Abstract
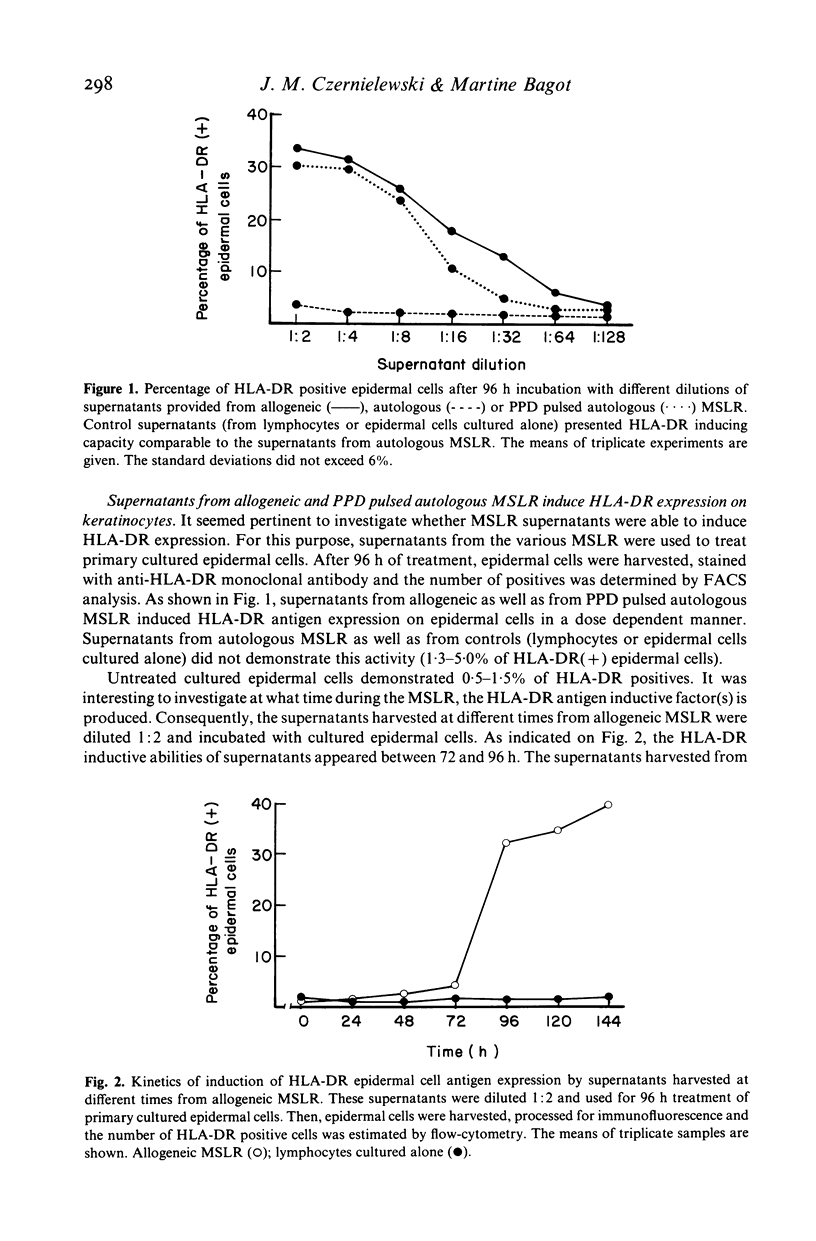
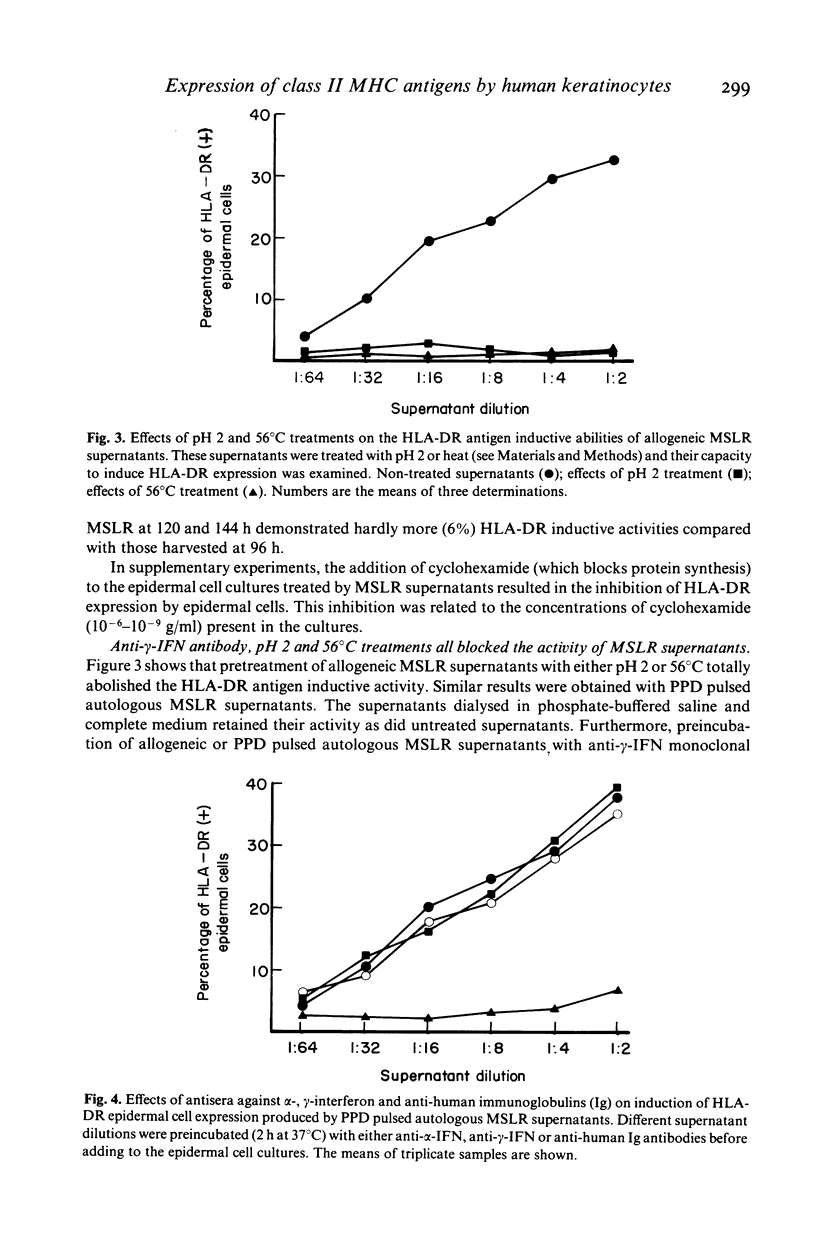
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were co-cultured with either allogeneic, autologous or purified protein derivative of tuberculin (PPD) pulsed autologous epidermal cells. In these mixed skin cell-lymphocyte culture reactions (MSLR), lymphocytes are stimulated to proliferate by epidermal cells. The supernatants of MSLR were examined for their capacity to induce class II MHC antigen expression on separately cultured epidermal cells. It is shown that supernatants from allogeneic and PPD pulsed autologous MSLR contained the factor(s) which stimulated HLA-DR antigen synthesis and expression by 30-40% of cultured epidermal cells. Kinetic analysis revealed a production rate maximum between 72 and 96 h of lympho-epidermal co-cultures. The factor mediating the induction of HLA-DR antigen expression on epidermal cells is thought to be gamma-interferon, because it was sensitive to pH 2 as well as heat incubation. Furthermore, anti-gamma-interferon monoclonal antibody abolished its activity. It is proposed, that HLA-DR antigen expression by keratinocytes observed in vivo in different dermatological inflammatory disorders originates from lympho-epidermal interactions and local gamma-interferon production as documented here in experiments in vitro.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagot M., Heslan M., Roujeau J. C., Lebon P., Lévy J. P. Human epidermal cells are more potent than peripheral blood mononuclear cells for the detection of weak allogeneic or virus-specific primary responses in vitro. Cell Immunol. 1985 Aug;94(1):215–224. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90098-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barclay A. N., Mason D. W. Induction of Ia antigen in rat epidermal cells and gut epithelium by immunological stimuli. J Exp Med. 1982 Dec 1;156(6):1665–1676. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.6.1665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basham T. Y., Merigan T. C. Recombinant interferon-gamma increases HLA-DR synthesis and expression. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1492–1494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basham T. Y., Nickoloff B. J., Merigan T. C., Morhenn V. B. Recombinant gamma interferon induces HLA-DR expression on cultured human keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 1984 Aug;83(2):88–90. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12262597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braathen L. R., Thorsby E. Studies on human epidermal langerhans cells. IV. HLA-D restriction of langerhans cell-dependent antigen activation of T lymphocytes. Scand J Immunol. 1982 Jan;15(1):55–61. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1982.tb00621.