Abstract
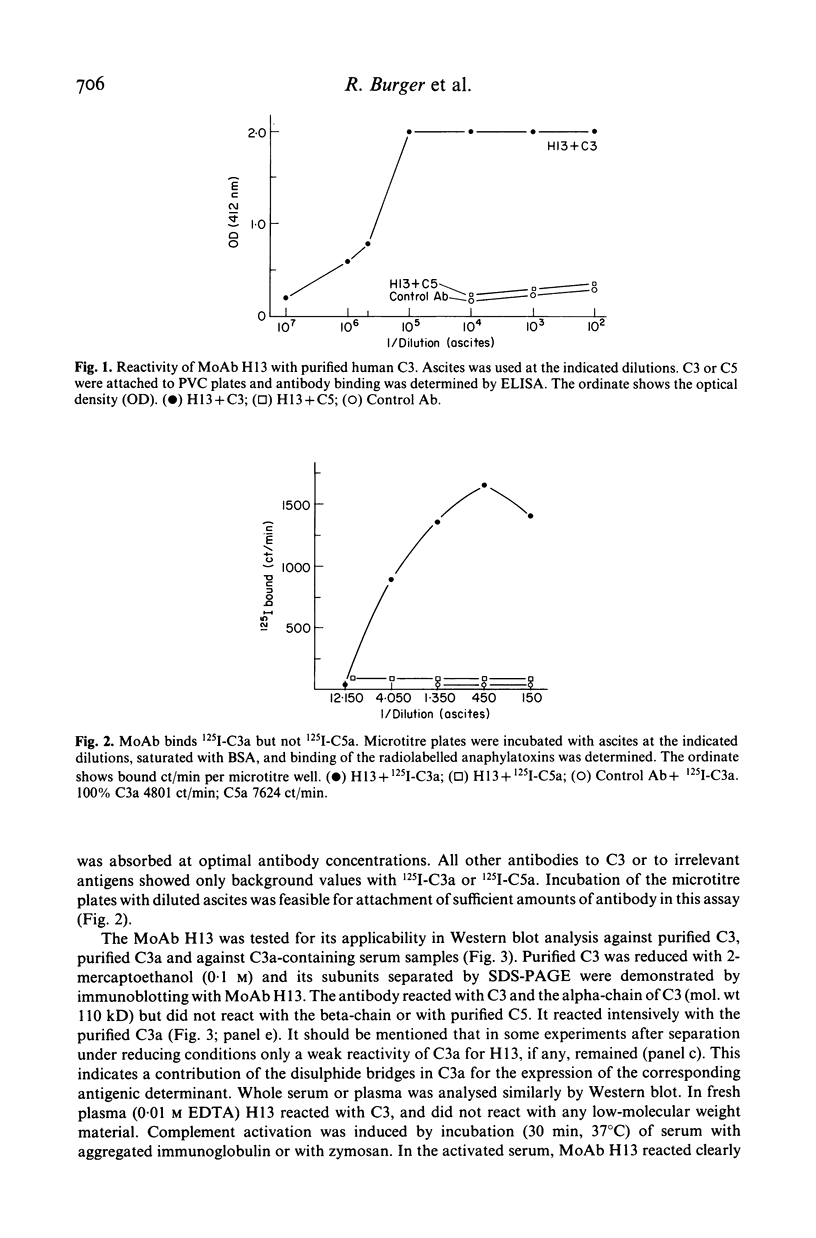
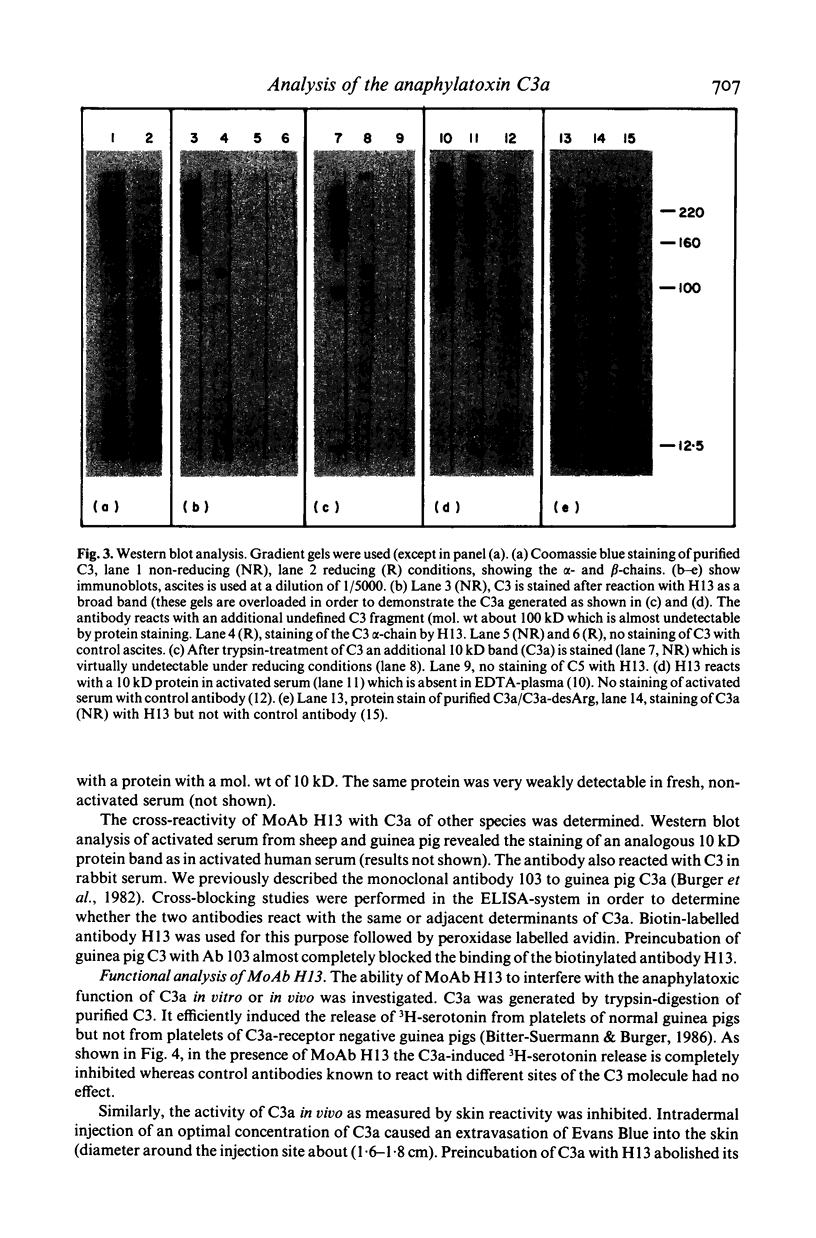
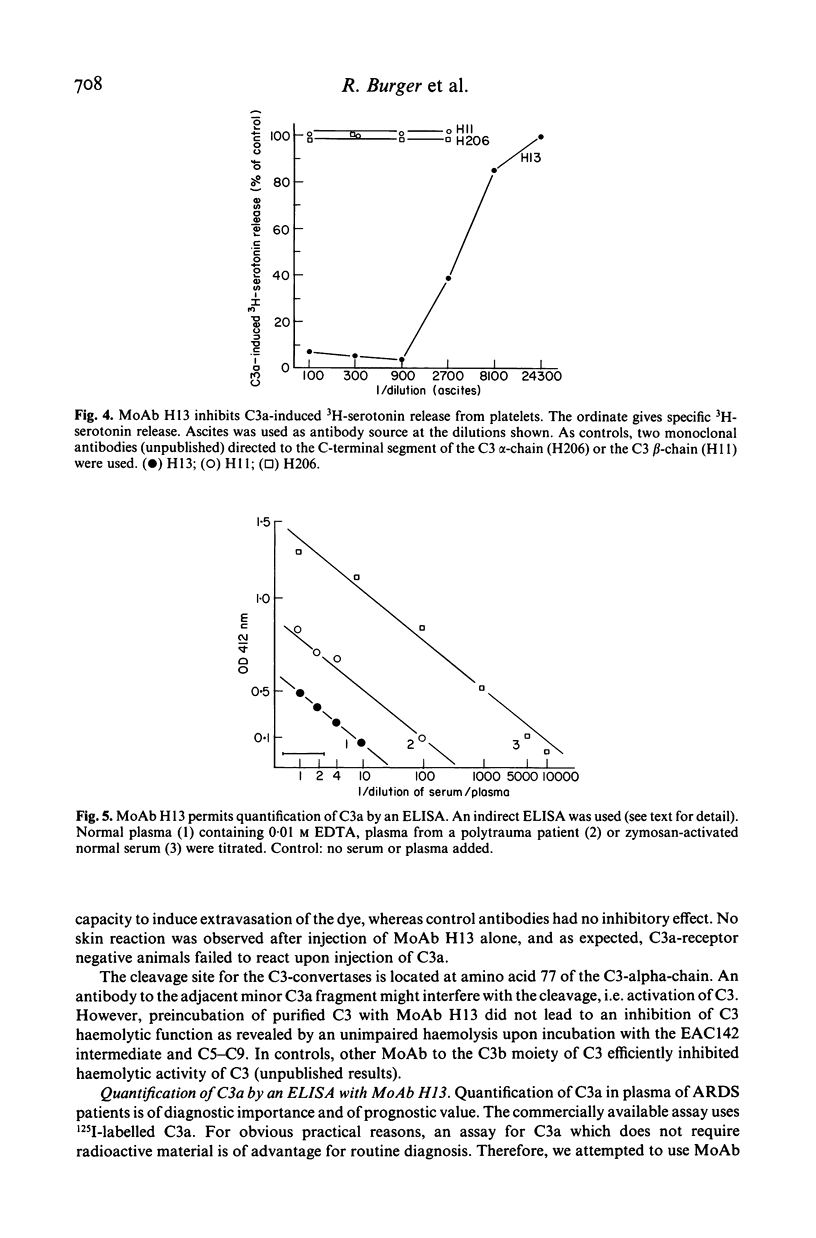
The C3 fragment C3a belongs to the anaphylatoxins. It has immune regulatory activity and contributes to the pathogenesis of the adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). The low molecular weight (9 kD) of C3a complicates the production of antibodies to C3a. We obtained a monoclonal antibody (designated H13) to human C3a. It reacts with C3a or C3a-desArg and with native C3 but not with C5 or C5a. In immunoblot analysis it reacts with the alpha- but not with beta-chain of C3 and binds to a protein with a mol. wt of about 10 kD present in zymosan-activated sera which is only marginally detectable in nonactivated serum and absent in plasma. H13 crossreacts with the analogous proteins of rabbit, guinea pig and sheep. H13 has the capacity to bind 125I-radiolabelled C3a efficiently but fails totally to react with 125I-C5a or with other C3 alpha-chain fragments. H13 blocks C3a functional activity. It markedly inhibits C3a-induced 3H-serotonin release from platelets in vitro and similarly inhibits the C3a-induced extravasation of Evans blue into the skin in vivo. H13 does not interfere with the haemolytic activity of C3. An ELISA system was established using H13 which permits quantification of C3a in sera of polytrauma patients. The antibody H13 should facilitate further functional analysis of C3a in experimental systems. It should be useful for quantification of C3a in diagnostic assays and also for application in immunopathology.