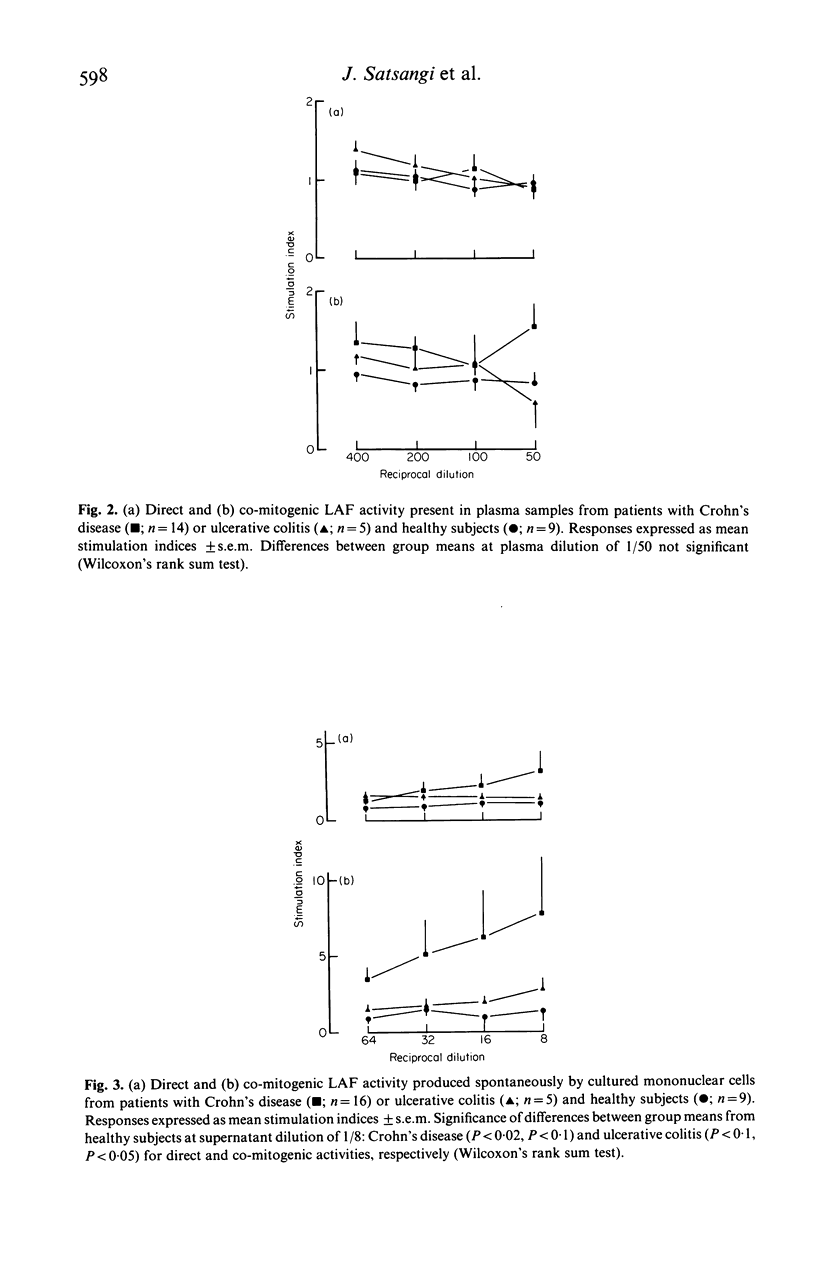
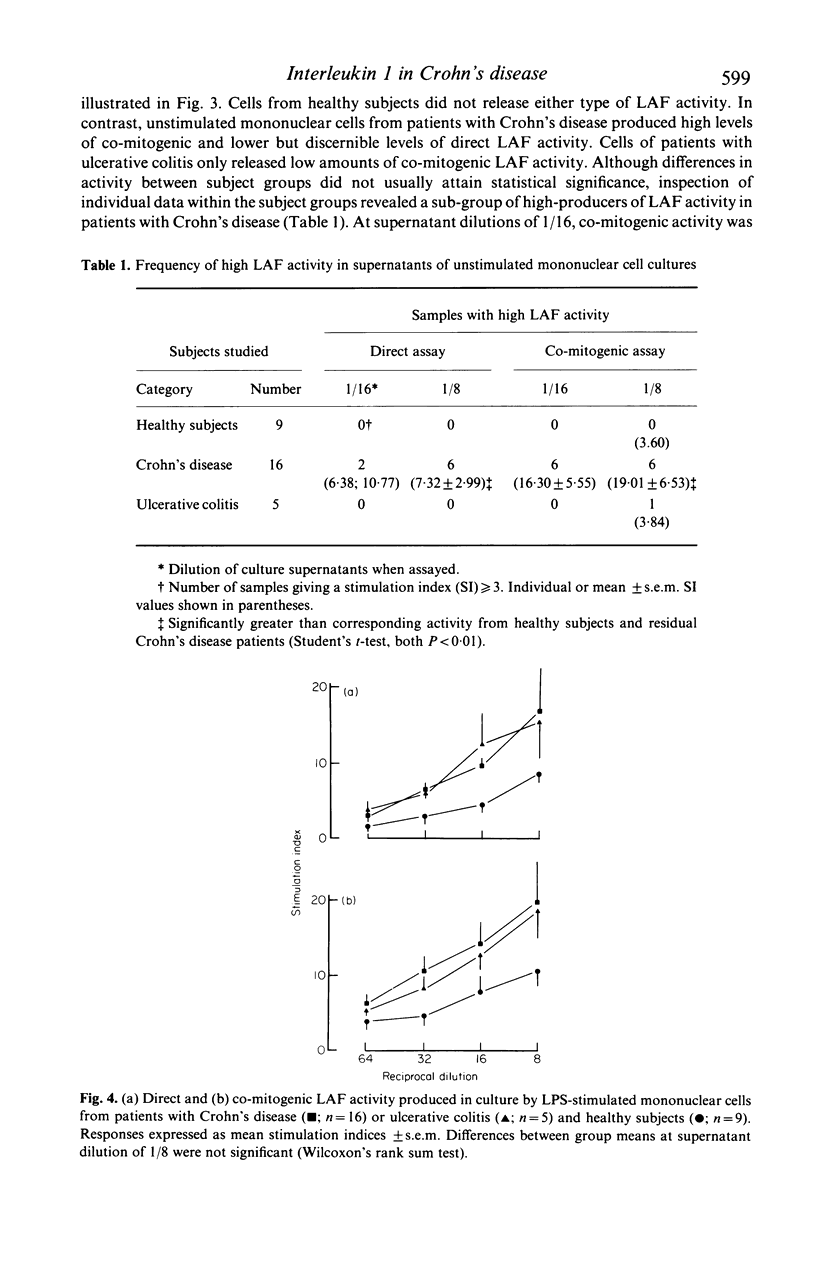
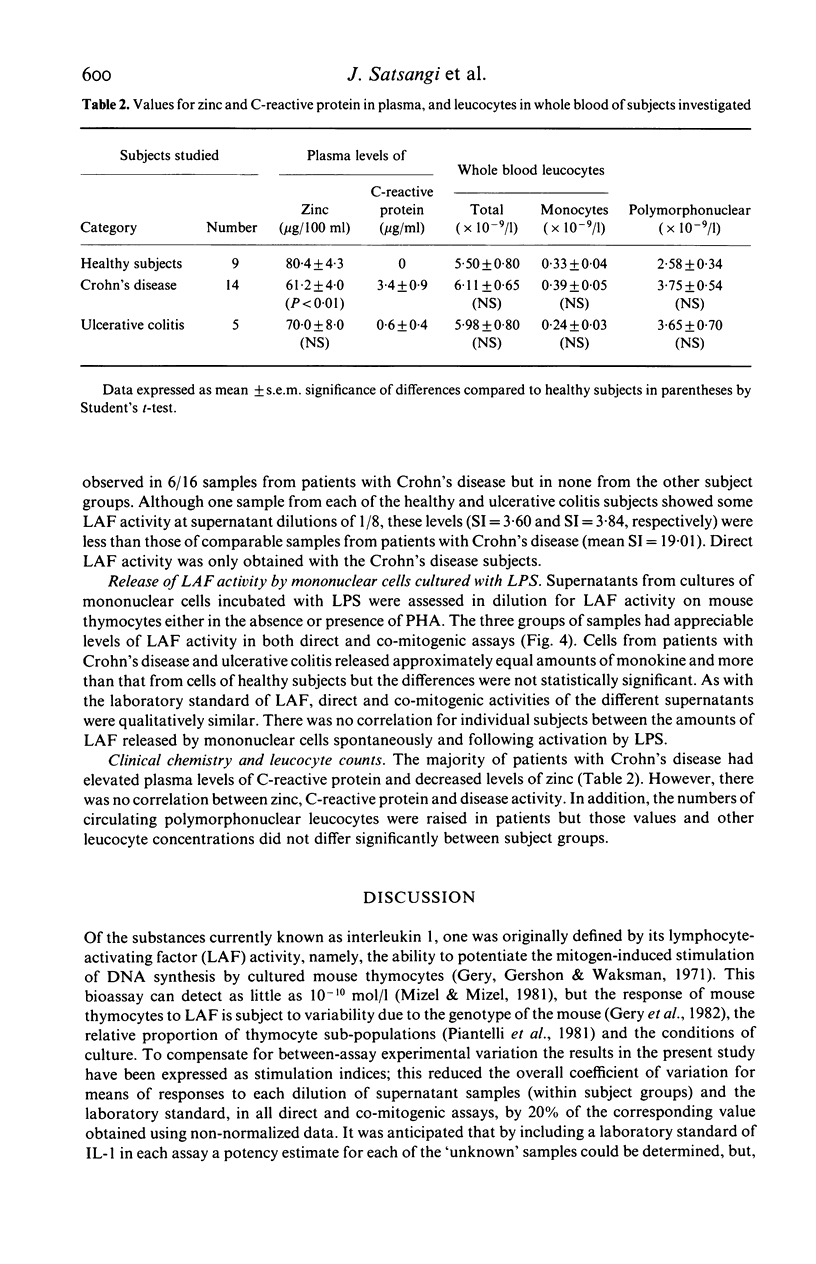
Abstract
A number of the activities currently ascribed to the mediator interleukin 1 (IL-1) are relevant to chronic inflammatory bowel disease. Using the mouse thymocyte stimulation assay, lymphocyte-activating factor (LAF) activity was measured in plasma samples and supernatants from cultures of peripheral blood mononuclear cells from 16 patients with Crohn's disease, six with ulcerative colitis, and 10 healthy subjects. Results were compared with disease activity, drug therapy, granulocyte count, and plasma levels of zinc and C-reactive protein (CRP). Very low levels of LAF were detected in a few plasma samples from each of the subject groups. Mononuclear cells from healthy subjects produced LAF only when cultured with lipopolysaccharide, but stimulated cells from patients produced greater amounts. Moreover, cells from six patients with Crohn's disease, not receiving steroids, produced LAF spontaneously. Crohn's disease patients also had low plasma zinc but elevated levels of CRP and granulocytes. This enhanced production of LAF in vitro may reflect a primary cellular defect in Crohn's disease, or a secondary consequence of monocyte activation.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baracos V., Rodemann H. P., Dinarello C. A., Goldberg A. L. Stimulation of muscle protein degradation and prostaglandin E2 release by leukocytic pyrogen (interleukin-1). A mechanism for the increased degradation of muscle proteins during fever. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 10;308(10):553–558. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303103081002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Jahreis G. P., Sauder D. N., Koj A. Human keratinocytes and monocytes release factors which regulate the synthesis of major acute phase plasma proteins in hepatic cells from man, rat, and mouse. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7331–7342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Best W. R., Becktel J. M., Singleton J. W., Kern F., Jr Development of a Crohn's disease activity index. National Cooperative Crohn's Disease Study. Gastroenterology. 1976 Mar;70(3):439–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein D. L. Leukocytic pyrogen: a major mediator of the acute phase reaction. