Abstract
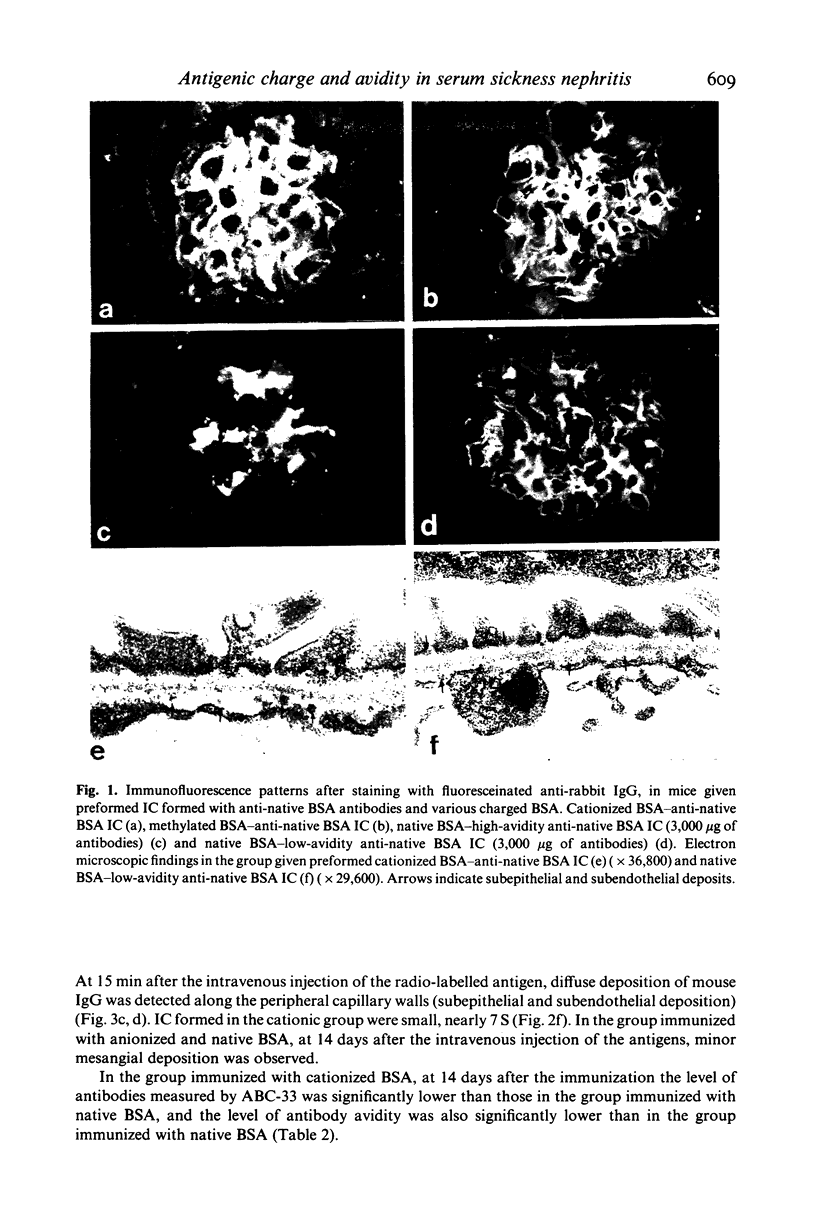
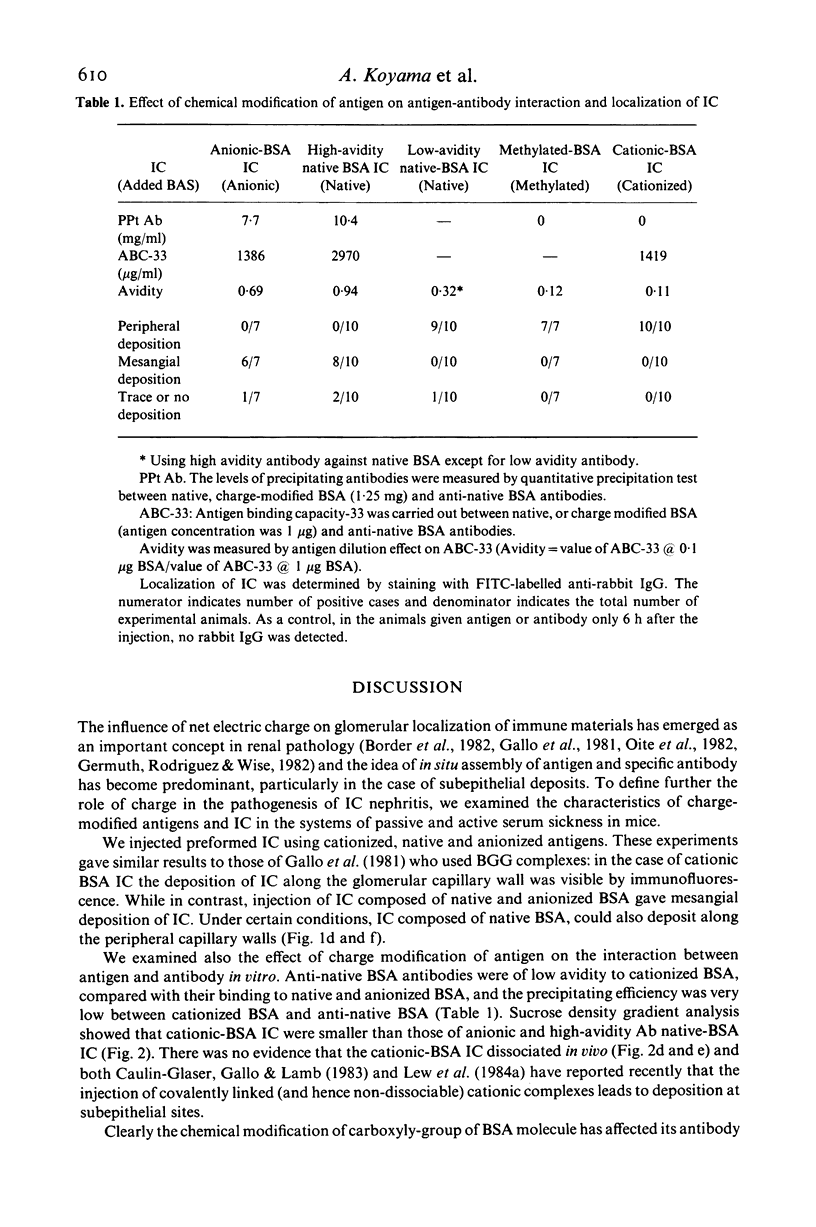
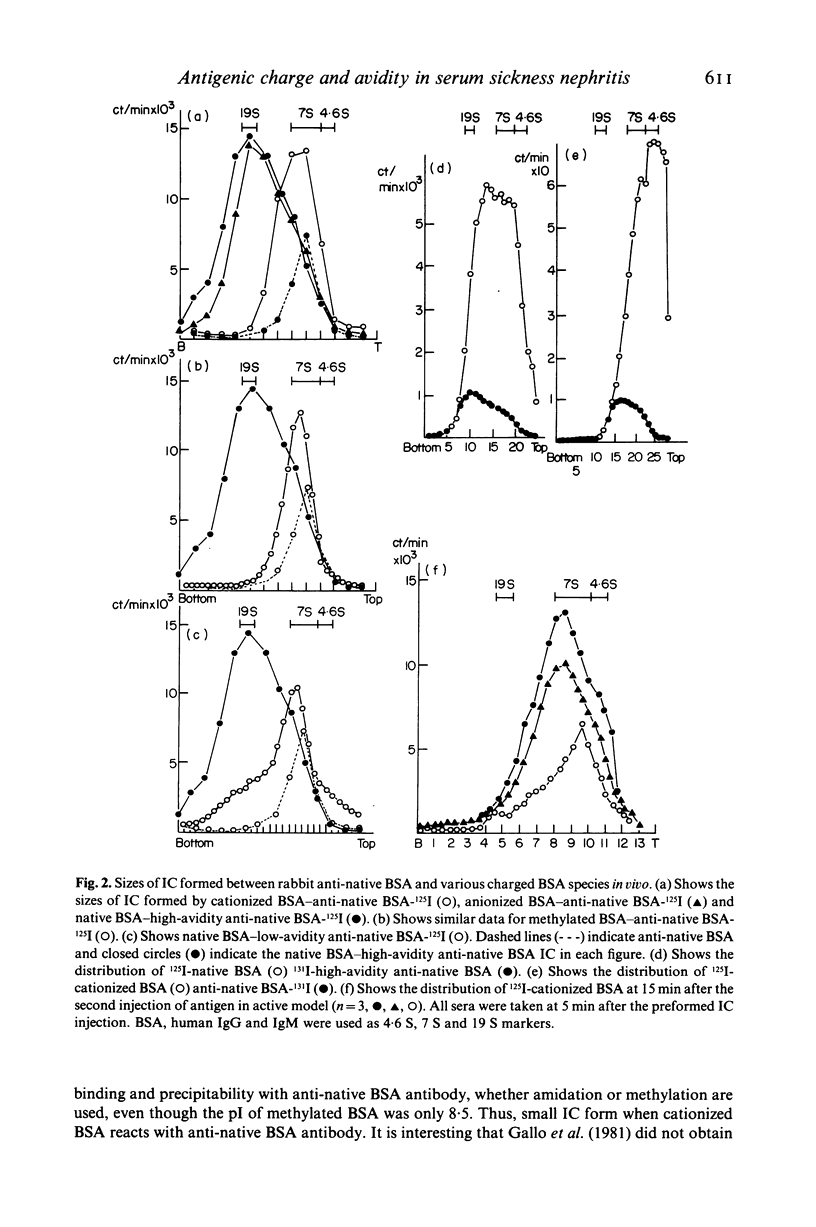
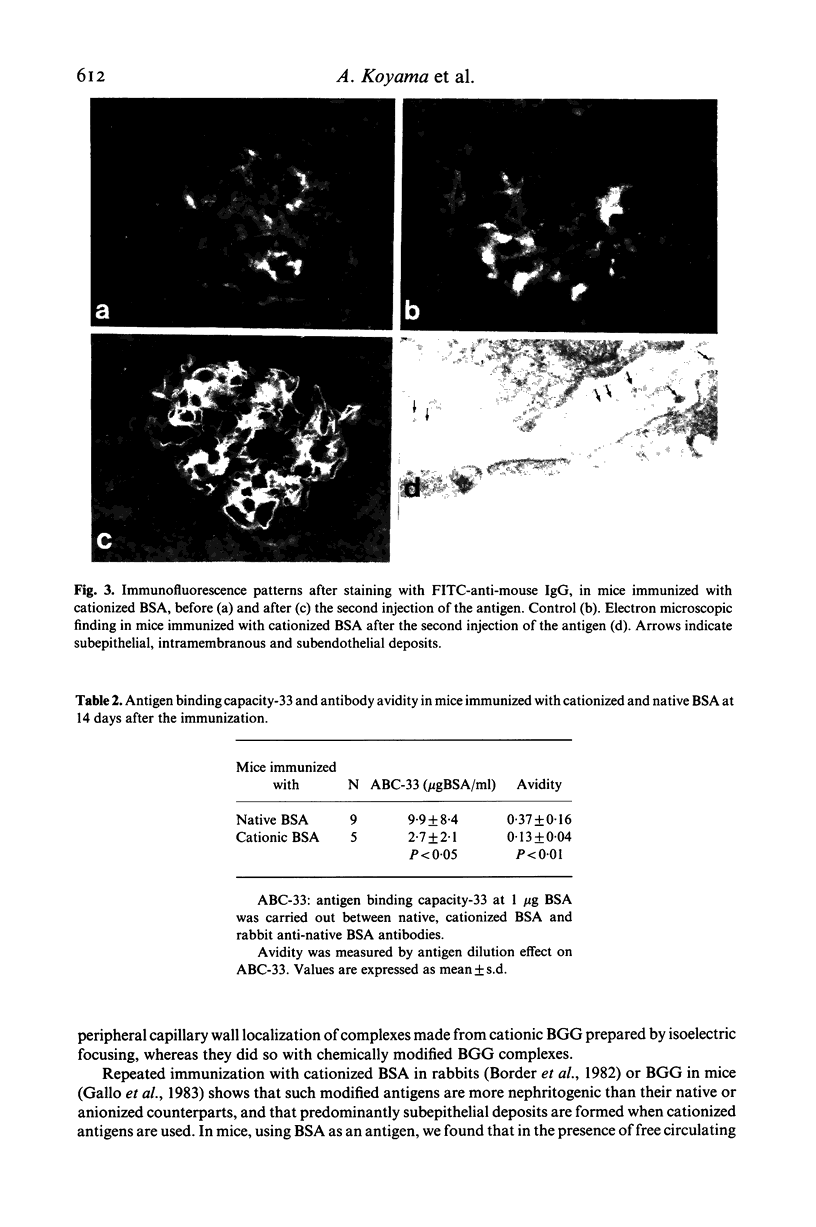
Passive injection of mice with preformed immune complexes (IC) made from cationized bovine serum albumin (BSA) and anti-native BSA antibody gave immune deposits along the glomerular capillary walls at predominantly subepithelial sites, while similar quantities of complexes made with native, anionized BSA did not deposit. Peripheral localization could be obtained also using low avidity antibody and a great excess of native BSA. Ultracentrifugation analysis showed that the size of IC in the animals given complexes containing cationized BSA was a little larger than 7 S, whereas those formed with the native or anionized BSA were around 19 S. The anti-native BSA antibody had a low avidity for cationized BSA in vitro, and thus all the IC which could deposit peripheral capillary walls were small and contained low avidity antibody. Chemical cationization of BSA alters the precipitability of the antibody and also the size and stability of the complexes formed. In an active model, injection of cationized BSA into mice preimmunized with cationized BSA caused localization of the BSA and its antibody in the peripheral capillary walls. Analysis of the circulating IC formed in this model also revealed low avidity of antibody and small-sized IC. From these results, it is clear that chemical cationization of antigen changes the characteristics of the antigen-antibody interaction, e.g. low precipitating efficiency and the formation of small-sized IC. Therefore, in addition to interaction of cationized IC with the polyanion layer of the glomerular basement membrane (GBM), the properties of antigen-antibody interaction play an important role in the deposition of IC along the peripheral capillary walls in a model of membranous glomerulonephritis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Border W. A., Ward H. J., Kamil E. S., Cohen A. H. Induction of membranous nephropathy in rabbits by administration of an exogenous cationic antigen. J Clin Invest. 1982 Feb;69(2):451–461. doi: 10.1172/JCI110469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caulin-Glaser T., Gallo G. R., Lamm M. E. Nondissociating cationic immune complexes can deposit in glomerular basement membrane. J Exp Med. 1983 Nov 1;158(5):1561–1572. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.5.1561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couser W. G., Salant D. J. In situ immune complex formation and glomerular injury. Kidney Int. 1980 Jan;17(1):1–13. doi: 10.1038/ki.1980.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couser W. G., Steinmuller D. R., Stilmant M. M., Salant D. J., Lowenstein L. M. Experimental glomerulonephritis in the isolated perfused rat kidney. J Clin Invest. 1978 Dec;62(6):1275–1287. doi: 10.1172/JCI109248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON F. J., FELDMAN J. D., VAZQUEZ J. J. Experimental glomerulonephritis. The pathogenesis of a laboratory model resembling the spectrum of human glomerulonephritis. J Exp Med. 1961 May 1;113:899–920. doi: 10.1084/jem.113.5.899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleuren G. J., vd Lee R., Greben H. A., Van Damme B. J., Hoedemaeker P. J. Experimental glomerulonephritis in the rat induced by antibodies directed against tubular antigens. IV. Investigations into the pathogenesis of the model. Lab Invest. 