Abstract
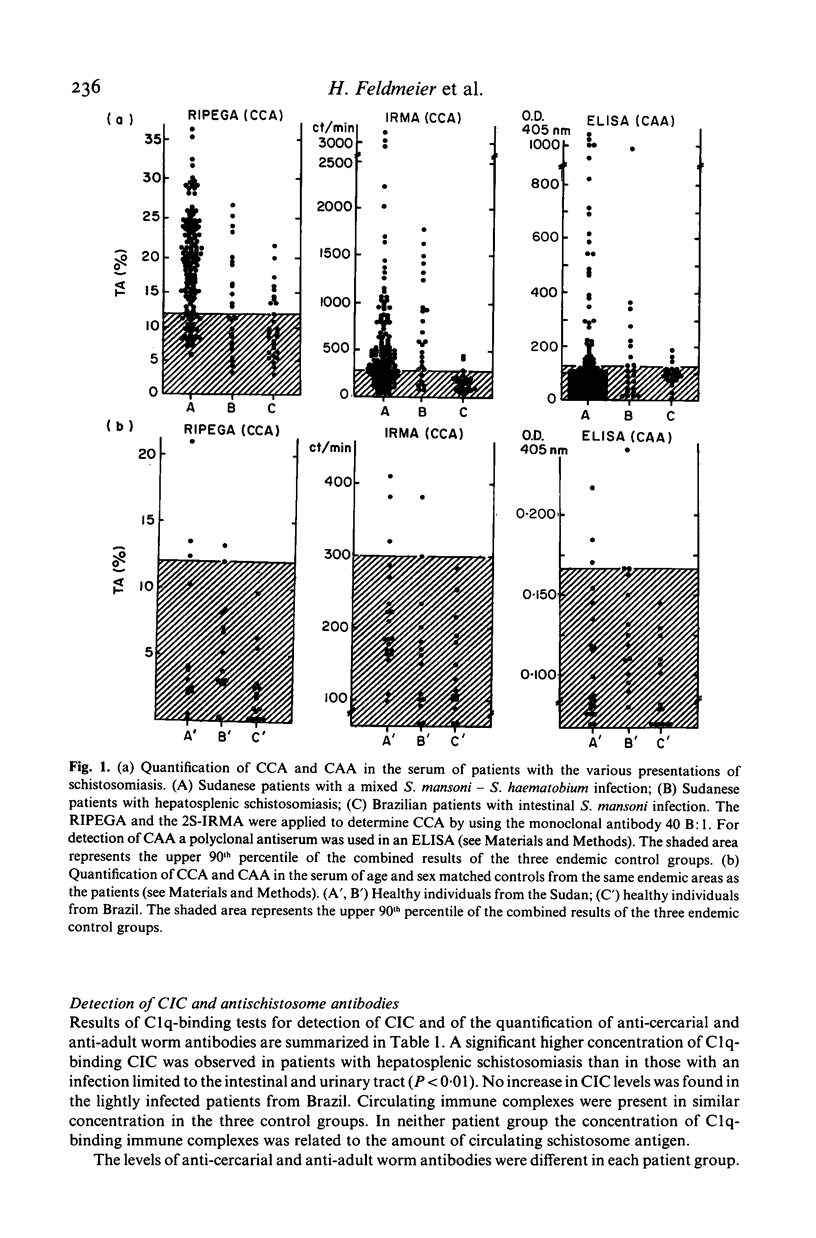
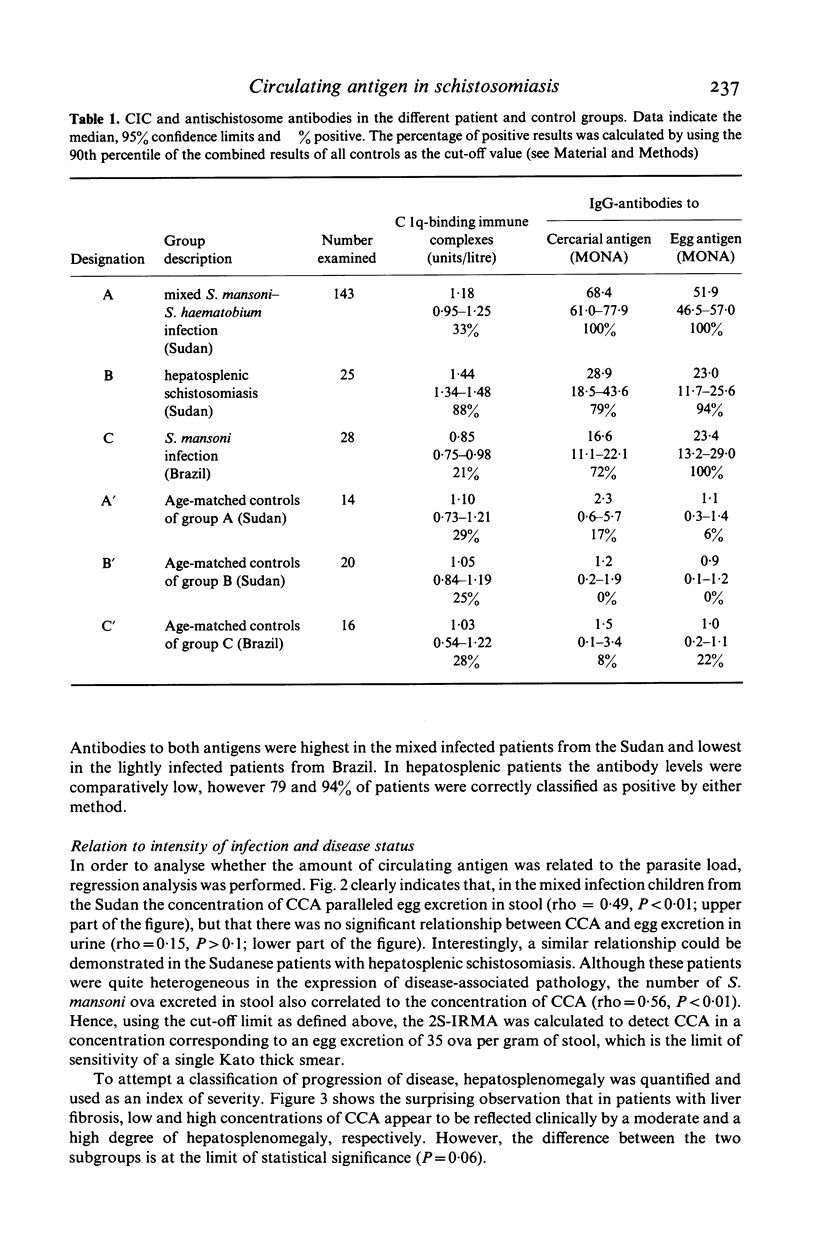
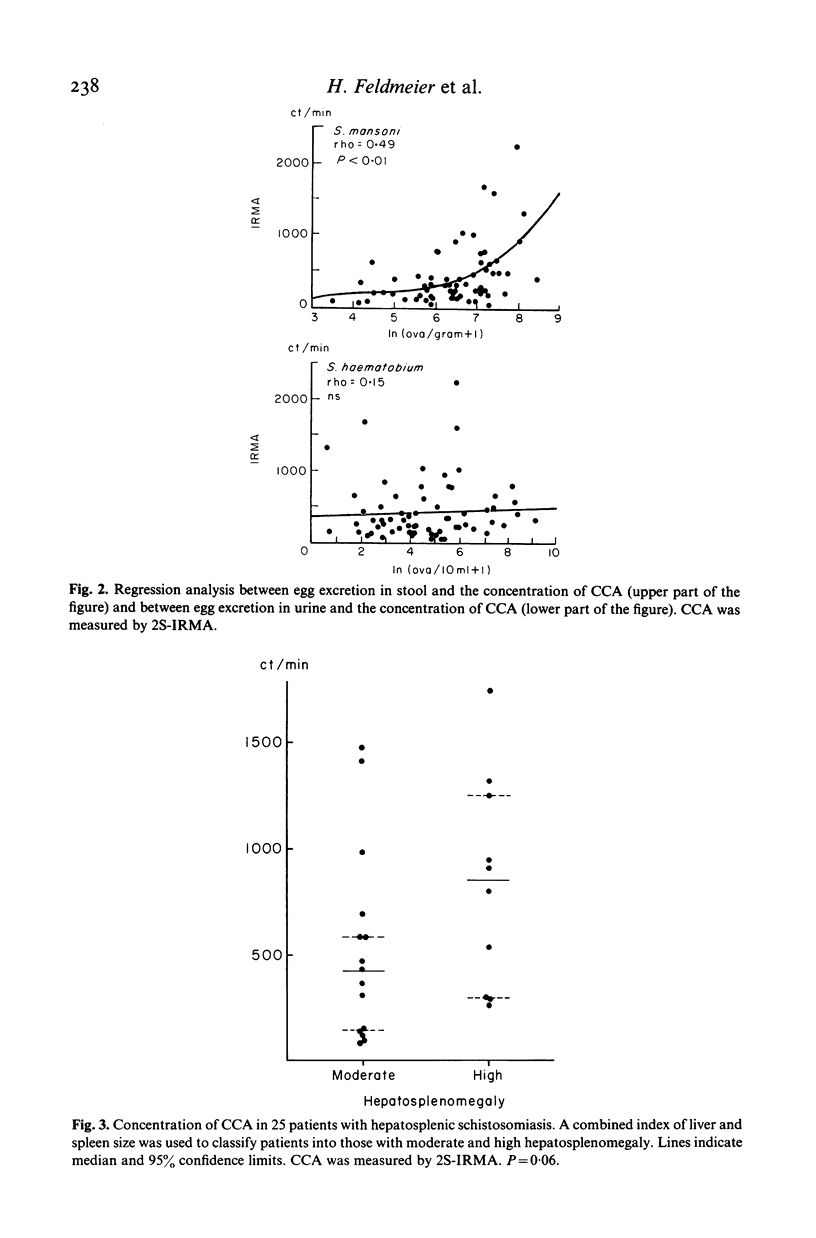
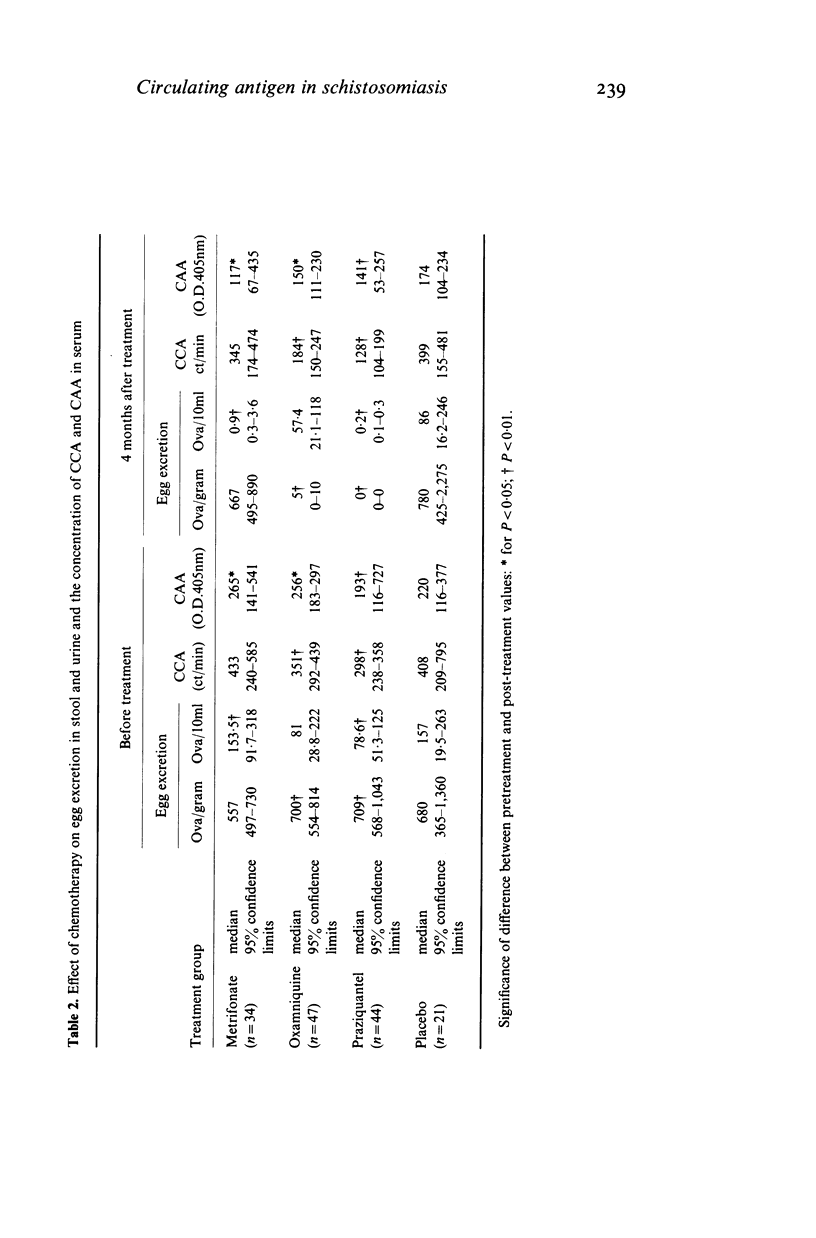
Circulating cathodic and circulating anodic antigens were quantified in sera of patients infected with S. mansoni, S. haematobium or both parasites. A monoclonal antibody and a polyclonal antiserum were applied in precipitation and solid phase immunosorbent techniques using radio- and enzyme-labelled antibody as a tracer to detect the cathodic and anodic antigen respectively. The results show that circulating cathodic antigen can frequently be detected in an immunoprecipitation or an immunoradiometric assay in serum of infected patients. The serum concentration of this antigen was found to be significantly correlated to the number of S. mansoni worms and to be higher in patients with the hepatosplenic form of the disease than in those without such complications. Examining paired serum samples before and after specific treatment the determination of this antigen by monoclonal antibody reliably indicated efficacy of chemotherapy in patients having received different forms of treatment.
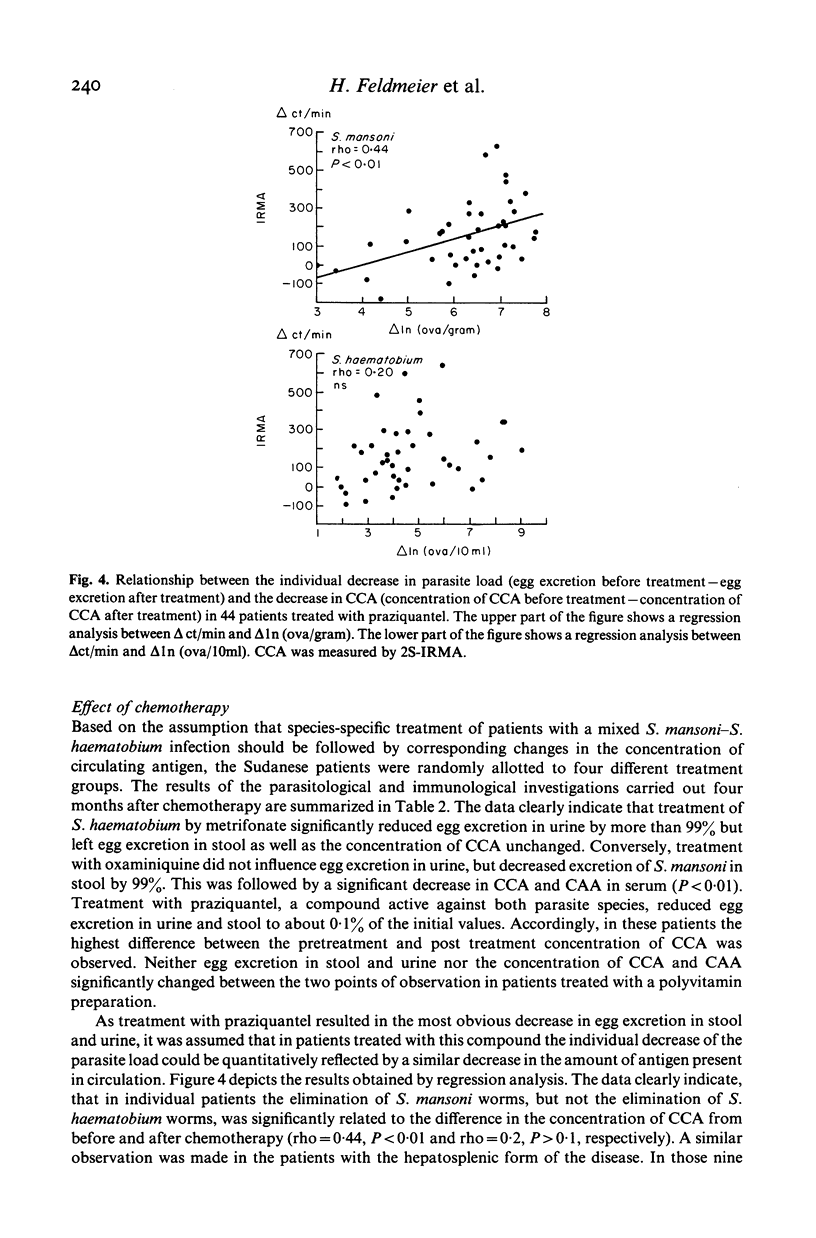
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdel-Hafez S. K., Phillips S. M., Zodda D. M. Schistosoma mansoni: detection and characterization of antigens and antigenemia by inhibition enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (IELISA). Exp Parasitol. 1983 Apr;55(2):219–232. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(83)90016-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Hafez S. K., Phillips S. M., Zodda D. M. Schistosoma mansoni: detection and characterization of schistosome derived antigens by inhibition enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (IELISA) utilizing monoclonal antibodies. Z Parasitenkd. 