Abstract
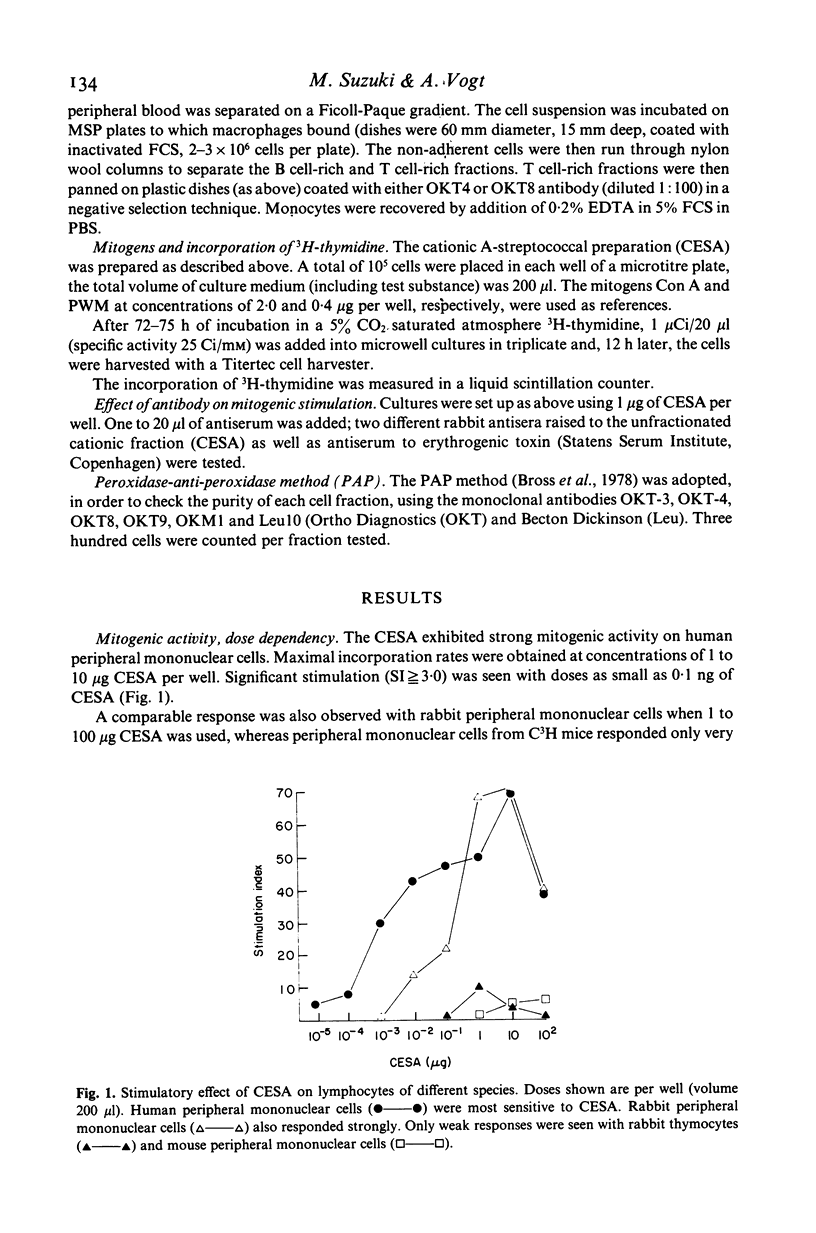
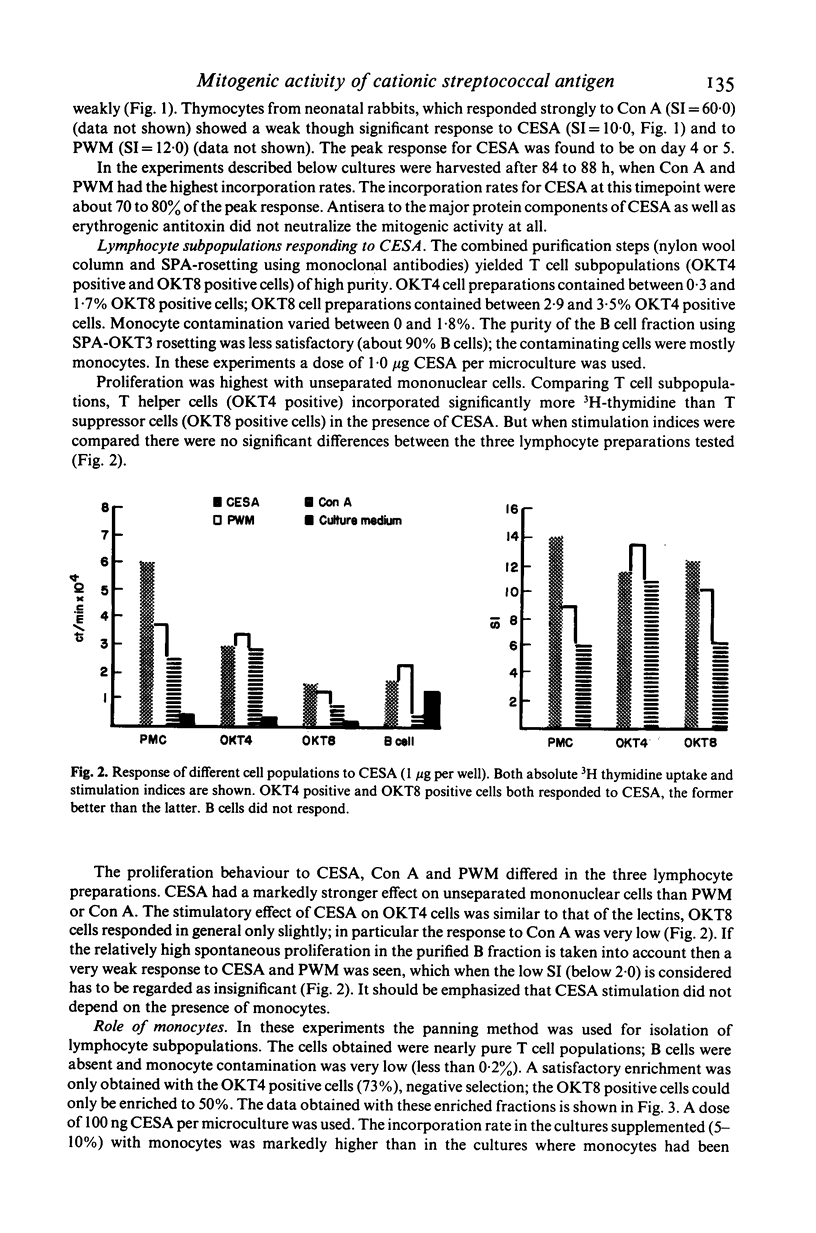
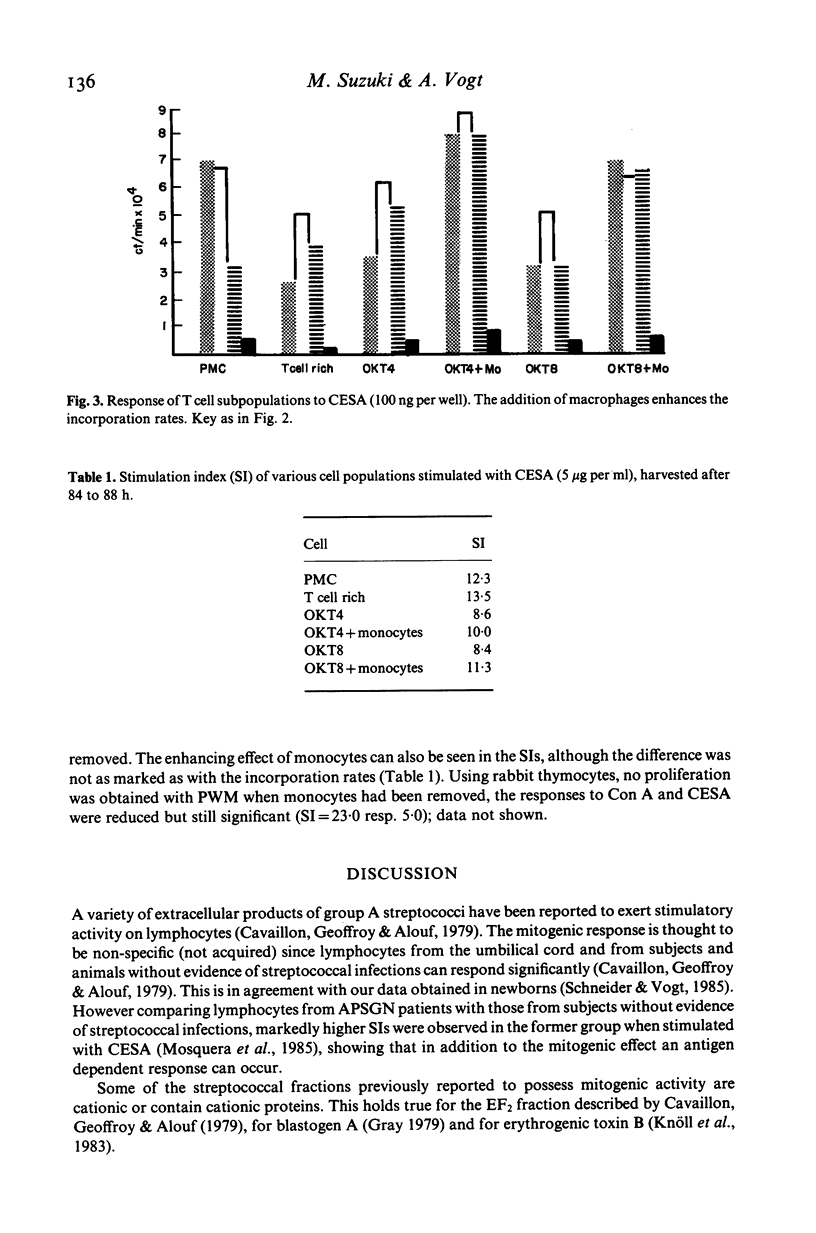
The cationic fraction (isoelectric point greater than 8.5) of supernatant products of group A streptococcal cultures exerted a strong mitogenic effect on human peripheral lymphocytes at concentrations as low as 1 ng/well. Incorporation rates were highest at concentrations of 1-10 micrograms; rabbit peripheral lymphocytes also responded strongly, only a weak response was seen with mouse peripheral lymphocytes and rabbit thymocytes. Purified OKT4 positive (T helper) and OKT8 positive (T suppressor) lymphocyte subpopulations both responded, the former more strongly. Although accessory cells (monocytes) were not absolutely necessary, in their presence higher incorporation of 3H-thymidine was observed. Isolated B cells did not respond.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barsumian E. L., Schlievert P. M., Watson D. W. Nonspecific and specific immunological mitogenicity by group A streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxins. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):681–688. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.681-688.