Abstract
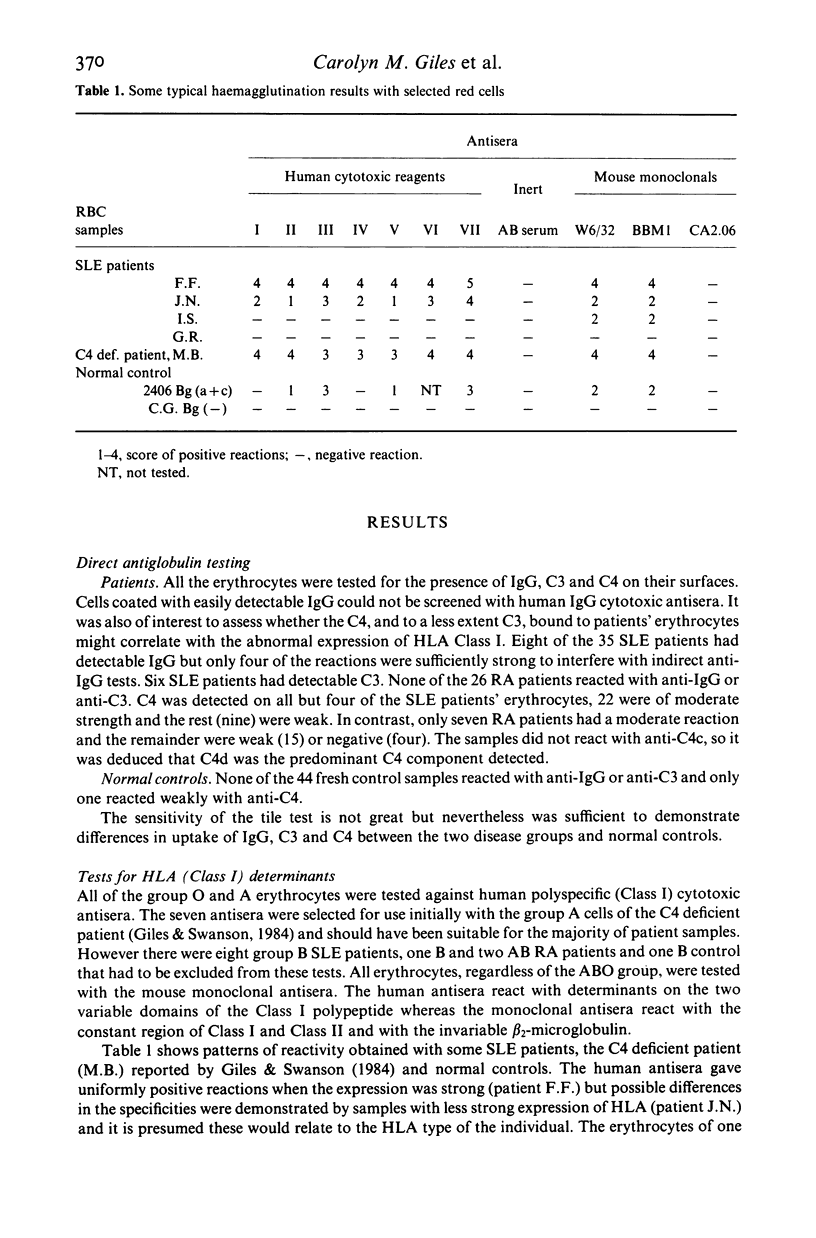
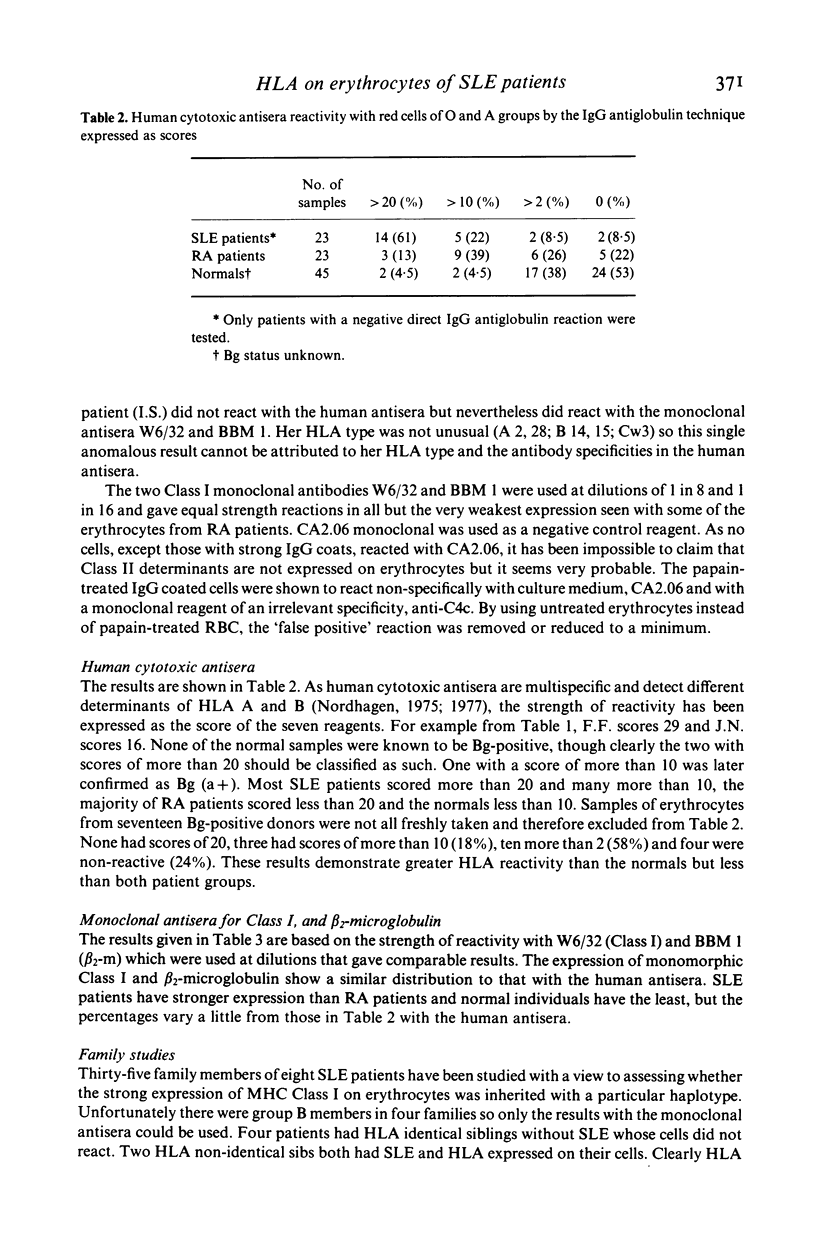
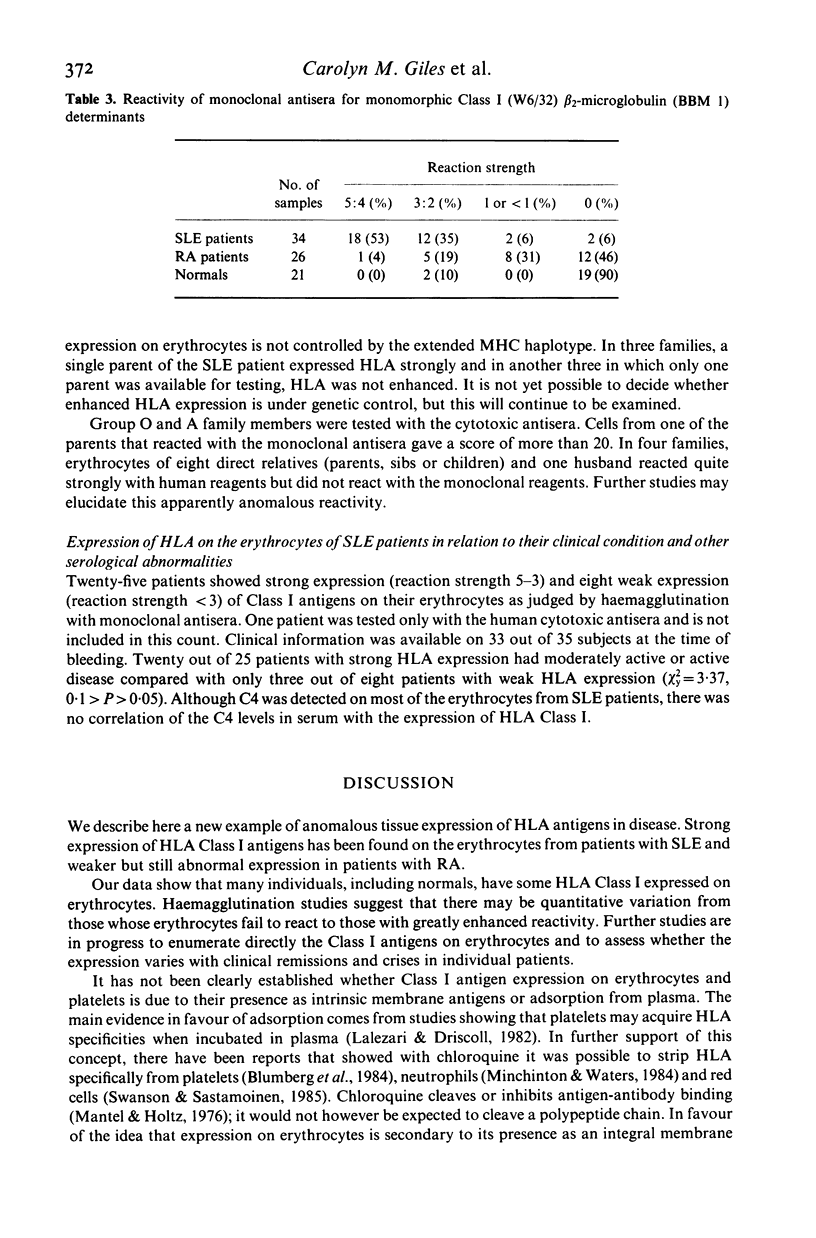
Strong expression of MHC Class I determinants had been observed on the erythrocytes of three genetically C4 deficient patients who all had SLE. In a study of 35 other SLE patients who were not C4 deficient, 30 showed a marked increase in the expression of MHC Class I on their erythrocytes. There was a correlation between the expression of erythrocyte Class I and disease activity. The polymorphic HLA determinants were detected by haemagglutination with human cytotoxic antisera from untransfused pregnant women. A shared monomorphic epitope of HLA-A, -B and -C, and beta 2-microglobulin were detected by haemagglutination with monoclonal antibodies. A monoclonal antibody for a monomorphic epitope on MHC Class II alpha and beta chains did not react. Erythrocytes from a group of RA patients and a group of normal controls had moderate and low expression respectively. We suggest that MHC Class I may be induced on erythrocytes maturing in a milieu containing mediators derived from activated cells of the immune system. Aberrant tissue expression of MHC antigens may be more widespread than has been previously recognized in diseases mediated by immune mechanisms.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. J., Berkowitz R. S. Gamma-interferon enhances expression of Class I MHC antigens in the weakly HLA+ human choriocarcinoma cell line BeWo, but does not induce MHC expression in the HLA- choriocarcinoma cell line Jar. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2498–2501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUCHANAN D. I., AFAGANIS A. The Bennett-Goodspeed-Sturgeon or "Donna" red cell antigen and antibody. Vox Sang. 1963 Mar-Apr;8:213–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1963.tb03295.