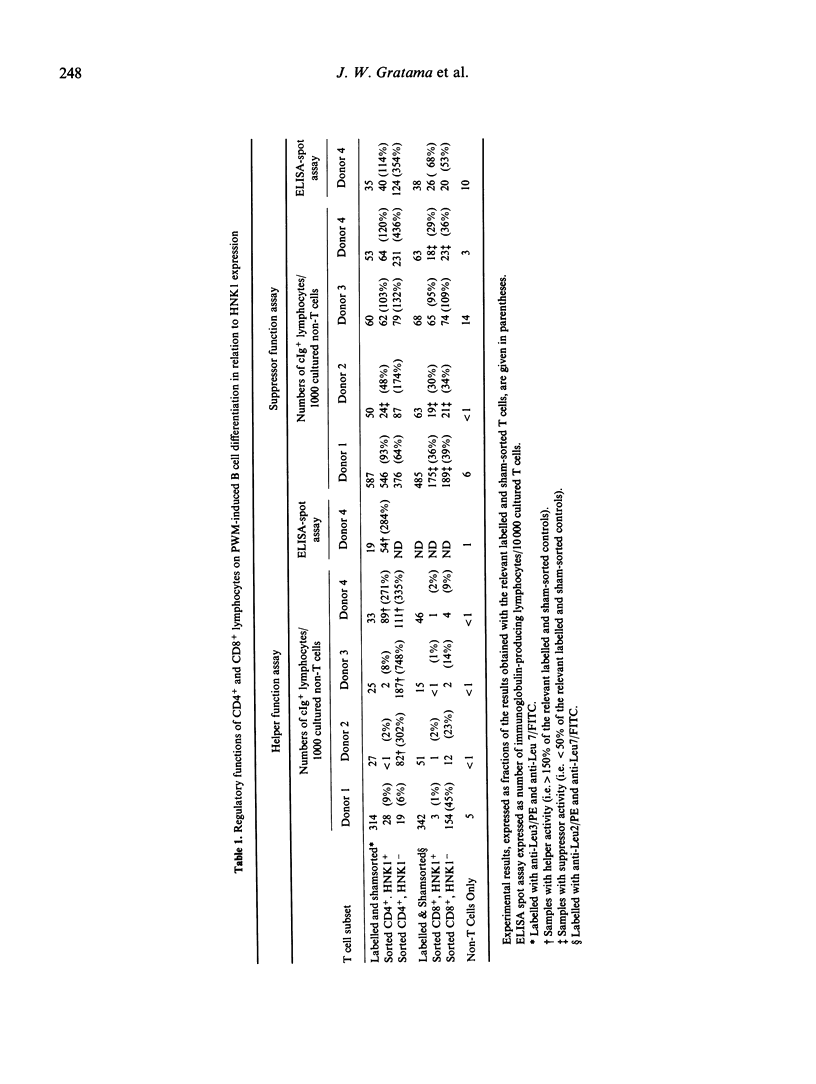
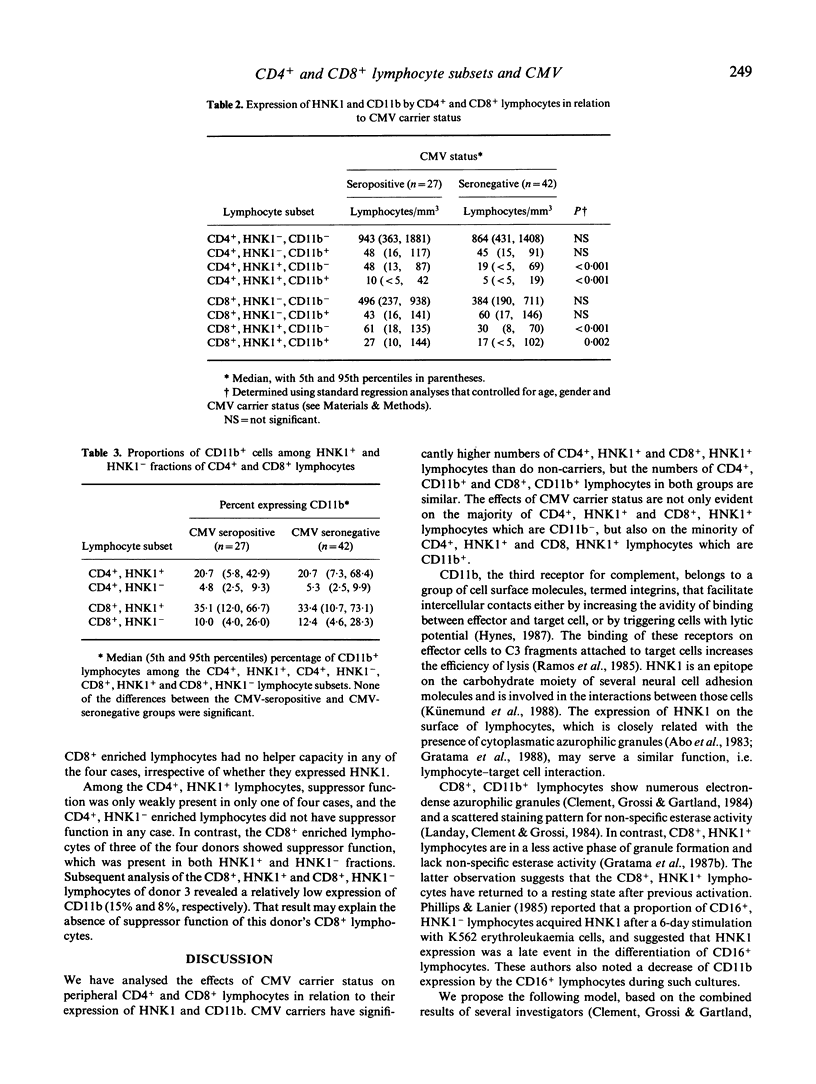
A characteristic of active cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection is its suppressive effect on in vitro assays of immune function. The expression of CD11b by the Cd4+ and Cd8+ lymphocytes allows the identification of subsets with distinct regulatory functions of pokeweed mitogen (PWM) induced B cell differentiation. In order to relate that result with our previous observation that CMV carriers have significantly increased numbers of CD4+, HNK1+ and CD8+, HNK1+ lymphocytes in their peripheral blood compared with non-carriers, we performed a three-colour flow cytometric analysis of the co-expression of Cd11b and HNK1 by CD4+ and CD8+ lymphocytes obtained from 27 CMV carriers and 42 non-carriers. The differences between CMV carriers and non-carriers were significant for the CD4+, HNK1+ lymphocytes (median [5th and 95th percentiles], 59 [18 and 123 versus 24/7 and 73 per mm3, respectively; P less than 0.001) and CD8+, HNK1+ lymphocytes (59 [18 259] versus 52 [23 and 139] per mm3; P less than 0.001), but not for the CD4+, CD11b+ lymphocytes (59 [18 and 135] versus 52 [17 and 104] per mm3) and the CD8+, CD11b+ lymphocytes (85 [34 and 293] versus 82 [21 and 248] per mm3). The CD4+, HNK1+ and CD8+, HNK1+ lymphocytes that were increased in CMV carriers compared with non-carriers included mostly CD11b-, but also CD11b+ lymphocytes. After sorting CD4+ and CD8+ lymphocytes for four CMV carriers into HNK1+ and HNK1- fractions, we analyzed their regulatory functions on PWM-driven B cell Helper function to PWM-driven B cell differentiation was exclusively associated with the CD4+, HNK1- lymphocytes; the CD4+, HNK1+ generally did not show helper or suppressor activity in this assay. Both CD8+, HNK1+ and CD8+, HNK1- lymphocytes showed suppressor activity. Thus, the NHK1 marker does not constitute a phenotypical correlate for suppressor cells of PWM-driven B-cell differentiation.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abo T., Miller C. A., Gartland G. L., Balch C. M. Differentiation stages of human natural killer cells in lymphoid tissues from fetal to adult life. J Exp Med. 1983 Jan 1;157(1):273–284. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.1.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abo W., Gray J. D., Bakke A. C., Horwitz D. A. Studies on human blood lymphocytes with iC3b (type 3) complement receptors. II. Characterization of subsets which regulate pokeweed mitogen-induced lymphocyte proliferation and immunoglobulin synthesis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Mar;67(3):544–555. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney W. P., Iacoviello V., Hirsch M. S. Functional properties of T lymphocytes and their subsets in cytomegalovirus mononucleosis. J Immunol. 1983 Jan;130(1):390–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cauda R., Grossi C. E., Whitley R. J., Tilden A. B. Analysis of immune function in herpes zoster patients: demonstration and characterization of suppressor cells. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 15;138(4):1229–1233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clement L. T., Grossi C. E., Gartland G. L. Morphologic and phenotypic features of the subpopulation of Leu-2+ cells that suppresses B cell differentiation. J Immunol. 1984 Nov;133(5):2461–2468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Waele M., Thielemans C., Van Camp B. K. Characterization of immunoregulatory T cells in EBV-induced infectious mononucleosis by monoclonal antibodies. N Engl J Med. 1981 Feb 19;304(8):460–462. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198102193040804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebel H. M., Kaizer H., Landay A. L. Characterization of circulating suppressor T lymphocytes in bone marrow transplant recipients. Transplantation. 1987 Feb;43(2):258–263. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198702000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gratama J. W., Kardol M., Naipal A. M., Slats J., Den Ouden A., Stijnen T., D'Amaro J., The T. H., Bruning J. W. The influence of cytomegalovirus carrier status on lymphocyte subsets and natural immunity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Jul;69(1):16–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gratama J. W., Kluin-Nelemans H. C., Langelaar R. A., den Ottolander G. J., Stijnen T., D'Amaro J., Torensma R., Tanke H. J. Flow cytometric and morphologic studies of HNK1+ (Leu 7+) lymphocytes in relation to cytomegalovirus carrier status. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Nov;74(2):190–195. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gratama J. W., Schuurman R. K., Van Leeuwen A., Jansen J., Oljans P., Tanke H. J., Van Rood J. J. Comparison of complement-dependent cytotoxicity and indirect immunofluorescence for enumeration of T-cell subpopulations in human peripheral blood. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Nov 11;64(1-2):99–108. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90388-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: a family of cell surface receptors. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):549–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Künemund V., Jungalwala F. B., Fischer G., Chou D. K., Keilhauer G., Schachner M. The L2/HNK-1 carbohydrate of neural cell adhesion molecules is involved in cell interactions. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;106(1):213–223. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.1.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landay A., Clement L. T., Grossi C. E. Phenotypically and functionally distinct subpopulations of human lymphocytes with T cell markers also exhibit different cytochemical patterns of staining for lysosomal enzymes. Blood. 1984 May;63(5):1067–1071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landay A., Gartland G. L., Clement L. T. Characterization of a phenotypically distinct subpopulation of Leu-2+ cells that suppresses T cell proliferative responses. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):2757–2761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leroy E., Calvo C. F., Divine M., Gourdin M. F., Baujean F., Ben Aribia M. H., Mishal Z., Vernant J. P., Farcet J. P., Senik A. Persistence of T8+/HNK-1+ suppressor lymphocytes in the blood of long-term surviving patients after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 1;137(7):2180–2189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logtenberg T., Jonker M., Kroon A., Gmelig-Meyling F. H., Ballieux R. E. Enumeration of (auto)antibody producing cells in human using the "spot-ELISA". Immunol Lett. 1985;9(6):343–347. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(85)90060-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher P., O'Toole C. M., Wreghitt T. G., Spiegelhalter D. J., English T. A. Cytomegalovirus infection in cardiac transplant recipients associated with chronic T cell subset ratio inversion with expansion of a Leu-7+ TS-C+ subset. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Dec;62(3):515–524. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morishita Y., Martin P. J., Bean M. A., Yamada H., Hansen J. A. Antigen-specific functions of a CD4+ subset of human T lymphocytes with granular morphology. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 15;136(6):2095–2102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips J. H., Lanier L. L. A model for the differentiation of human natural killer cells. Studies on the in vitro activation of Leu-11+ granular lymphocytes with a natural killer-sensitive tumor cell, K562. J Exp Med. 1985 Jun 1;161(6):1464–1482. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.6.1464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips J. H., Lanier L. L. Lectin-dependent and anti-CD3 induced cytotoxicity are preferentially mediated by peripheral blood cytotoxic T lymphocytes expressing Leu-7 antigen. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 1;136(5):1579–1585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos O. F., Sármay G., Klein E., Yefenof E., Gergely J. Complement-dependent cellular cytotoxicity: lymphoblastoid lines that activate complement component 3 (C3) and express C3 receptors have increased sensitivity to lymphocyte-mediated lysis in the presence of fresh human serum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5470–5474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., O'Brien C., Rosenthal P., Schlossman S. F. The cellular basis for viral-induced immunodeficiency: analysis by monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1980 Sep;125(3):1269–1274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie A. W., Oswald I., Micklem H. S., Boyd J. E., Elton R. A., Jazwinska E., James K. Circadian variation of lymphocyte subpopulations: a study with monoclonal antibodies. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Jun 4;286(6380):1773–1775. doi: 10.1136/bmj.286.6380.1773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundqvist V. A. Frequency and specificity of varicella zoster virus IgM response. J Virol Methods. 1982 Nov;5(3-4):219–227. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(82)90012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundqvist V. A., Wahren B. An interchangeable ELISA for cytomegalovirus antigen and antibody. J Virol Methods. 1981 Apr;2(5):301–312. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(81)90029-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi T., DiMaggio M., Levine H., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. CD11 molecule defines two types of suppressor cells within the T8+ population. Cell Immunol. 1988 Feb;111(2):398–409. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(88)90103-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trask B., van den Engh G., Landegent J., in de Wal N. J., van der Ploeg M. Detection of DNA sequences in nuclei in suspension by in situ hybridization and dual beam flow cytometry. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1401–1403. doi: 10.1126/science.2416058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velardi A., Clement L. T., Grossi C. E. Quantitative and functional analysis of a human lymphocyte subset with the T-helper (Leu 3/T 4+) phenotype and natural killer (NK)-cell characteristics in patients with malignancy. J Clin Immunol. 1985 Sep;5(5):329–339. doi: 10.1007/BF00918252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velardi A., Mingari M. C., Moretta L., Grossi C. E. Functional analysis of cloned germinal center CD4+ cells with natural killer cell-related features. Divergence from typical T helper cells. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 1;137(9):2808–2813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velardi A., Prchal J. T., Prasthofer E. F., Grossi C. E. Expression of NK-lineage markers on peripheral blood lymphocytes with T-helper (Leu3+/T4+) phenotype in B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 1985 Jan;65(1):149–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velardi A., Tilden A. B., Millo R., Grossi C. E. Isolation and characterization of Leu 7+ germinal-center cells with the T helper-cell phenotype and granular lymphocyte morphology. J Clin Immunol. 1986 May;6(3):205–215. doi: 10.1007/BF00918700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdonck L. F., de Gast G. C. Is cytomegalovirus infection a major cause of T cell alterations after (autologous) bone-marrow transplantation? Lancet. 1984 Apr 28;1(8383):932–935. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92391-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Würsch A. M., Gratama J. W., Middeldorp J. M., Nissen C., Gratwohl A., Speck B., Jansen J., D'Amaro J., The T. H., De Gast G. C. The effect of cytomegalovirus infection on T lymphocytes after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Nov;62(2):278–287. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Gast G. C., Platts-Mills T. A. Functional studies on lymphocytes in adult human bone marrow. I. Immunoglobulin production in vitro after fractionation on a sucrose gradient and T/non-T cell separation. J Immunol. 1979 Jan;122(1):280–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


