Abstract
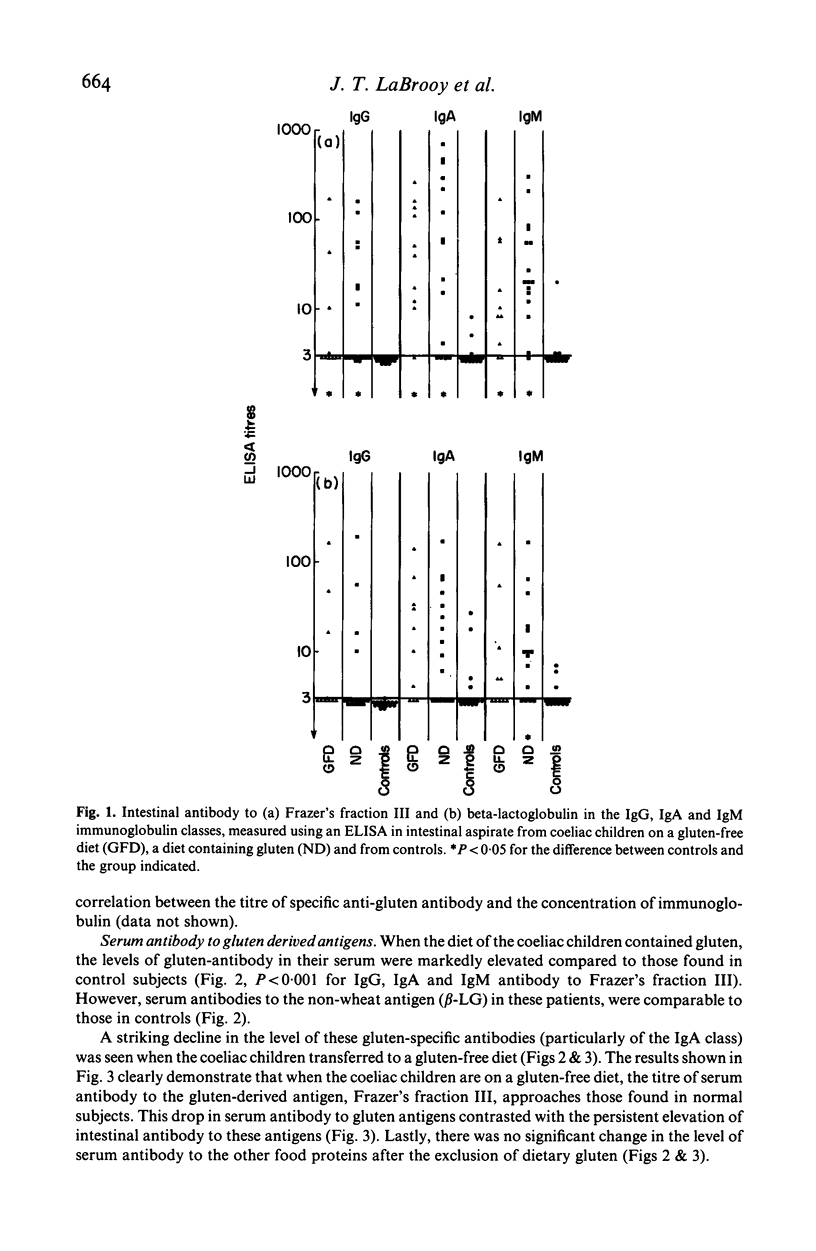
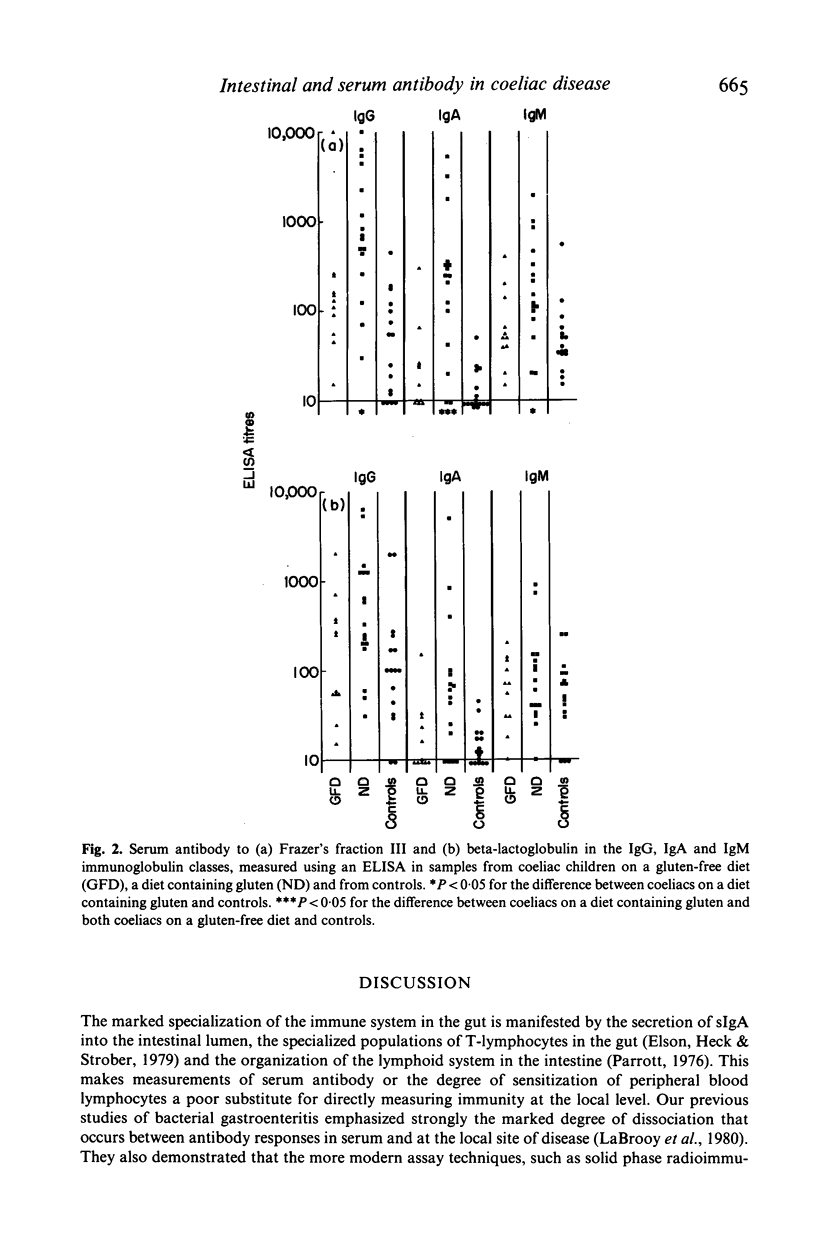
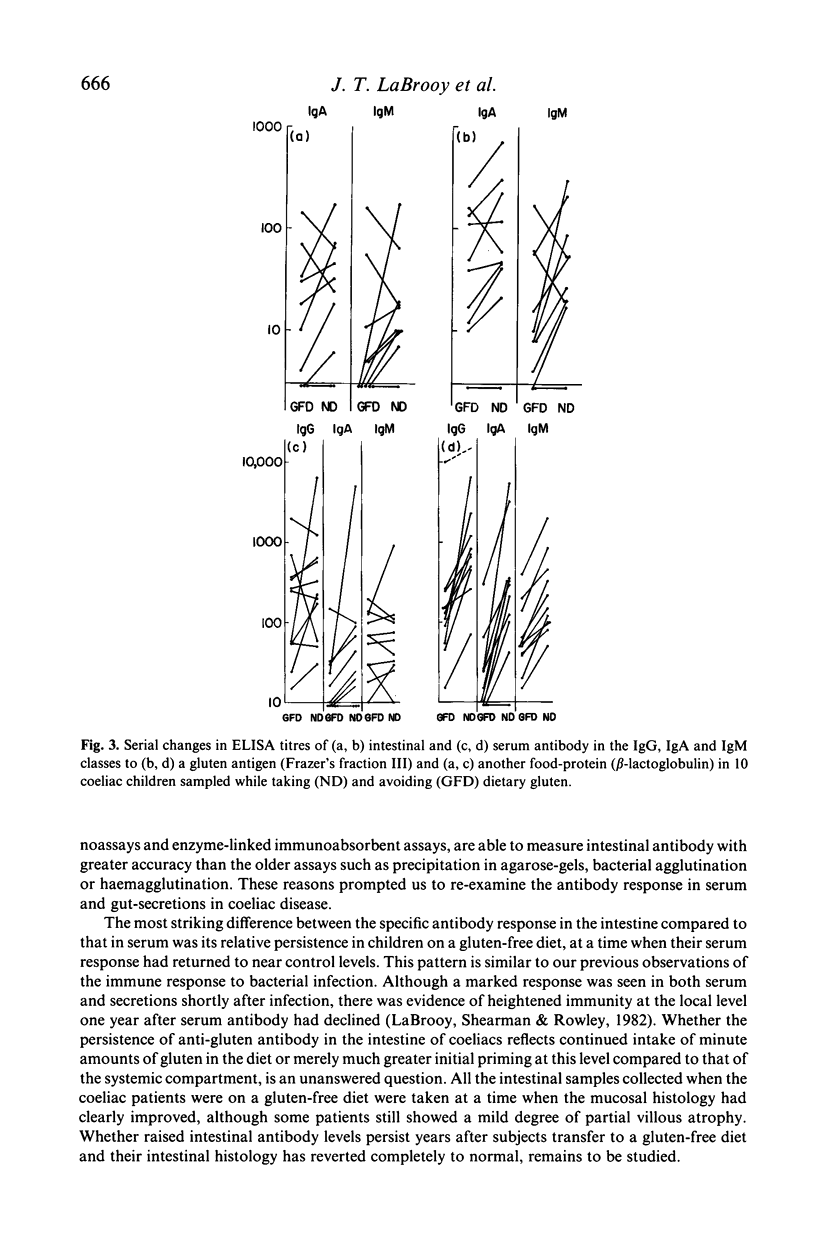
Intestinal and serum antibody to antigens derived from gluten and other food proteins in 16 children with coeliac disease and 15 control subjects was measured using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). High concentrations of antibody to gluten antigens were found in children with coeliac disease who were on a diet which contained gluten. This antibody was predominantly in the IgA and IgM classes in intestinal fluid, and in the IgG and IgA classes in serum. When coeliac children transferred to a gluten-free diet for 6 months or more, anti-gluten antibody fell much more rapidly in serum than in intestinal fluid. Although no single measure of antibody, in any immunoglobulin class, to a gluten-derived antigen proved sufficiently discriminating to be suggested as a diagnostic test for coeliac disease, serum antibody, particularly in the IgA class, may be of value in following the progress of patients and in assessing their adherence to a gluten-free diet.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bjarnason I., Peters T. J., Veall N. A persistent defect in intestinal permeability in coeliac disease demonstrated by a 51Cr-labelled EDTA absorption test. Lancet. 1983 Feb 12;1(8320):323–325. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91628-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bürgin-Wolff A., Bertele R. M., Berger R., Gaze H., Harms H. K., Just M., Khanna S., Schürmann K., Signer E., Tomovic D. A reliable screening test for childhood celiac disease: fluorescent immunosorbent test for gliadin antibodies. A prospective multicenter study. J Pediatr. 1983 May;102(5):655–660. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(83)80229-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornell H. J., Townley R. R. Investigation of possible intestinal peptidase deficiency in coeliac disease. Clin Chim Acta. 1973 Jan 10;43(1):113–125. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(73)90126-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson M., Waserman R. The iritable colon of childhood (chronic nonspecific diarrhea syndrome). J Pediatr. 1966 Dec;69(6):1027–1038. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(66)80292-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson C. O., Heck J. A., Strober W. T-cell regulation of murine IgA synthesis. J Exp Med. 1979 Mar 1;149(3):632–643. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.3.632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRAZER A. C., FLETCHER R. F., ROSS C. A., SHAW B., SAMMONS H. G., SCHNEIDER R. Gluten-induced enteropathy: the effect of partially digested gluten. Lancet. 1959 Sep 5;2(7097):252–255. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(59)92051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falchuk Z. M., Strober W. Gluten-sensitive enteropathy: synthesis of antigliadin antibody in vitro. Gut. 1974 Dec;15(12):947–952. doi: 10.1136/gut.15.12.947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson A., Carswell F. Precipitins to dietary proteins in serum and upper intestinal secretions of coeliac children. Br Med J. 1972 Jan 8;1(5792):75–77. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5792.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firer M. A., Hosking C. S., Hill D. J. Effect of antigen load on development of milk antibodies in infants allergic to milk. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Sep 12;283(6293):693–696. doi: 10.1136/bmj.283.6293.693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford R. P. A simple method of duodenal juice collection in association with small bowel biopsy in children. Aust Paediatr J. 1981 Mar;17(1):54–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1754.1981.tb00015.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohmann A., LaBrooy J., Davidson G. P., Shearman D. J. Measurement of specific antibodies in human intestinal aspirate: effect of the protease inhibitor phenylmethylsulphonyl fluoride. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Nov 11;64(1-2):199–204. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90398-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz J., Kantor F. S., Herskovic T. Intestinal antibodies to wheat fractions in celiac disease. Ann Intern Med. 1968 Dec;69(6):1149–1153. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-69-6-1149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King L. S. Making an outline. JAMA. 1968 Mar 4;203(10):877–878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Brooy J. T., Davidson G. P., Sherman D. J., Rowley D. The antibody response to bacterial gastroenteritis in serum and secretions. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Aug;41(2):290–296. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Brooy J. T., Shearman D. J., Rowley D. Antibodies in serum and secretions 1 year after salmonella gastroenteritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Jun;48(3):551–554. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb P. M., Strober W., Falchuk Z. M., Laster L. Incorporation of L-leucine-14C into immunoglobulins by jejunal biopsies of patients with celiac sprue and other gastrointestinal diseases. J Clin Invest. 