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnstable C. J., Bodmer W. F., Brown G., Galfre G., Milstein C., Williams A. F., Ziegler A. Production of monoclonal antibodies to group A erythrocytes, HLA and other human cell surface antigens-new tools for genetic analysis. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90296-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg N., Masel D., Mayer T., Horan P., Heal J. Removal of HLA-A,B antigens from platelets. Blood. 1984 Feb;63(2):448–450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky F. M., Bodmer W. F., Parham P. Characterization of a monoclonal anti-beta 2-microglobulin antibody and its use in the genetic and biochemical analysis of major histocompatibility antigens. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Jul;9(7):536–545. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown G., Biberfeld P., Christensson B., Mason D. Y. The distribution of HLA on human lymphoid, bone marrow and peripheral blood cells. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Apr;9(4):272–275. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charron D. J., McDevitt H. O. Analysis of HLA-D region-associated molecules with monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6567–6571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford M. N., Schroeder M. L. Bga and Bgb correlations with HLA antigens by capillary tube technique. Transfusion. 1980 Sep-Oct;20(5):594–596. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1980.20581034518.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giles C. M., Swanson J. L. Anti-C4 in the serum of a transfused C4-deficient patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. Vox Sang. 1984;46(5):291–299. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1984.tb00089.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauptmann G., Goetz J., Uring-Lambert B., Grosshans E. Component deficiencies. 