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bitter-Suermann D., Burger R. Guinea pigs deficient in C2, C4, C3 or the C3a receptor. Prog Allergy. 1986;39:134–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokisch V. A., Müller-Eberhard H. J., Cochrane C. G. Isolation of a fragment (C3a) of the third component of human complement containing anaphylatoxin and chemotactic activity and description of an anaphylatoxin inactivator of human serum. J Exp Med. 1969 May 1;129(5):1109–1130. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.5.1109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger R., Deubel U., Hadding U., Bitter-Suermann D. Identification of functionally relevant determinants on the complement component C3 with monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1982 Nov;129(5):2042–2050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane C. G., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The derivation of two distinct anaphylatoxin activities from the third and fifth components of human complement. J Exp Med. 1968 Feb 1;127(2):371–386. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.2.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T., Wong W. W. Complement ligand-receptor interactions that mediate biological responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:243–271. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.001331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer C. H., Wirtz G. H., Renfer L., Gresham H. D., Tack B. F. Large scale isolation of functionally active components of the human complement system. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3995–4006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartung H. P., Hadding U. Synthesis of complement by macrophages and modulation of their functions through complement activation. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1983;6(4):283–326. doi: 10.1007/BF02116277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugli T. E., Gerard C., Kawahara M., Scheetz M. E., 2nd, Barton R., Briggs S., Koppel G., Russell S. Isolation of three separate anaphylatoxins from complement-activated human serum. Mol Cell Biochem. 1981 Dec 4;41:59–66. doi: 10.1007/BF00225297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugli T. E. Structure and function of the anaphylatoxins. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1984;7(2-3):193–219. doi: 10.1007/BF01893020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugli T. E. The structural basis for anaphylatoxin and chemotactic functions of C3a, C4a, and C5a. Crit Rev Immunol. 1981 Feb;1(4):321–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyers T. M., Fowler A. A. Adult respiratory distress syndrome: causes, morbidity, and mortality. Fed Proc. 1986 Jan;45(1):25–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel S. L., