Abstract
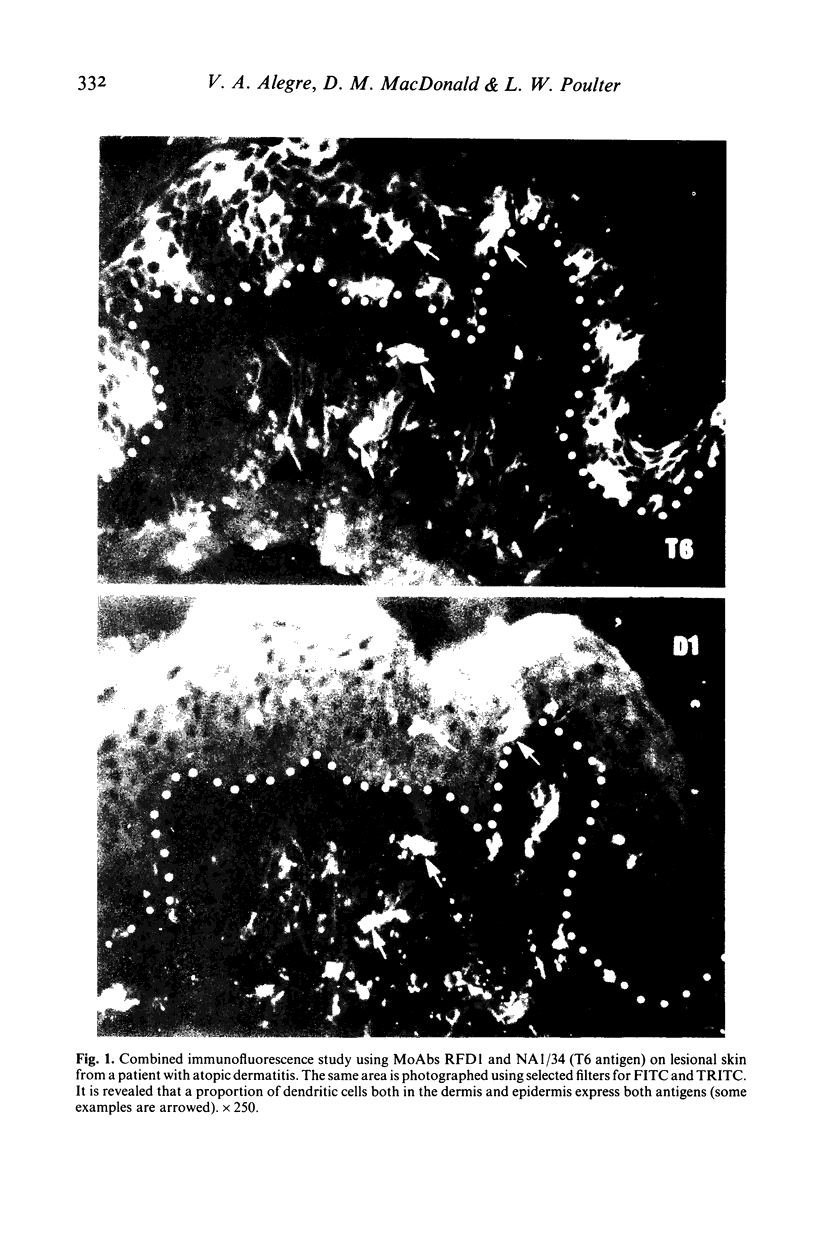
Immunohistological studies have been performed on tissues from various dermatological conditions using two monoclonal antibodies, RFD1 and NA1/34. These reagents were used to determine whether antigen expression restricted to interdigitating cells (RFD1+) and Langerhans' cells (NA1/34+) in normal tissues might occur together on dendritic cells involved in cutaneous inflammatory reactions. The results presented demonstrate that in psoriasis, allergic contact dermatitis and atopic dermatitis a proportion of the inflammatory dendritic cells express both antigens.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bos J. D., Huisman P. M., Krieg S. R., Faber W. R. Pityriasis rosea (Gibert): abnormal distribution pattern of antigen presenting cells in situ. Acta Derm Venereol. 1985;65(2):132–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach A. S. Branched cells in the epidermis: an overview. J Invest Dermatol. 1980 Jul;75(1):6–11. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12521029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach A. S. Prosser White Oration 1976. Electron micrographs from a collection. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1977 Mar;2(1):1–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2230.1977.tb01531.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsum U., Claesson K., Hjelm E., Karlsson-Parra A., Klareskog L., Scheynius A., Tjernlund U. Class II transplantation antigens: distribution in tissues and involvement in disease. Scand J Immunol. 1985 May;21(5):389–396. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1985.tb01823.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janossy G., Thomas J. A., Goldstein G., Bollum F. J. The human thymic environment. Ciba Found Symp. 1981;84:193–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz S. I., Tamaki K., Sachs D. H. Epidermal Langerhans cells are derived from cells originating in bone marrow. Nature. 1979 Nov 15;282(5736):324–326. doi: 10.1038/282324a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klareskog L., Tjernlund U., Forsum U., Peterson P. A. Epidermal Langerhans cells express Ia antigens. Nature. 1977 Jul 21;268(5617):248–250. doi: 10.1038/268248a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulter L. W. Antigen presenting cells in situ: their identification and involvement in immunopathology. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Sep;53(3):513–520. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulter L. W., Janossy G. The involvement of dendritic cells in chronic inflammatory disease. Scand J Immunol. 1985 May;21(5):401–407. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1985.tb01825.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulter L. W., Seymour G. J., Duke O., Janossy G., Panayi G. Immunohistological analysis of delayed-type hypersensitivity in man. Cell Immunol. 1982 Dec;74(2):358–369. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(82)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowden G., Boudreau S., Higley H. Langerhans cells and extra-epidermal dendritic cells. An investigation in laboratory animals and man with immunomorphological methods. Scand J Immunol. 1985 May;21(5):471–478. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1985.tb01834.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberberg-Sinakin I., Thorbecke G. J., Baer R. L., Rosenthal S. A., Berezowsky V. Antigen-bearing langerhans cells in skin, dermal lymphatics and in lymph nodes. Cell Immunol. 1976 Aug;25(2):137–151. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(76)90105-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uno H., Hanifin J. M. Langerhans cells in acute and chronic epidermal lesions of atopic dermatitis, observed by L-dopa histofluorescence, glycol methacrylate thin secretion, and electron microscopy. J Invest Dermatol. 1980 Jul;75(1):52–60. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12521130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