2. The fourth component. Prog Allergy. 1986;39:232–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalezari P., Driscoll A. M. Ability of thrombocytes to acquire HLA specificity from plasma. Blood. 1982 Jan;59(1):167–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantel W., Holtz G. Characterisation of autoantibodies to erythrocytes in autoimmune haemolytic anaemia by chloroquine. Vox Sang. 1976;30(6):453–463. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1976.tb02851.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minchinton R. M., Waters A. H. Chloroquine stripping of HLA antigens from neutrophils without removal of neutrophil specific antigens. Br J Haematol. 1984 Aug;57(4):703–706. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1984.tb02948.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton J. A., Pickles M. M., Darley J. H. Increase in strength of red cell Bga antigen following infectious mononucleosis. Vox Sang. 1977;32(1):26–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1977.tb00600.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton J. A., Pickles M. M., Sutton L. The correlation of the Bga blood group with the HL-47 leucocyte group: demonstration of antigenic sites on red cells and leucocytes. Vox Sang. 1969 Dec;17(6):536–547. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1969.tb00428.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordhagen R. Association between HL-A and red cell antigens. III. Studies of haemagglutinins in cytotoxic anti-HL-A7 and anti-HL-A5 related sera. Vox Sang. 1975;29(1):23–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1975.tb00474.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordhagen R. Association between HLA and red cell antigens. IV. Further studies of haemagglutinins in cytotoxic HLA antisera. Vox Sang. 1977;32(2):82–89. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1977.tb00610.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordhagen R. Association between HLA and red cell antigens. V. A further study of the nature and behaviour of the HLA antigens on red blood cells and their corresponding haemagglutinins. Vox Sang. 1978 Jul-Aug;35(1-2):49–57. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1978.tb02900.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordhagen R. HLA antigens on red blood cells. Two donors with extraordinarily strong reactivity. Vox Sang. 1979;37(4):209–215. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1979.tb02293.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivera R., Scornik J. C. HLA antigens on red cells. Implications for achieving low HLA antigen content in blood transfusions. Transfusion. 1986 Jul-Aug;26(4):375–381. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1986.26486262749.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoso S., Mueller-Eckhardt G., Santoso S., Kiefel V., Mueller-Eckhardt C. HLA antigens on platelet membranes. In vitro and in vivo studies. Vox Sang. 1986;51(4):327–333. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1986.tb01979.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spack E., Jr, Edidin M. The class I MHC antigens of erythrocytes: a serologic and biochemical study. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 15;136(8):2943–2952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. L., Sastamoinen R. Chloroquine stripping of HLA A,B antigens from red cells. Transfusion. 1985 Sep-Oct;25(5):439–440. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1985.25586020120.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urowitz M. B., Gladman D. D., Tozman E. C., Goldsmith C. H. The lupus activity criteria count (LACC). J Rheumatol. 1984 Dec;11(6):783–787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