1971 Mar;50(3):559–569. doi: 10.1172/JCI106525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeish A. S., Harms H. K., Rey J., Shmerling D. H., Visakorpi J. K., Walker-Smith J. A. The diagnosis of coeliac disease. A commentary on the current practices of members of the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition (ESPGAN). Arch Dis Child. 1979 Oct;54(10):783–786. doi: 10.1136/adc.54.10.783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrelly C., Feighery C., Greally J. F., Weir D. G. Cellular response to alpha-gliadin in untreated coeliac disease. Gut. 1982 Jan;23(1):83–87. doi: 10.1136/gut.23.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrelly C., Kelly J., Hekkens W., Bradley B., Thompson A., Feighery C., Weir D. G. Alpha gliadin antibody levels: a serological test for coeliac disease. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Jun 25;286(6383):2007–2010. doi: 10.1136/bmj.286.6383.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrott D. M. The gut as a lymphoid organ. Clin Gastroenterol. 1976 May;5(2):211–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savilahti E., Viander M., Perkkiö M., Vainio E., Kalimo K., Reunala T. IgA antigliadin antibodies: a marker of mucosal damage in childhood coeliac disease. Lancet. 1983 Feb 12;1(8320):320–322. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91627-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unsworth D. J., Kieffer M., Holborow E. J., Coombs R. R., Walker-Smith J. A. IgA anti-gliadin antibodies in coeliac disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Nov;46(2):286–293. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J. B., Austin R. K., Schanfield M. S., Kagnoff M. F. Gluten-sensitive enteropathy. Immunoglobulin G heavy-chain (Gm) allotypes and the immune response to wheat gliadin. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):96–101. doi: 10.1172/JCI110988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