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;389:323–337. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb22147.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon J. G., Kluger M. J. Endogenous pyrogen activity in human plasma after exercise. Science. 1983 May 6;220(4597):617–619. doi: 10.1126/science.6836306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clowes G. H., Jr, George B. C., Villee C. A., Jr, Saravis C. A. Muscle proteolysis induced by a circulating peptide in patients with sepsis or trauma. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 10;308(10):545–552. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303103081001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Clowes G. H., Jr, Gordon A. H., Saravis C. A., Wolff S. M. Cleavage of human interleukin 1: isolation of a peptide fragment from plasma of febrile humans and activated monocytes. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1332–1338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1 and the pathogenesis of the acute-phase response. N Engl J Med. 1984 Nov 29;311(22):1413–1418. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198411293112205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evêquoz V., Bettens F., Kristensen F., Trechsel U., Stadler B. M., Dayer J. M., De Weck A. L., Fleisch H. Interleukin 2-independent stimulation of rabbit chondrocyte collagenase and prostaglandin E2 production by an interleukin 1-like factor. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Jun;14(6):490–495. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830140603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn A. Stimulation of interleukin-1 production from placental monocytes. Lymphokine Res. 1984;3(1):1–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George D. T., Abeles F. B., Mapes C. A., Sobocinski P. Z., Zenser T. V., Powanda M. C. Effect of leukocytic endogenous mediators on endocrine pancreas secretory responses. Am J Physiol. 1977 Sep;233(3):E240–E245. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1977.233.3.E240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gery I., Gershon R. K., Waksman B. H. Potentiation of cultured mouse thymocyte responses by factors released by peripheral leucocytes. J Immunol. 1971 Dec;107(6):1778–1780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gery I., Gershon R. K., Waksman B. H. Potentiation of the T-lymphocyte response to mitogens. I. The responding cell. J Exp Med. 1972 Jul 1;136(1):128–142. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.1.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Watson J. Interleukin-2 dependent culture of cytolytic T cell lines. Immunol Rev. 1981;54:81–109. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1981.tb00435.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudspith B. N., Brostoff J., McNicol M. W., Johnson N. M. Anergy in sarcoidosis: the role of interleukin-1 and prostaglandins in the depressed in vitro lymphocyte response. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Aug;57(2):324–330. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jewell D. P., Patel C. Immunology of inflammatory bowel disease. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1985;114:119–126. doi: 10.3109/00365528509093772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kampschmidt R. F., Upchurch H. F., Pulliam L. A. Characterization of a leukocyte-derived endogenous mediator responsible for increased plasma fibrinogen. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;389:338–353. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb22148.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klasing K. C. Effect of inflammatory agents and interleukin 1 on iron and zinc metabolism. Am J Physiol. 1984 Nov;247(5 Pt 2):R901–R904. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1984.247.5.R901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempner M. S., Dinarello C. A., Gallin J. I. Human leukocytic pyrogen induces release of specific granule contents from human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1978 May;61(5):1330–1336. doi: 10.1172/JCI109050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koretzky G. A., Elias J. A., Kay S. L., Rossman M. D., Nowell P. C., Daniele R. P. Spontaneous production of interleukin-1 by human alveolar macrophages. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1983 Dec;29(3):443–450. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(83)90047-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao Z., Haimovitz A., Chen Y., Chan J., Rosenstreich D. L. Characterization of a human interleukin 1 inhibitor. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):3882–3886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- March C. J., Mosley B., Larsen A., Cerretti D. P., Braedt G., Price V., Gillis S., Henney C. S., Kronheim S. R., Grabstein K. Cloning, sequence and expression of two distinct human interleukin-1 complementary DNAs. Nature. 1985 Jun 20;315(6021):641–647. doi: 10.1038/315641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizel S. B., Mizel D. Purification to apparent homogeneity of murine interleukin 1. J Immunol. 1981 Mar;126(3):834–837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nouri A. M., Panayi G. S., Goodman S. M. Cytokines and the chronic inflammation of rheumatic disease. I. The presence of interleukin-1 in synovial fluids. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Feb;55(2):295–302. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim J. J., Shneyour A., Kook A. I. Enhancement of DNA synthesis and cAMP content of mouse thymocytes by mediator(s) derived from adherent cells. J Immunol. 1976 May;116(5):1466–1472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penhaligon M., Anthoons J., Pilkington D., Wolstencroft R. A., Bates T., Nias A. H. Antimetastatic effect of cimetidine on mice bearing a C3H mouse mammary adenocarcinoma: survival and lymphocyte function studies. Clin Exp Metastasis. 1984 Jan-Mar;2(1):37–53. doi: 10.1007/BF00132305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postlethwaite A. E., Lachman L. B., Kang A. H. Induction of fibroblast proliferation by interleukin-1 derived from human monocytic leukemia cells. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Sep;27(9):995–1001. doi: 10.1002/art.1780270905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson H. J., Elford P. R., Sharrard R. M., Meats J. E., Russell R. G. Modulation of connective tissue metabolism by partially purified human interleukin 1. Cell Immunol. 1985 Jan;90(1):41–51. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90167-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J. A., Mizel S. B., Cohen D., Green I. Interleukin 1, a potential regulator of fibroblast proliferation. J Immunol. 1982 May;128(5):2177–2182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sztein M. B., Vogel S. N., Sipe J. D., Murphy P. A., Mizel S. B., Oppenheim J. J., Rosenstreich D. L. The role of macrophages in the acute-phase response: SAA inducer is closely related to lymphocyte activating factor and endogenous pyrogen. Cell Immunol. 1981 Sep 1;63(1):164–176. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90037-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRUELOVE S. C., WITTS L. J. Cortisone in ulcerative colitis; final report on a therapeutic trial. Br Med J. 1955 Oct 29;2(4947):1041–1048. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.4947.1041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner A. R., Arthur M. J., Wright R. Macrophage activation, chronic inflammation and gastrointestinal disease. Gut. 1984 Jul;25(7):760–783. doi: 10.1136/gut.25.7.760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treves A. J., Barak V., Tal T., Fuks Z. Constitutive secretion of interleukin 1 by human monocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Aug;13(8):647–651. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830130808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker S. B., Pierre R. V., Jordon R. E. Rapid identification of monocytes in a mixed mononuclear cell preparation. J Immunol Methods. 1977;14(3-4):267–269. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90137-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turchik J. B., Bornstein D. L. Role of the central nervous system in acute-phase responses to leukocytic pyrogen. Infect Immun. 1980 Nov;30(2):439–444. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.2.439-444.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wannemacher R. W., Jr, DuPont H. L., Pekarek R. S., Powanda M. C., Schwartz A., Hornick R. B., Beisel W. R. An endogenous mediator of depression of amino acids and trace metals in serum during typhoid fever. J Infect Dis. 1972 Jul;126(1):77–86. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.1.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S., Bullock W., Nelson K., Schauf V., Gelber R., Jacobson R. Interleukin 1 production by peripheral blood mononuclear cells from leprosy patients. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):787–789. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.787-789.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilders M. M., Drexhage H. A., Kokjé M., Verspaget H. W., Meuwissen S. G. Veiled cells in chronic idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Feb;55(2):377–387. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood P. R., Andrus L., Clark I. A. Production of lymphocyte activating factor in vivo. Immunology. 1983 Dec;50(4):637–644. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


