Abstract
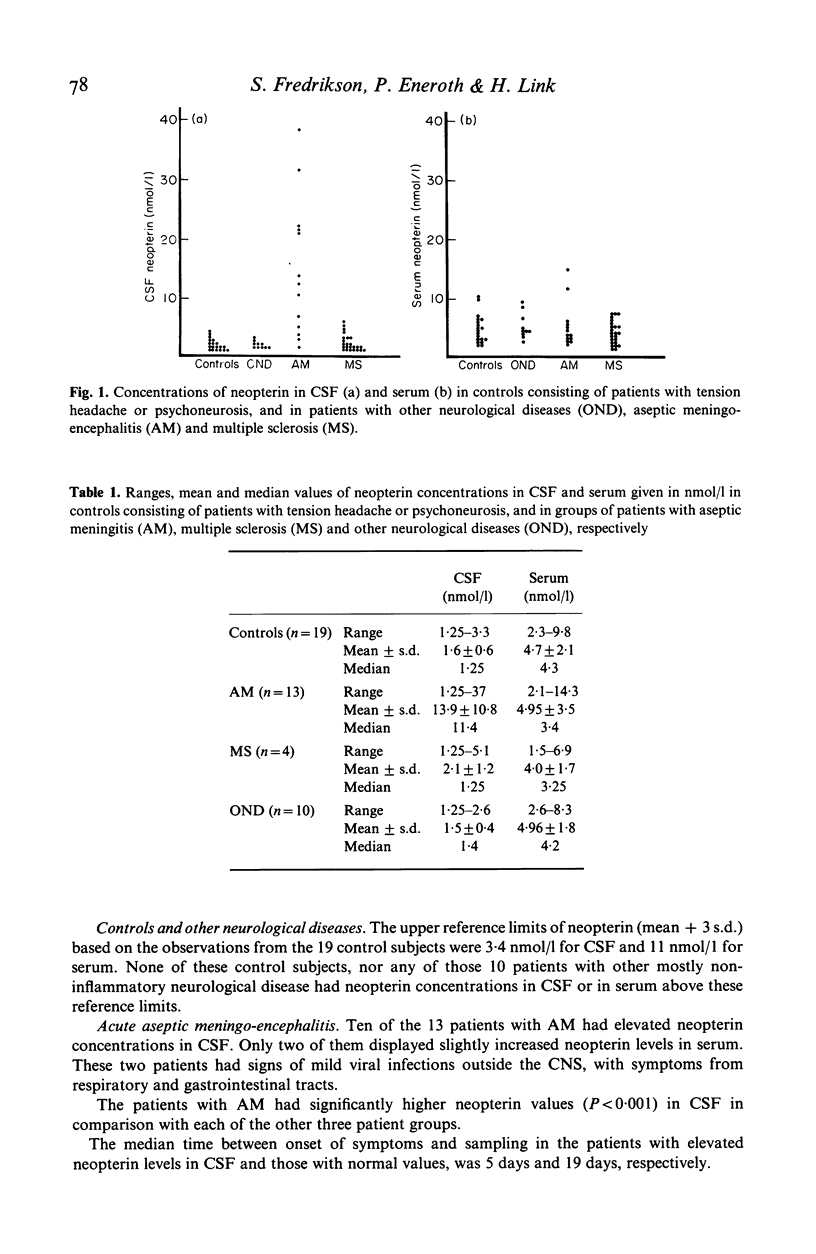
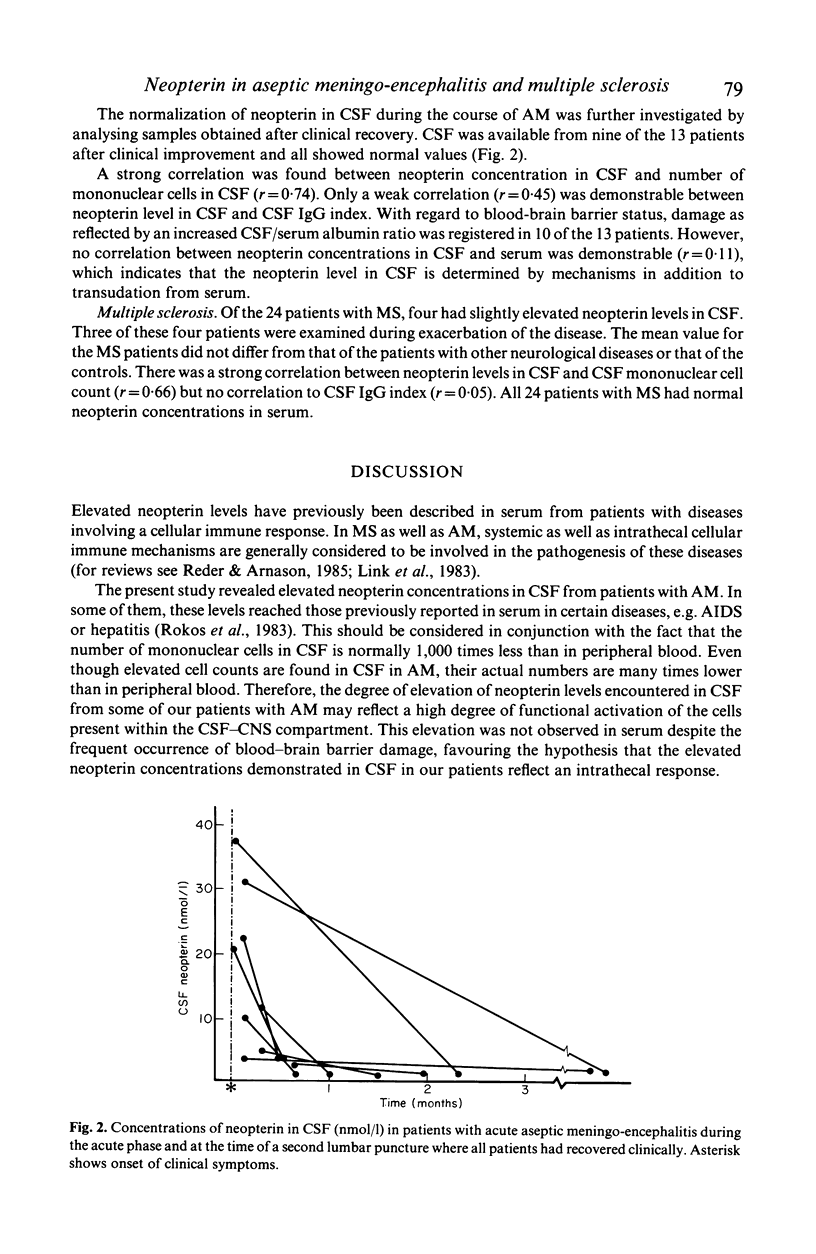
Neopterin levels in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and serum were measured with a sensitive radioimmunoassay in patients with multiple sclerosis (MS), aseptic meningo-encephalitis (AM), other mostly non-inflammatory neurological diseases, and controls with tension headache or psychoneurosis. Elevated levels of neopterin were found in CSF in most patients during acute phase of AM, and normalization after clinical recovery. The elevation in CSF was not reflected in serum. Only four of 24 MS patients--three of them examined during exacerbation--had slight elevation of neopterin in CSF and all had normal serum levels. Neopterin levels in CSF correlated with mononuclear cell count. The elevation of neopterin observed in CSF in inflammatory CNS diseases despite low cell numbers in CSF compared to blood might reflect a high activation level of cells locally in the CNS. Neopterin in CSF is a valuable marker of acute cellular immune response.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bach M. A., Phan-Dinh-Tuy F., Tournier E., Chatenoud L., Bach J. F., Martin C., Degos J. D. Deficit of suppressor T cells in active multiple sclerosis. Lancet. 1980 Dec 6;2(8206):1221–1223. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)92480-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs D., Granditsch G., Hausen A., Reibnegger G., Wachter H. Urinary neopterin excretion in coeliac disease. Lancet. 1983 Aug 20;2(8347):463–464. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90437-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafler D. A., Fox D. A., Manning M. E., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L., Weiner H. L. In vivo activated T lymphocytes in the peripheral blood and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med. 1985 May 30;312(22):1405–1411. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198505303122201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber C., Batchelor J. R., Fuchs D., Hausen A., Lang A., Niederwieser D., Reibnegger G., Swetly P., Troppmair J., Wachter H. Immune response-associated production of neopterin. Release from macrophages primarily under control of interferon-gamma. J Exp Med. 1984 Jul 1;160(1):310–316. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.1.310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber C., Fuchs D., Hausen A., Margreiter R., Reibnegger G., Spielberger M., Wachter H. Pteridines as a new marker to detect human T cells activated by allogeneic or modified self major histocompatibility complex (MHC) determinants. J Immunol. 1983 Mar;130(3):1047–1050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber C., Fuchs D., Niederwieser D., Hausen A., Reibnegger G., Nilsson K., Wachter H. Neopterin, ein neuer biochemischer Marker zur klinischen Erfassung zellulärer Immunreaktionen. Klin Wochenschr. 1984 Feb 1;62(3):103–113. doi: 10.1007/BF01738700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern P., Rokos H., Dietrich M. Raised serum neopterin levels and imbalances of T-lymphocyte subsets in viral diseases, acquired immune deficiency and related lymphadenopathy syndromes. Biomed Pharmacother. 1984;38(8):407–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Link H., Kostulas V. Utility of isoelectric focusing of cerebrospinal fluid and serum on agarose evaluated for neurological patients. Clin Chem. 1983 May;29(5):810–815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Link H., Tibbling G. Principles of albumin and IgG analyses in neurological disorders. III. Evaluation of IgG synthesis within the central nervous system in multiple sclerosis. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1977 Sep;37(5):397–401. doi: 10.1080/00365517709091498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margreiter R., Fuchs D., Hausen A., Huber C., Reibnegger G., Spielberger M., Wachter H. Neopterin as a new biochemical marker for diagnosis of allograft rejection. Experience based upon evaluation of 100 consecutive cases. Transplantation. 1983 Dec;36(6):650–653. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198336060-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noronha A. B., Richman D. P., Arnason B. G. Detection of in vivo stimulated cerebrospinal-fluid lymphocytes by flow cytometry in patients with multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med. 1980 Sep 25;303(13):713–717. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198009253031301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Weiner H. L., Hauser S. L., Cohen J. A., Distaso J. A., Schlossman S. F. Loss of suppressor T cells in active multiple sclerosis. Analysis with monoclonal antibodies. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jul 17;303(3):125–129. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198007173030303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice G. P., Finney D., Braheny S. L., Knobler R. L., Sipe J. C., Oldstone M. B. Disease activity markers in multiple sclerosis. Another look at suppressor cells defined by monoclonal antibodies OKT4, OKT5, and OKT8. J Neuroimmunol. 1984 Apr;6(2):75–84. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(84)90028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHUMACHER G. A., BEEBE G., KIBLER R. F., KURLAND L. T., KURTZKE J. F., MCDOWELL F., NAGLER B., SIBLEY W. A., TOURTELLOTTE W. W., WILLMON T. L. PROBLEMS OF EXPERIMENTAL TRIALS OF THERAPY IN MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS: REPORT BY THE PANEL ON THE EVALUATION OF EXPERIMENTAL TRIALS OF THERAPY IN MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Mar 31;122:552–568. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb20235.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tibbling G., Link H., Ohman S. Principles of albumin and IgG analyses in neurological disorders. I. Establishment of reference values. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1977 Sep;37(5):385–390. doi: 10.1080/00365517709091496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachter H., Hausen A., Grassmayr K. Erhöhte Ausscheidung von Neopterin im Harn von Patienten mit malignen Tumoren und mit Viruserkrankungen. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1979 Dec;360(12):1957–1960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waksman B. H., Reynolds W. E. Multiple sclerosis as a disease of immune regulation. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1984 Mar;175(3):282–294. doi: 10.3181/00379727-175-41798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabriskie J. B., Mayer L., Fu S. M., Yeadon C., Cam V., Plank C. T-cell subsets in multiple sclerosis: lack of correlation between helper and suppressor T cells and the clinical state. J Clin Immunol. 1985 Jan;5(1):7–12. doi: 10.1007/BF00915162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