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bross K. J., Pangalis G. A., Staatz C. G., Blume K. G. Demonstration of cell surface antigens and their antibodies by the peroxidase-antiperoxidase method. Transplantation. 1978 Jun;25(6):331–334. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197806000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerlach D., Knöll H., Köhler W., Ozegowski J. H., Hríbalova V. Isolation and characterization of erythrogenic toxins. V. Communication: identity of erythrogenic toxin type B and streptococcal proteinase precursor. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1983 Sep;255(2-3):221–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray E. D. Purification and properties of an extracellular blastogen produced by group A streptococci. J Exp Med. 1979 Jun 1;149(6):1438–1449. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.6.1438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronowicz E., Coutinho A., Melchers F. A plaque assay for all cells secreting Ig of a given type or class. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Aug;6(8):588–590. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seravalli E., Taranta A. Lymphocyte transformation and macrophage migration inhibition by electrofocused and gel-filtered fractions of group A streptococcal filtrate. Cell Immunol. 1974 Dec;14(3):366–375. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(74)90186-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchiyama T., Nelson D. L., Fleisher T. A., Waldmann T. A. A monoclonal antibody (anti-Tac) reactive with activated and functionally mature human T cells. II. Expression of Tac antigen on activated cytotoxic killer T cells, suppressor cells, and on one of two types of helper T cells. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1398–1403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt A., Batsford S., Rodríguez-Iturbe B., García R. Cationic antigens in poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis. Clin Nephrol. 1983 Dec;20(6):271–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabriskie J. B., Lewshenia R., Möller G., Wehle B., Falk R. E. Lymphocytic responses to streptococcal antigens in glomerulonephritic patients. Science. 1970 May 29;168(3935):1105–1108. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3935.1105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Rijn I., Kessler R. E. Growth characteristics of group A streptococci in a new chemically defined medium. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):444–448. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.444-448.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


