Abstract
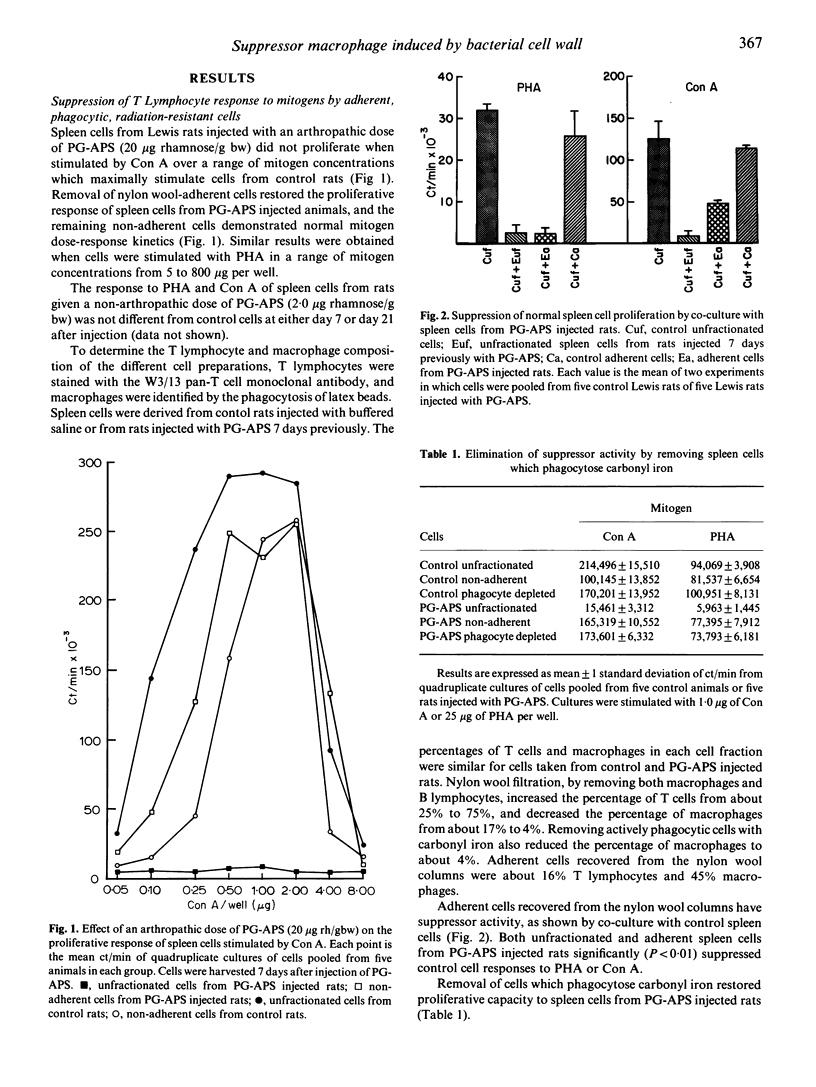
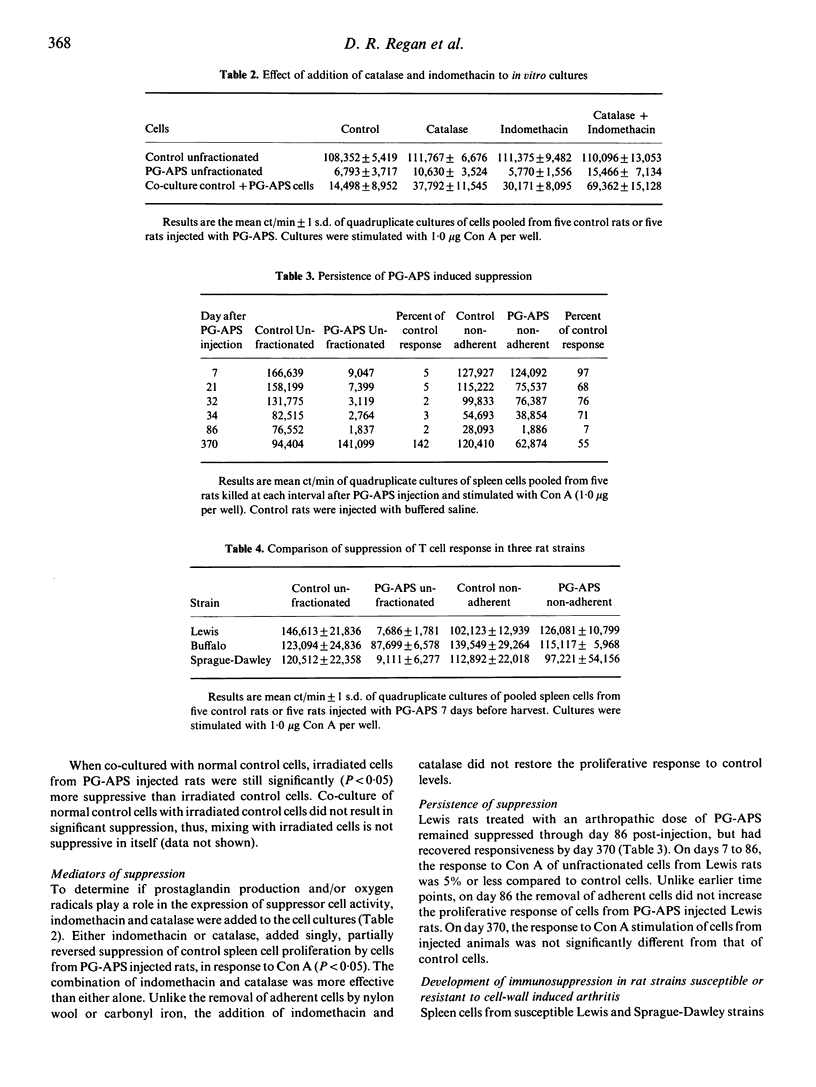
Rats injected with peptidoglycan-polysaccharide polymers derived from group A streptococcal cell walls (PG-APS) develop a chronic, remittant, erosive synovitis. Spleen cells from injected rats failed to proliferate when stimulated in vitro by Con A or PHA, unless nylon wool adherent cells were first removed. The suppression could also be reversed by removing phagocytic cells which had ingested carbonyl iron. Cells from control rats were suppressed in vitro by co-culture with unfractionated or nylon wool-adherent cells from PG-APS injected rats, and the suppressor activity was still expressed after exposure of the suppressor cells to 3,000 rad of irradiation. Addition of catalase and indomethacin to cultures only partially reversed the suppression. T lymphocytes from rats given a single arthropathic dose of PG-APS remained suppressed for at least 86 days after injection. Cells from rats given a low, non-arthropathic dose of PG-APS did not become suppressed. Cells from the Buffalo rat, which is resistant to development of PG-APS-induced chronic arthritis, showed less suppression than cells from the susceptible Lewis and Sprague-Dawley rat strains.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen J. B., Malone D. G., Wahl S. M., Calandra G. B., Wilder R. L. Role of the thymus in streptococcal cell wall-induced arthritis and hepatic granuloma formation. Comparative studies of pathology and cell wall distribution in athymic and euthymic rats. J Clin Invest. 1985 Sep;76(3):1042–1056. doi: 10.1172/JCI112057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrianakos A. A., Sharp J. T., Person D. A., Lidsky M. D., Duffy J. Cell-mediated immunity in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1977 Feb;36(1):13–20. doi: 10.1136/ard.36.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. L., Cuttino J. T., Jr, Anderle S. K., Cromartie W. J., Schwab J. H. Radiologic analysis of arthritis in rats after systemic injection of streptococcal cell walls. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Jan;22(1):25–35. doi: 10.1002/art.1780220105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cromartie W. J., Craddock J. G., Schwab J. H., Anderle S. K., Yang C. H. Arthritis in rats after systemic injection of streptococcal cells or cell walls. J Exp Med. 1977 Dec 1;146(6):1585–1602. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.6.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalldorf F. G., Cromartie W. J., Anderle S. K., Clark R. L., Schwab J. H. The relation of experimental arthritis to the distribution of streptococcal cell wall fragments. Am J Pathol. 1980 Aug;100(2):383–402. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin J. S., Bankhurst A. D., Messner R. P. Suppression of human T-cell mitogenesis by prostaglandin. Existence of a prostaglandin-producing suppressor cell. J Exp Med. 1977 Dec 1;146(6):1719–1734. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.6.1719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter N., Anderle S. K., Brown R. R., Dalldorf F. G., Clark R. L., Cromartie W. J., Schwab J. H. Cell-mediated immune response during experimental arthritis induced in rats with streptococcal cell walls. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Dec;42(3):441–449. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattingly J. A., Eardley D. D., Kemp J. D., Gershon R. K. Induction of suppressor cells in rat spleen: influence of microbial stimulation. J Immunol. 1979 Mar;122(3):787–790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger Z., Hoffeld J. T., Oppenheim J. J. Macrophage-mediated suppression. I. Evidence for participation of both hdyrogen peroxide and prostaglandins in suppression of murine lymphocyte proliferation. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):983–988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muraguchi A., Tachibana T., Miki Y., Kuritani T., Kishi H., Kishimoto S., Yamamura Y., Kishimoto T. Depressed functions of T cells and the presence of suppressor macrophages in patients with sarcoidosis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1982 May;23(2):189–201. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(82)90107-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickerson D. A., Havens R. A., Bullock W. E. Immunoregulation in disseminated histoplasmosis: characterization of splenic suppressor cell populations. Cell Immunol. 1981 May 15;60(2):287–297. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90270-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panush R. S. Nonspecific suppressor function in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1982 Oct;9(1):59–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petit J. C., Richard G., Burghoffer B., Daguet G. L. Suppression of cellular immunity to Listeria monocytogenes by activated macrophages: mediation by prostaglandins. Infect Immun. 1985 Aug;49(2):383–388. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.2.383-388.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope B. L., Whitney R. B., Levy J. G., Kilburn D. G. Suppressor cells in the spleens of tumor-bearing mice: enrichment by centrifugation on hypaque-ficoll and characterization of the suppressor population. J Immunol. 1976 May;116(5):1342–1346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff H. V., Hinrichs D. J. Suppressor cell infleunce in selected strains of inbred rats. II. Macrophage-associated suppression of cell-mediated immune responsiveness. Cell Immunol. 1977 Mar 1;29(1):109–117. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90279-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice L., Laughter A. H., Twomey J. J. Three suppressor systems in human blood that modulate lymphoproliferation. J Immunol. 1979 Mar;122(3):991–996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridge S. C., Zabriske J. B., Oronsky A. L., Kerwar S. S. Streptococcal cell wall arthritis: studies with nude (athymic) inbred Lewis rats. Cell Immunol. 1985 Nov;96(1):231–234. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90354-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridge S. C., Zabriskie J. B., Osawa H., Diamantstein T., Oronsky A. L., Kerwar S. S. Administration of group A streptococcal cell walls to rats induces an interleukin 2 deficiency. J Exp Med. 1986 Jul 1;164(1):327–332. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.1.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salgame P. R., Mahadevan P. R., Antia N. H. Mechanism of immunosuppression in leprosy: presence of suppressor factor(s) from macrophages of lepromatous patients. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):1119–1126. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.1119-1126.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seitz M., Deimann W., Gemsa D. The influence of synovial fluid from patients with rheumatoid arthritis on the proliferation of peripheral blood lymphocytes and the prostanoid release from monocytes. Agents Actions. 1981 Dec;11(6-7):606–608. doi: 10.1007/BF01978760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver R. M., Redelman D., Zvaifler N. J. Studies of rheumatoid synovial fluid lymphocytes. II. A comparison of their behavior with blood mononuclear cells in the autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction and response to TCGF. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1983 Apr;27(1):15–27. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(83)90052-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sopori M. L., Sheil J. M., Roszman T. L., Brooks W. H. T-lymphocyte heterogeneity in rat: role of adherent T-cell subpopulation in the regulation of cytotoxic T-cell response to alloantigens. Cell Immunol. 1981 Nov 15;65(1):103–114. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90056-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vetvicka V., Fornůsek L., Tlaskalová H. Comparison of different methods for separation of human, mouse and rat macrophages and lymphocytes. Folia Biol (Praha) 1981;27(3):194–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadee A. A., Mendelsohn D., Rabson A. R. Characterization of a suppressor cell-activating factor (SCAF) released by adherent cells treated with M. tuberculosis. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2266–2270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman J., Lockshin M. D., Schnapp J. J., Doneson I. N. Cellular immunity in rheumatic diseases. I. Rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1973 Jul-Aug;16(4):499–506. doi: 10.1002/art.1780160410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilder R. L., Allen J. B., Wahl L. M., Calandra G. B., Wahl S. M. The pathogenesis of group A streptococcal cell wall-induced polyarthritis in the rat. Comparative studies in arthritis resistant and susceptible inbred rat strains. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Dec;26(12):1442–1451. doi: 10.1002/art.1780261205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zembala M., Lemmel E. M. Inhibitory factor(s) of lymphoproliferation produced by synovial fluid mononuclear cells from rheumatoid arthritis patients: the role of monocytes in suppression. J Immunol. 1980 Sep;125(3):1087–1092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


