Abstract
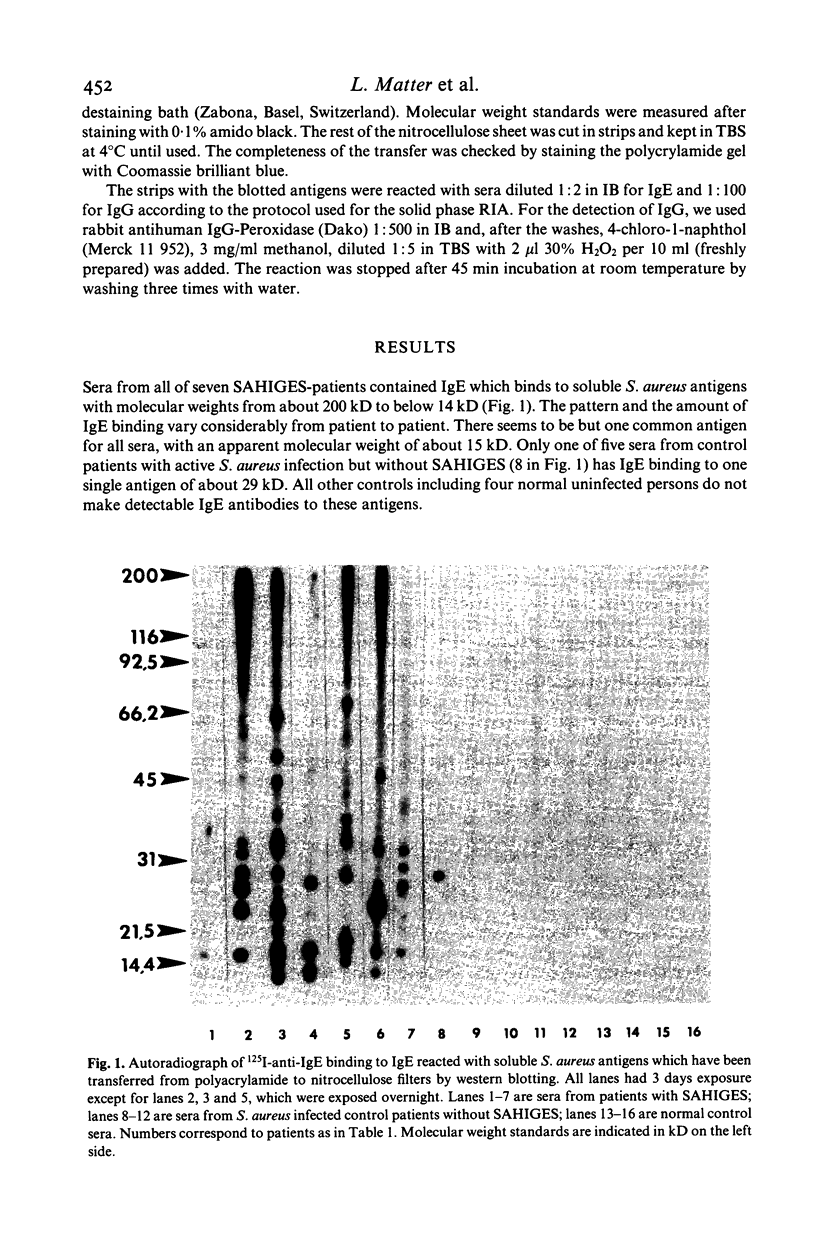
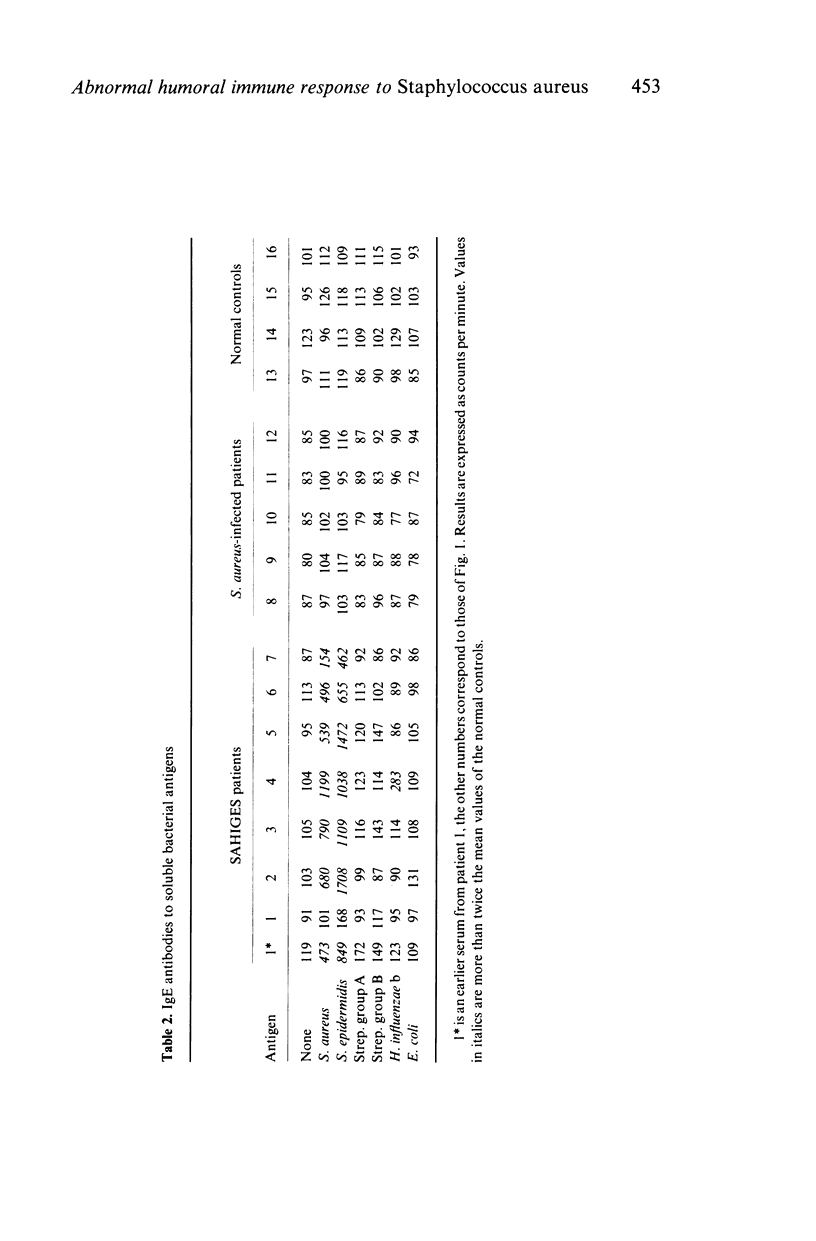
Patients with the S. aureus hyper IgE syndrome (SAHIGES) have an abnormal IgE response to cell wall and surface antigens of S. aureus. In this paper we describe the detection of IgE antibodies to soluble antigens of staphylococci (S. aureus and S. epidermidis) and qualitative abnormalities of the IgG response to soluble S. aureus antigens in patients with SAHIGES. These findings may be of pathogenetic importance and help to delineate SAHIGES from other diseases.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berger M., Kirkpatrick C. H., Goldsmith P. K., Gallin J. I. IgE antibodies to Staphylococcus aureus and Candida albicans in patients with the syndrome of hyperimmunoglobulin E and recurrent infections. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2437–2443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donabedian H., Gallin J. I. Mononuclear cells from patients with the hyperimmunoglobulin E-recurrent infection syndrome produce an inhibitor of leukocyte chemotaxis. J Clin Invest. 1982 May;69(5):1155–1163. doi: 10.1172/JCI110551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donabedian H., Gallin J. I. Two inhibitors of neutrophil chemotaxis are produced by hyperimmunoglobulin E recurrent infection syndrome mononuclear cells exposed to heat-killed staphylococci. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):1030–1037. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.1030-1037.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreskin S. C., Goldsmith P. K., Gallin J. I. Immunoglobulins in the hyperimmunoglobulin E and recurrent infection (Job's) syndrome. Deficiency of anti-Staphylococcus aureus immunoglobulin A. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jan;75(1):26–34. doi: 10.1172/JCI111683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geha R. S., Reinherz E., Leung D., McKee K. T., Jr, Schlossman S., Rosen F. S. Deficiency of suppressor T cells in the hyperimmunoglobulin E syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1981 Sep;68(3):783–791. doi: 10.1172/JCI110315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser C., Wuethrich B., Matter L., Wilhelm J. A., Schopfer K. Immune response to Staphylococcus aureus in atopic dermatitis. Dermatologica. 1985;170(3):114–120. doi: 10.1159/000249514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mawhinney H., Killen M., Fleming W. A., Roy A. D. The hyperimmunoglobulin E syndrome--a neutrophil chemotactic defect reversible by histamine H2 receptor blockade? Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1980 Dec;17(4):483–491. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(80)90144-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schopfer K., Baerlocher K., Price P., Krech U., Quie P. G., Douglas S. D. Staphylococcal IgE antibodies, hyperimmunoglobulinemia E and Staphylococcus aureus infections. N Engl J Med. 1979 Apr 12;300(15):835–838. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197904123001506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schopfer K., Douglas S. D., Wilkinson B. J. Immunoglobulin E antibodies against Staphylococcus aureus cell walls in the sera of patients with hyperimmunoglobulinemia E and recurrent staphylococcal infection. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):563–568. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.563-568.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schopfer K., Feldges A., Baerlocher K., Parisot R. F., Wilhelm J. A., Matter L. Systemic lupus erythematosus in Staphylococcus aureus hyperimmunoglobulinaemia E syndrome. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Aug 20;287(6391):524–526. doi: 10.1136/bmj.287.6391.524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]