1978 Apr;38(4):496–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo G. R., Caulin-Glaser T., Emancipator S. N., Lamm M. E. Nephritogenicity and differential distribution of glomerular immune complexes related to immunogen charge. Lab Invest. 1983 Mar;48(3):353–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo G. R., Caulin-Glaser T., Lamm M. E. Charge of circulating immune complexes as a factor in glomerular basement membrane localization in mice. J Clin Invest. 1981 May;67(5):1305–1313. doi: 10.1172/JCI110159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germuth F. G., Jr, Rodriguez E., Lorelle C. A., Trump E. I., Milano L. L., Wise O. Passive immune complex glomerulonephritis in mice: models for various lesions found in human disease. II. Low avidity complexes and diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis with subepithelial deposits. Lab Invest. 1979 Oct;41(4):366–371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germuth F. G., Jr, Senterfit L. B., Dreesman G. R. Immune complex disease. V. The nature of the circulating complexes associated with glomerular alterations in the chronic BSA-rabbit system. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1972 Jun;130(6):344–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germuth F. G., Rodriguez E., Wise O. L. Passive immune complex glomerulonephritis in mice. III. Clearance kinetics and properties of circulating complexes. Lab Invest. 1982 May;46(5):515–519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoare D. G., Koshland D. E., Jr A method for the quantitative modification and estimation of carboxylic acid groups in proteins. J Biol Chem. 1967 May 25;242(10):2447–2453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew A. M., Staines N. A., Steward M. W. Glomerulonephritis induced by pre-formed immune complexes containing monoclonal antibodies of defined affinity and isotype. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Aug;57(2):413–422. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew A. M., Tovey D. G., Steward M. W. Localization of covalent immune complexes on the epithelial side of the glomerular basement membrane in mice. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1984;75(3):242–249. doi: 10.1159/000233623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oite T., Batsford S. R., Mihatsch M. J., Takamiya H., Vogt A. Quantitative studies of in situ immune complex glomerulonephritis in the rat induced by planted, cationized antigen. J Exp Med. 1982 Feb 1;155(2):460–474. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.2.460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SRI RAM J., MAURER P. H. Modified bovine serum albumin. VII. Studies on the role of free carboxyl groups of the protein in the interaction with its antibodies. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 Jul;83(1):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90027-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Damme B. J., Fleuren G. J., Bakker W. W., Vernier R. L., Hoedemaeker P. J. Experimental glomerulonephritis in the rat induced by antibodies directed against tubular antigens. V. Fixed glomerular antigens in the pathogenesis of heterologous immune complex glomerulonephritis. Lab Invest. 1978 Apr;38(4):502–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]