Abstract
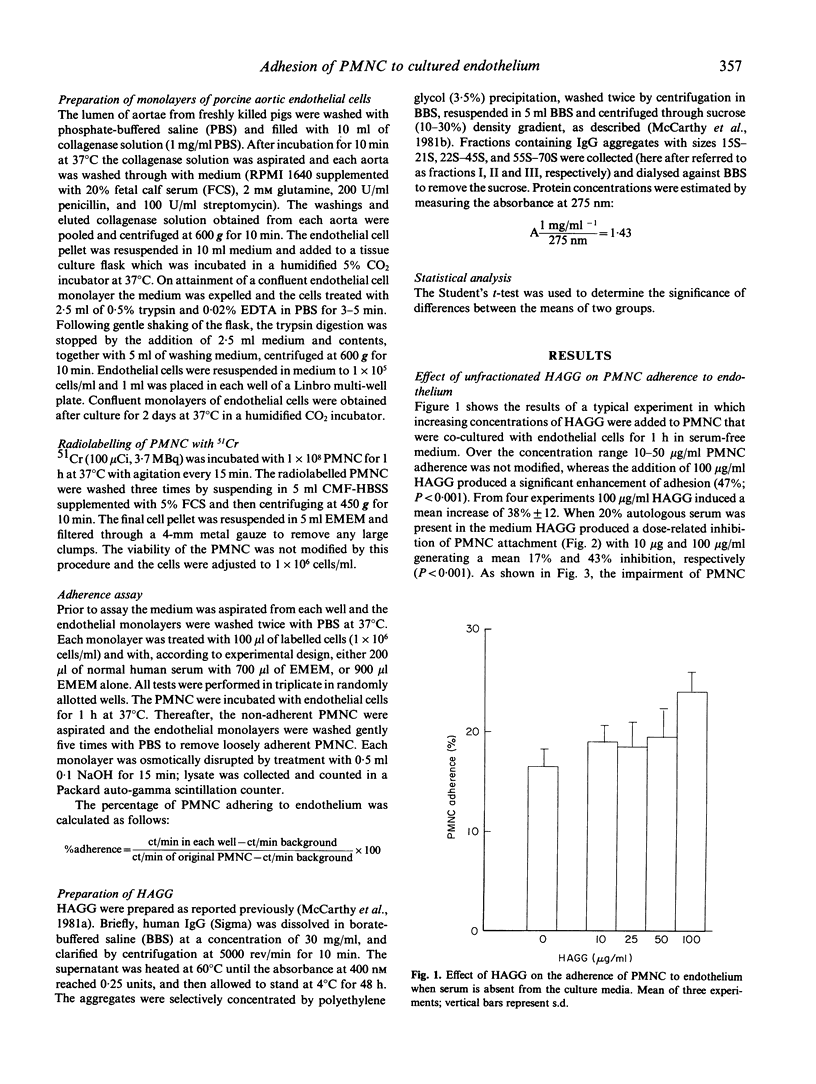
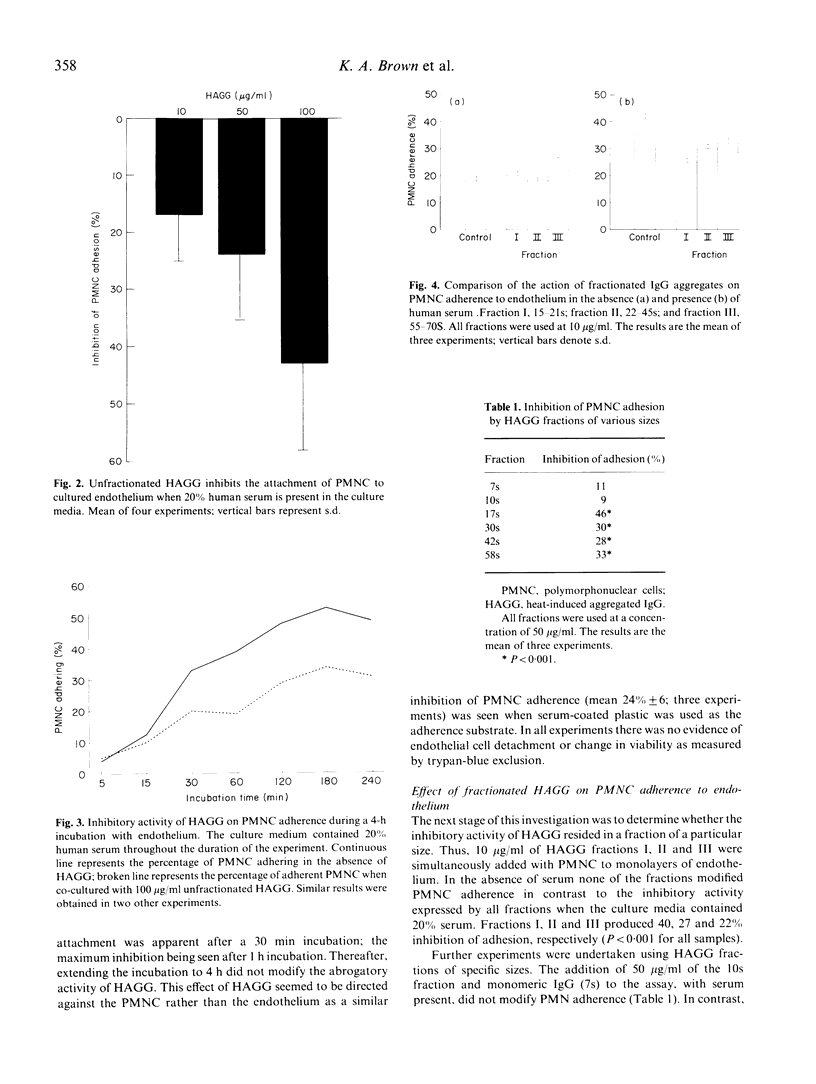
The adherence of human blood polymorphonuclear cells (PMNC) to cultured porcine aortic endothelium was enhanced by high concentrations of heat-stable IgG aggregates (HAGG) when sera was omitted from the culture media. With 20% human serum present in the media, HAGG induced a dose-related inhibition of PMNC adhesions with concentrations as low as 10 micrograms/ml producing a significant effect. This inhibitory action of HAGG, which was optimally expressed after 30 min of incubation, seemed to be directed at the PMNC rather than the endothelium. Heat-inactivation of the sera resulted in a marked decline of the inhibitory activity of HAGG. Aggregates of size 15-21 s were demonstrated to be most effective in inhibiting PMNC attachment and it is complexes of this size which are commonly found in the circulation of patients with chronic inflammatory diseases. Immune complex modification of PMNC adherence may control leucocyte extravasation during inflammation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreis M., Hurd E. R., Lospalluto J., Ziff M. Comparison of the presence of immune complexes in Felty's syndrome and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1978 Apr;21(3):310–315. doi: 10.1002/art.1780210304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjursten L. M., Thomsen P., Ahlstedt S., Bagge U. The kinetics of leucocyte migration into rabbit knee joints elicited by preformed immune complexes with different in vitro characteristics. Immunology. 1983 Jun;49(2):205–213. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. A., McCarthy D., Perry J. D., Dumonde D. C. Reduction of the surface charge of blood polymorphonuclear cells by rheumatoid sera and heat induced aggregated human IgG (HAGG). Ann Rheum Dis. 1988 May;47(5):359–363. doi: 10.1136/ard.47.5.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. A., Perry J. D., Black C., Dumonde D. C. Identification by cell electrophoresis of a subpopulation of polymorphonuclear cells which is increased in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and certain other rheumatological disorders. Ann Rheum Dis. 1988 May;47(5):353–358. doi: 10.1136/ard.47.5.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camussi G., Tetta C., Cappio F. C. Detection of immune complexes on the surface of polymorphonuclear neutrophils. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1979;58(2):135–139. doi: 10.1159/000232185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chasty R. C., Brown K. A., Sheehan N. J., Kirk A. P., Perry J. D., McCarthy D., Dumonde D. C. Rheumatoid blood decreases the adherence of polymorphonuclear cells (PMNs) to cultured endothelium. Ann Rheum Dis. 1987 Feb;46(2):98–103. doi: 10.1136/ard.46.2.98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cines D. B., Lyss A. P., Bina M., Corkey R., Kefalides N. A., Friedman H. M. Fc and C3 receptors induced by herpes simplex virus on cultured human endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jan;69(1):123–128. doi: 10.1172/JCI110422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIOGUARDI N., AGOSTONI A., FIORELLI G., LOMANTO B. Characterization of lactic dehydrogenase of normal human granulocytes. J Lab Clin Med. 1963 May;61:713–723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fillit H. M., Jaffe E. A., Zabriskie J. B. In vitro correlates of endothelial injury and repair. Lab Invest. 1982 Jan;46(1):1–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin J. I. Degranulating stimuli decrease the neagative surface charge and increase the adhesiveness of human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1980 Feb;65(2):298–306. doi: 10.1172/JCI109672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin J. I. Degranulating stimuli decrease the neagative surface charge and increase the adhesiveness of human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1980 Feb;65(2):298–306. doi: 10.1172/JCI109672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goddard D. H., Kirk A. P., Brown K. A., McCarthy D., Johnson G. D., Holborow E. J. Changes in normal polymorphonuclear leucocyte motility after ingestion of IgG aggregates. Ann Rheum Dis. 1984 Apr;43(2):146–150. doi: 10.1136/ard.43.2.146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson G. K., Starkebaum G. A., Benditt E. P., Schwartz S. M. Fc-mediated binding of IgG to vimentin-type intermediate filaments in vascular endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3103–3107. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto Y., Hurd E. R. Human neutrophil aggregation and increased adherence to human endothelial cells induced by heat-aggregated IgG and immune complexes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Jun;44(3):538–547. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy D., Goddard D. H., Holborow E. J., Horsfall A. C., Mumford P. A., Maini R. N. The effect of IgG aggregate size and concentration on reactivity in immune complex assays. J Immunol Methods. 1981;47(3):349–358. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90291-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nydegger U. E., Lambert P. H., Gerber H., Miescher P. A. Circulating immune complexes in the serum in systemic lupus erythematosus and in carriers of hepatitis B antigen. Quantitation by binding to radiolabeled C1q. J Clin Invest. 1974 Aug;54(2):297–309. doi: 10.1172/JCI107765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope R. M., Teller D. C., Mannik M. Intermediate complexes formed by self-association of IgG-rheumatoid factors. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 13;256:82–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb36037.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan U. S., Schultz D. R., Del Vecchio P. J., Ryan J. W. Endothelial cells of bovine pulmonary artery lack receptors for C3b and for the Fc portion of immunoglobulin G. Science. 1980 May 16;208(4445):748–749. doi: 10.1126/science.7367890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan U. S., Schultz D. R., Ruan J. W. Fc and C3b receptors on pulmonary endothelial cells: induction by injury. Science. 1981 Oct 30;214(4520):557–558. doi: 10.1126/science.6270789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheehan N. J., Brown K. A., Perry J. D., Chasty R. C., Yates D. A., Dumonde D. C. Adherence of rheumatoid polymorphonuclear cells (PMNs) to cultured endothelial cell monolayers. Ann Rheum Dis. 1987 Feb;46(2):93–97. doi: 10.1136/ard.46.2.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A., Anderson D. C. The importance of the Mac-1, LFA-1 glycoprotein family in monocyte and granulocyte adherence, chemotaxis, and migration into inflammatory sites: insights from an experiment of nature. Ciba Found Symp. 1986;118:102–126. doi: 10.1002/9780470720998.ch8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theofilopoulos A. N., Burtonboy G., LoSpalluto J. J., Ziff M. IgM rheumatoid factor and low molecular weight IgM. An association with vasculitis. Arthritis Rheum. 1974 May-Jun;17(3):272–284. doi: 10.1002/art.1780170312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Rao P. E., Van Voorhis W. C., Craigmyle L. S., Iida K., Talle M. A., Westberg E. F., Goldstein G., Silverstein S. C. Identification of the C3bi receptor of human monocytes and macrophages by using monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5699–5703. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


