Abstract
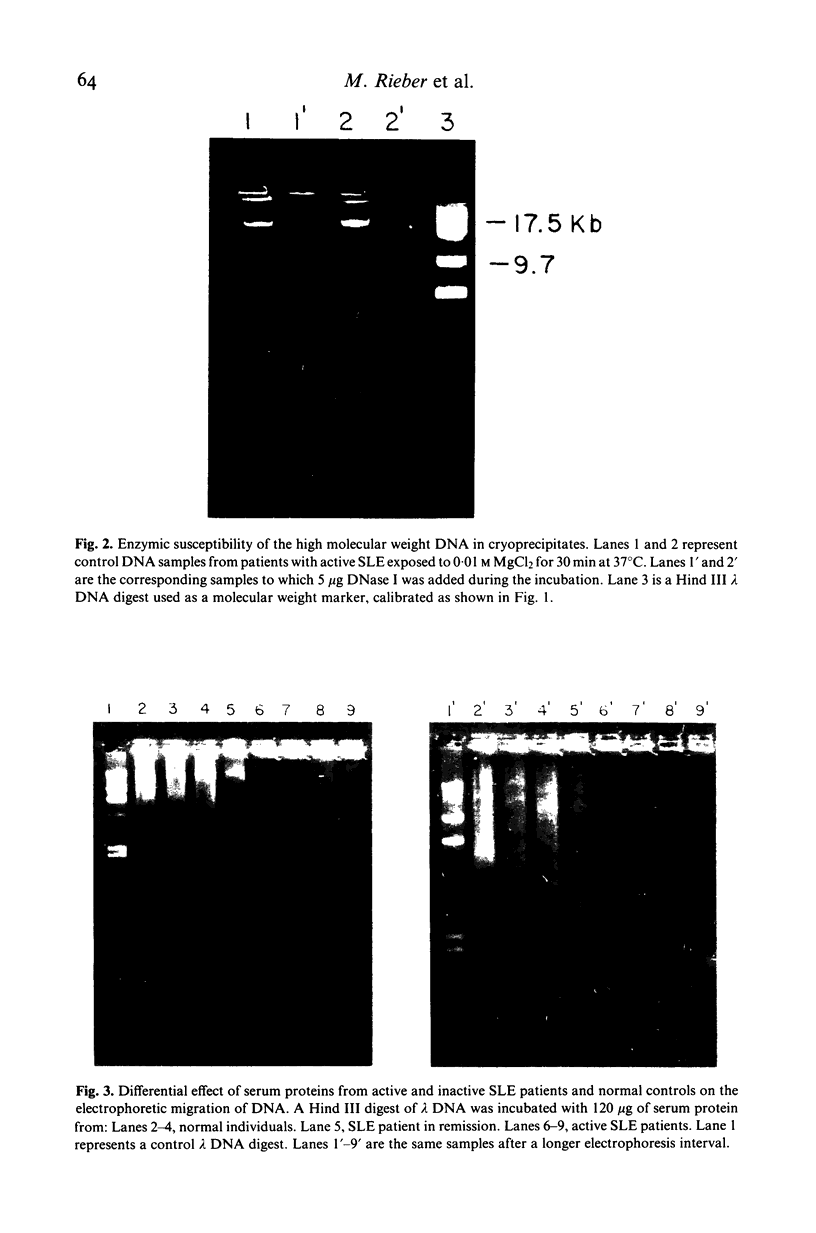
Agarose gel electrophoresis of cryoprecipitates from systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients revealed the presence of a slowly migrating DNAse I-sensitive DNA species at the top of the gel. Upon deproteinization, electrophoretic migration was modified favouring the migration of a 17.5 kb DNA fragment. Mixing experiments adding human serum or plasma to a lambda phage DNA digest revealed a DNA-protein interaction shown by an accumulation of high mol. wt polynucleotide at the top of the gels, and a slowed migration of the DNA bands. No comparable effect was observed when serum albumin was added to the lambda DNA digest. Dot hybridization analysis showed preferential reactivity of the 17.5 kb DNA to human DNA, implying its human origin. Our data suggests that most of this high molecular weight DNA exists as a DNA-2 protein complex. Our mixing experiments also suggest the occurrence of an excess of free DNA antibodies. We propose that the DNA-protein association may play a role in the stabilization and immunogenicity of the nucleoprotein complex.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adu D., Dobson J., Williams D. G. DNA-anti-DNA circulating complexes in the nephritis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Mar;43(3):605–614. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruneau C., Benveniste J. Circulating DNA:anti-DNA complexes in systemic lupus erythematosus. Detection and characterization by ultracentrifugation. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jul;64(1):191–198. doi: 10.1172/JCI109439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burdick G., Emlen W. Effect of antibody excess on the size, stoichiometry, and DNAse resistance of DNA anti-DNA immune complexes. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2593–2597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contreras C. E., Orozco A., Sánchez P., Ortega G., Bianco N. E. Physiological aspects of circulating immune complexes in the normal population. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Jun;48(3):693–699. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. S., Godfrey S. M., Winfield J. B. Direct evidence for circulating DNA/anti-DNA complexes in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1978 Jan-Feb;21(1):17–22. doi: 10.1002/art.1780210104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emlen W., Mannik M. Effect of DNA size and strandedness on the in vivo clearance and organ localization of DNA. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Apr;56(1):185–192. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoch S. O., McVey E. Purification and characterization of two major DNA-binding proteins in human serum. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):1881–1887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikebe K., Gupta R. C., Tan E. M. Characterization of DNA in polyethylene glycol precipitated immune complexes from sera of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Oct;54(1):169–177. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalovidouris A. E., Johnson R. L. Rapid cryoglobulin screening: an aid to the clinician. Ann Rheum Dis. 1978 Oct;37(5):444–448. doi: 10.1136/ard.37.5.444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koffler D., Carr R., Agnello V., Thoburn R., Kunkel H. G. Antibodies to polynucleotides in human sera: antigenic specificity and relation to disease. J Exp Med. 1971 Jul 1;134(1):294–312. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.1.294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langone J. J. Protein A of Staphylococcus aureus and related immunoglobulin receptors produced by streptococci and pneumonococci. Adv Immunol. 1982;32:157–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LePecq J. B., Paoletti C. A fluorescent complex between ethidium bromide and nucleic acids. Physical-chemical characterization. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jul 14;27(1):87–106. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90353-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCoubrey-Hoyer A., Okarma T. B., Holman H. R. Partial purification and characterization of plasma DNA and its relation to disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Med. 1984 Jul;77(1):23–34. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90431-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano H., Morimoto C. Isolation of DNA from DNA/anti-DNA antibody immune complexes in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1981 Feb;126(2):538–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winfield J. B., Koffler D., Kunkel H. G. Specific concentration of polynucleotide immune complexes in the cryoprecipitates of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1975 Sep;56(3):563–570. doi: 10.1172/JCI108125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