1984;70(1):105–117. doi: 10.1007/BF00929580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLAGG W., SCHLOEGEL E. L., MANSOUR N. S., KHALAF G. I. A new concentration technic for the demonstration of protozoa and helminth eggs in feces. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1955 Jan;4(1):23–28. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1955.4.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlier Y., Bout D., Bina J. C., Camus D., Figueiredo J. F., Capron A. Immunological studies in human schistosomiasis. I. Parasitic antigen in urine. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1975 Nov;24(6 Pt 1):949–954. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1975.24.949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlier Y., Bout D., Capron A. Detection of Schistosoma mansoni M antigen in circulating immune-complexes and in kidneys of infected hamsters. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1980;74(4):534–538. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(80)90072-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlier Y., Bout D., Strecker G., Debray H., Capron A. Purification, immunochemical, and biologic characterization of the Schistosoma circulating M antigen. J Immunol. 1980 May;124(5):2442–2450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deelder A. M., Klappe H. T., van den Aardweg G. J., van Meerbeke E. H. Schistosoma mansoni: demonstration of two circulating antigens in infected hamsters. Exp Parasitol. 1976 Oct;40(2):189–197. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(76)90081-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deelder A. M., Kornelis D., Van Marck E. A., Eveleigh P. C., Van Egmond J. G. Schistosoma mansoni: characterization of two circulating polysaccharide antigens and the immunological response to these antigens in mouse, hamster, and human infections. Exp Parasitol. 1980 Aug;50(1):16–32. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(80)90004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Digeon M., Droz D., Noel L. H., Riza J., Rieumailhol C., Bach J. F., Santoro F., Capron A. The role of circulating immune complexes in the glomerular disease of experimental hepatosplenic schistosomiasis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Mar;35(3):329–337. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Dosoky I., Van Marck E. A., Deelder A. M. Presence of Schistosoma mansoni antigens in liver, spleen and kidney of infected mice: a sequential study. Z Parasitenkd. 1984;70(4):491–497. doi: 10.1007/BF00926690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa. 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldmeier H., Bienzle U., Dietrich M., Sievertsen H. J. Combination of a viability test and a quantification method for Schistosoma haematobium eggs (filtration--trypan blue-staining-technique). Tropenmed Parasitol. 1979 Dec;30(4):417–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldmeier H., Büttner D. W. Immunodiagnosis of Schistosomiasis haematobium and schistosomiasis mansoni in man. Application of crude extracts from adult worms and cercariae in the IHA and the ELISA. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1983 Sep;255(2-3):413–421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgner P. Stepless antibody determination with the stick-ELISA technique. Results expressed as multiple of normal activity (MONA). Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1978 Nov;242(1):100–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galvão-Castro B., Bina J. C., Prata A., Lambert P. H. Correlation of circulating immune complexes and complement breakdown products with the severity of the disease in human schistosomiasis mansoni. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1981 Nov;30(6):1238–1246. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1981.30.1238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold R., Rosen F. S., Weller T. H. A specific circulating antigen in hamsters infected with Schistosoma mansoni. Detection of antigen in serum and urine, and correlation between antigenic concentration and worm burden. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1969 Jul;18(4):545–552. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1969.18.545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino-Shimizu S., De Brito T., Kanamura H. Y., Canto A. L., Silva A. O., Campos A. R., Penna D. O., Da Silva L. C. Human schistosomiasis: Schistosoma mansoni antigen detection in renal glomeruli. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1976;70(5-6):492–496. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(76)90135-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ismail M. M., James C., Webbe G. The enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for the determination of circulating antigen and antibody in Schistosoma haematobium-infected baboons. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1981;75(4):542–548. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(81)90195-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunde M. N. A C1Q enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using polyethylene glycol for immune complexes. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1983 Mar;32(2):392–396. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1983.32.392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T. E. Factors that modulate clearance and ultimate fate of a specific schistosome antigen (GASP) in schistosome infections. J Immunol. 1982 Apr;128(4):1608–1613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T. E. Localization of the circulating antigen within the gut of Schistosoma mansoni. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1974 Nov;23(6):1085–1087. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1974.23.1085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T. E., Prescott B., Neva F. A. The characteristics of a circulating antigen in schistosomiasis. J Immunol. 1974 Apr;112(4):1500–1507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira-Queiroz J. A., Lutsch C., Capron M., Dessaint J. P., Capron A. Detection and quantification of circulating antigen in schistosomiasis by a monoclonal antibody. I. Specificity analysis of a monoclonal antibody with immunodiagnostic capacity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Aug;65(2):223–231. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian Z. L., Deelder A. M. Schistosoma japonicum: immunological characterization and detection of circulating polysaccharide antigens from adult worms. Exp Parasitol. 1983 Apr;55(2):168–178. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(83)90011-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed A. H., Henry R. J., Mason W. B. Influence of statistical method used on the resulting estimate of normal range. Clin Chem. 1971 Apr;17(4):275–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotmans J. P., Van der Voort M. J., Looze M., Mooij G. W., Deelder A. M. Schistosoma mansoni: characterization of antigens in excretions and secretions. Exp Parasitol. 1981 Oct;52(2):171–182. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(81)90072-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoro F., Borojevic R., Bout D., Tachon P., Bina J. C., Capron A. Mother-child relationship in human schistosomiasis mansoni. I. Parasitic antigens and antibodies in milk. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1977 Nov;26(6 Pt 1):1164–1168. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1977.26.1164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoro F., Prata A., Castro C. N., Capron A. Circulating antigens, immune complexes and C3d levels in human schistosomiasis: relationship with Schistosoma mansoni egg output. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Nov;42(2):219–225. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoro F., Prata A., Silva A. E., Capron A. Correlation between circulating antigens detected by the radioimmunoprecipitation-polyethylene glycol assay (RIPEGA) and C1q-binding immune complexes in human schistosomiasis mansoni. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1981 Sep;30(5):1020–1025. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1981.30.1020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoro F., Vandemeulebrouke B., Capron A. The use of the radioimmunoprecipitation-PEG assay (RIPEGA) to quantify circulating antigens in human and experimental schistosomiasis. J Immunol Methods. 1978;24(3-4):229–237. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(78)90127-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weltman J. K. Effect of praziquantel on antigenemia in murine schistosomiasis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1982 Nov;31(6):1294–1296. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1982.31.1294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