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang T. W., Testa D., Kung P. C., Perry L., Dreskin H. J., Goldstein G. Cellular origin and interactions involved in gamma-interferon production induced by OKt3 monoclonal antibody. J Immunol. 1982 Feb;128(2):585–589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czernielewski J. M. Mixed skin cell-lymphocyte culture reaction (MSLR) as a model for the study of lympho-epidermal interactions. Br J Dermatol. 1985 Jul;113 (Suppl 28):17–23. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1985.tb15622.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czernielewski J., Faure M., Schmitt D., Thivolet J. In vitro mixed skin cell lymphocyte culture reaction (MSLR) in man: analysis of the epidermal cell and T cell subpopulations. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Nov;50(2):426–433. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert I. A. Expression of HLA-DR (Ia like) antigen on epidermal keratinocytes in human dermatoses. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Jul;57(1):93–100. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert I. A., Suitters A. J., Chisholm P. M. Expression of Ia antigen on epidermal keratinocytes in graft-versus-host disease. Nature. 1981 Sep 10;293(5828):149–150. doi: 10.1038/293149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S. C., Eaton M. J., Karasek M. A. Growth characteristics of human epidermal keratinocytes from newborn foreskin in primary and serial cultures. In Vitro. 1979 Oct;15(10):813–822. doi: 10.1007/BF02618308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Main R. K., Cochrum K. C., Jones M. J., Kountz S. L. Immunological potential of the in vitro mixed skin cell-leukocyte reaction. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jan 20;229(3):89–91. doi: 10.1038/newbio229089a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natali P. G., De Martino C., Quaranta V., Nicotra M. R., Frezza F., Pellegrino M. A., Ferrone S. Expression of Ia-like antigens in normal human nonlymphoid tissues. Transplantation. 1981 Jan;31(1):75–78. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198101000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S., Collins T., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Cotran R. S., Gitlin J. D., Fiers W., Clayberger C., Krensky A. M., Burakoff S. J., Reiss C. S. Lymphocytes recognize human vascular endothelial and dermal fibroblast Ia antigens induced by recombinant immune interferon. Nature. 1983 Oct 20;305(5936):726–729. doi: 10.1038/305726a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts L. K., Spangrude G. J., Daynes R. A., Krueger G. G. Correlation between keratinocyte expression of Ia and the intensity and duration of contact hypersensitivity responses in mice. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):2929–2936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowden G., Lewis M. G., Sullivan A. K. Ia antigen expression on human epidermal Langerhans cells. Nature. 