Abstract
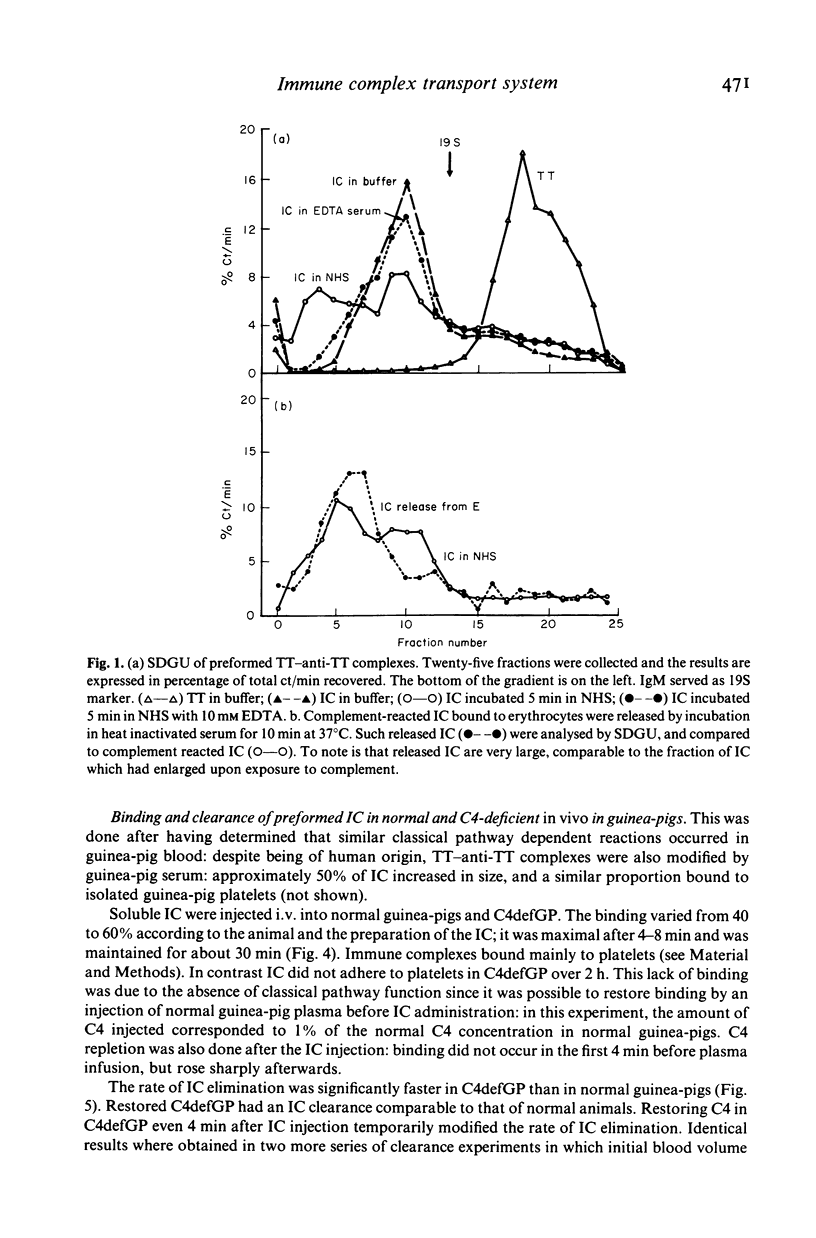
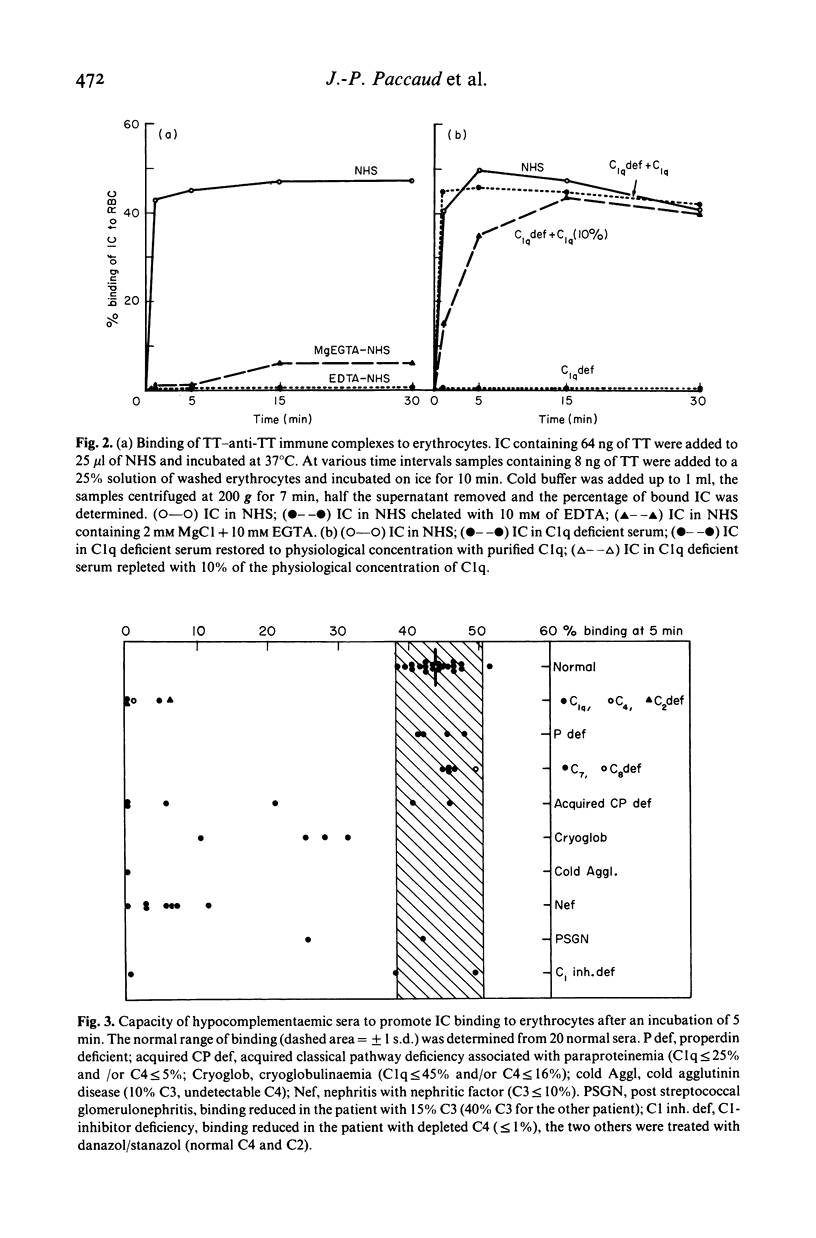
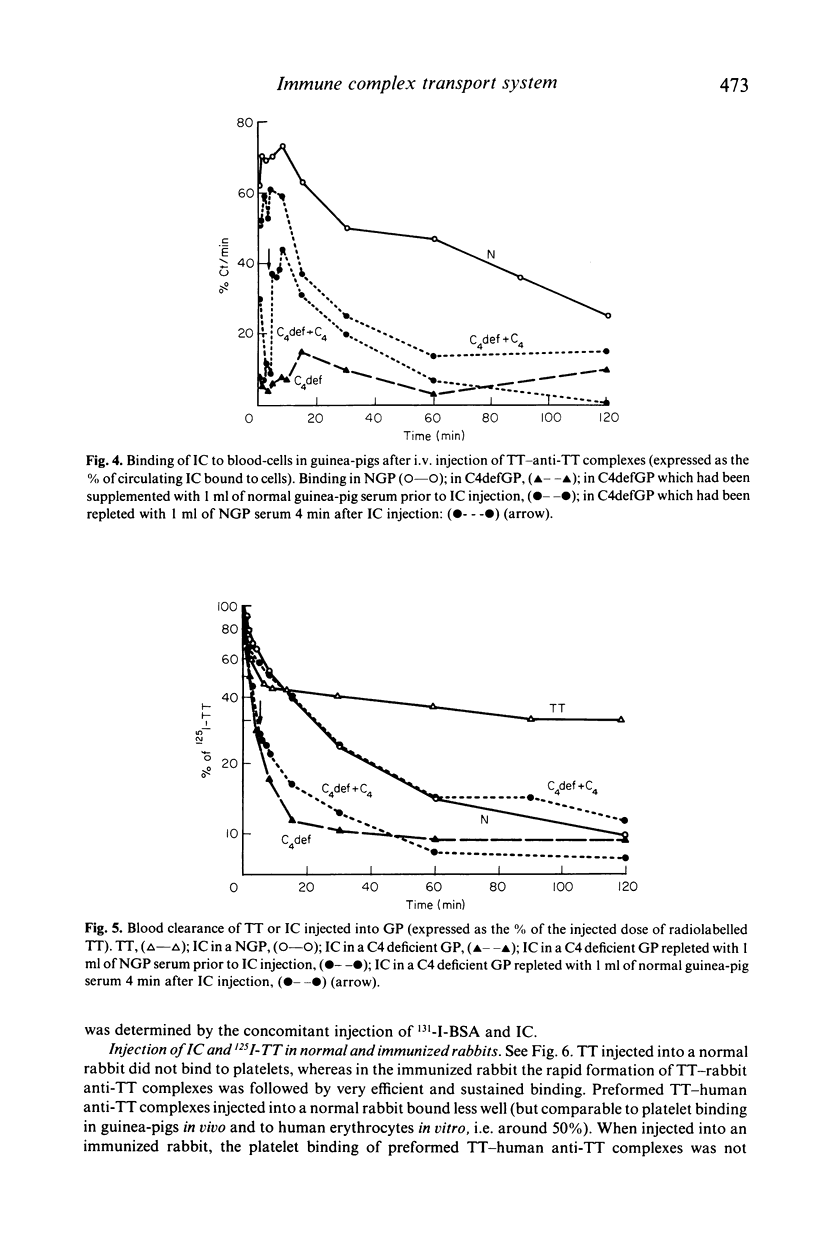
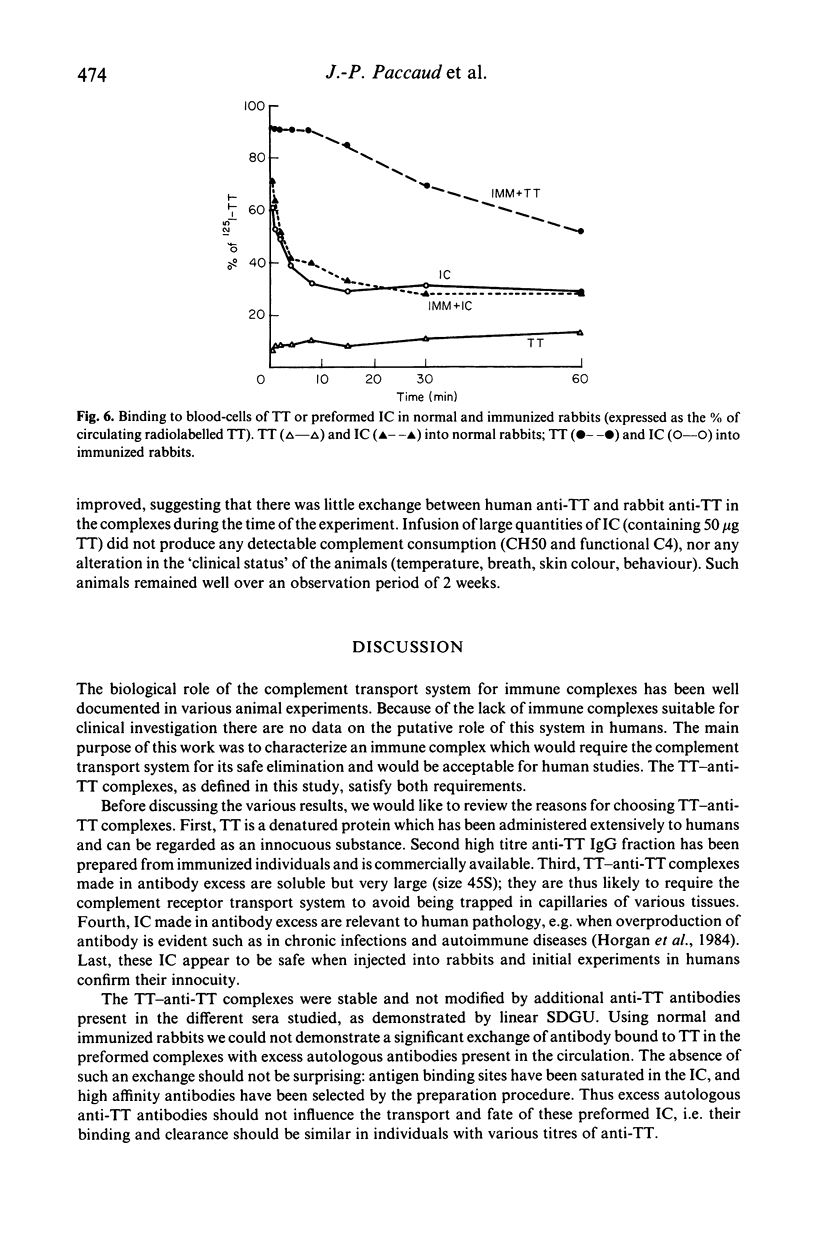
Complement and its receptor on erythrocytes appears to play a physiological role in the elimination of large immune complexes (IC) in monkeys, and a similar system is likely to work in humans. Here we define a safe IC model which is suitable for clinical investigations. Soluble tetanus toxoid (TT)-human anti-TT (IgG) antibody complexes were prepared in large antibody excess. The size of the complexes was approximately 45 S. When incubated in normal human serum, 50% of the IC increased further in size, but remained soluble, and bound rapidly to human erythrocytes in vitro. This binding was shown to require intact classical pathway function. When injected into normal guinea-pigs a comparable proportion of IC bound immediately to blood cells (mainly to platelets). No platelet binding of IC occurred in C4-deficient guinea-pigs, but this binding was restored when C4 was supplied. Initial immune complex elimination was faster in C4 deficient than in C4-supplemented and normal guinea pigs. Thus classical pathway function appeared to be necessary for the normal processing, transport and elimination of TT-anti-TT complexes.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ardlie N. G., Packham M. A., Mustard J. F. Adenosine diphosphate-induced platelet aggregation in suspensions of washed rabbit platelets. Br J Haematol. 1970 Jul;19(1):7–17. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1970.tb01596.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornacoff J. B., Hebert L. A., Smead W. L., VanAman M. E., Birmingham D. J., Waxman F. J. Primate erythrocyte-immune complex-clearing mechanism. J Clin Invest. 1983 Feb;71(2):236–247. doi: 10.1172/JCI110764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T. Identification of the membrane glycoprotein that is the C3b receptor of the human erythrocyte, polymorphonuclear leukocyte, B lymphocyte, and monocyte. J Exp Med. 1980 Jul 1;152(1):20–30. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.1.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer C. H., Wirtz G. H., Renfer L., Gresham H. D., Tack B. F. Large scale isolation of functionally active components of the human complement system. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3995–4006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horgan C., Burge J., Crawford L., Taylor R. P. The kinetics of [3H]-dsDNA/anti-DNA immune complex formation, binding by red blood cells, and release into serum: effect of DNA molecular weight and conditions of antibody excess. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):2079–2084. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johns P., Stanworth D. R. A simple numerical method for the construction of isokinetic sucrose density gradients, and their application to the characterisation of immunoglobulin complexes. J Immunol Methods. 1976 Mar;10(2-3):231–252. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(76)90174-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medicus R. G., Esser A. F., Fernandez H. N., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Native and activated properdin: interconvertibility and identity of amino- and carboxy-terminal sequences. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):602–606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G. W., Steinberg A. D., Green I., Nussenzweig V. Complement-dependent alterations in the handling of immune complexes by NZB/W mice. J Immunol. 1975 Apr;114(4):1166–1170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyakawa Y., Yamada A., Kosaka K., Tsuda F., Kosugi E., Mayumi M. Defective immune-adherence (C3b) receptor on erythrocytes from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet. 1981 Sep 5;2(8245):493–497. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90882-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross G. D., Medof M. E. Membrane complement receptors specific for bound fragments of C3. Adv Immunol. 1985;37:217–267. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schifferli J. A., Steiger G., Paccaud J. P. Complement mediated inhibition of immune precipitation and solubilization generate different concentrations of complement anaphylatoxins (C4a, C3a, C5a). Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 May;64(2):407–414. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel I., Liu T. L., Gleicher N. The red-cell immune system. Lancet. 1981 Sep 12;2(8246):556–559. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90941-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. P., Horgan C., Buschbacher R., Brunner C. M., Hess C. E., O'Brien W. M., Wanebo H. J. Decreased complement mediated binding of antibody/3H-dsDNA immune complexes to the red blood cells of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, and hematologic malignancies. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Jun;26(6):736–744. doi: 10.1002/art.1780260606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. P., Kujala G., Wilson K., Wright E., Harbin A. In vivo and in vitro studies of the binding of antibody/dsDNA immune complexes to rabbit and guinea pig platelets. J Immunol. 1985 Apr;134(4):2550–2558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenner A. J., Lesavre P. H., Cooper N. R. Purification and radiolabeling of human C1q. J Immunol. 1981 Aug;127(2):648–653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman F. J., Hebert L. A., Cornacoff J. B., VanAman M. E., Smead W. L., Kraut E. H., Birmingham D. J., Taguiam J. M. Complement depletion accelerates the clearance of immune complexes from the circulation of primates. J Clin Invest. 1984 Oct;74(4):1329–1340. doi: 10.1172/JCI111543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., Yukiyama Y., Miyamoto T. Interaction between immune complexes and C3b receptors on erythrocytes. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1986 May;39(2):213–221. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(86)90085-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