1977 Jul 21;268(5617):247–248. doi: 10.1038/268247a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauder D. N., Monick M. M., Hunninghake G. W. Epidermal cell-derived thymocyte activating factor (ETAF) is a potent T-cell chemoattractant. J Invest Dermatol. 1985 Nov;85(5):431–433. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12277126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauder D. N., Mounessa N. L., Katz S. I., Dinarello C. A., Gallin J. I. Chemotactic cytokines: the role of leukocytic pyrogen and epidermal cell thymocyte-activating factor in neutrophil chemotaxis. J Immunol. 1984 Feb;132(2):828–832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheynius A., Tjernlund U. Human keratinocytes express HLA-DR antigens in the tuberculin reaction. Scand J Immunol. 1984 Feb;19(2):141–147. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1984.tb00910.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sontheimer R. D. The mixed epidermal cell-lymphocyte reaction. I. Human epidermal cells elicit a greater allogeneic lymphocyte response than do autologous peripheral blood lymphoid cells. J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2612–2614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stingl G., Katz S. I., Clement L., Green I., Shevach E. M. Immunologic functions of Ia-bearing epidermal Langerhans cells. J Immunol. 1978 Nov;121(5):2005–2013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stingl G., Katz S. I., Shevach E. M., Wolff-Schreiner E., Green I. Detection of Ia antigens on Langerhans cells in guinea pig skin. J Immunol. 1978 Feb;120(2):570–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S., Sakai A. Stimulation of allogeneic lymphocytes by skin epidermal cells in the rat. Transplantation. 1979 Mar;27(3):194–199. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197903000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjernlund U. M. Epidermal expression of HLA-DR antigens in mycosis fungoides. Arch Dermatol Res. 1978 Feb 15;261(1):81–86. doi: 10.1007/BF00455380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjernlund U. M. Ia-like antigens in lichen planus. Acta Derm Venereol. 1980;60(4):309–314. doi: 10.2340/0001555560309314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volc-Platzer B., Leibl H., Luger T., Zahn G., Stingl G. Human epidermal cells synthesize HLA-DR alloantigens in vitro upon stimulation with gamma-interferon. J Invest Dermatol. 1985 Jul;85(1):16–19. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12274511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volc-Platzer B., Majdic O., Knapp W., Wolff K., Hinterberger W., Lechner K., Stingl G. Evidence of HLA-DR antigen biosynthesis by human keratinocytes in disease. J Exp Med. 1984 Jun 1;159(6):1784–1789. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.6.1784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


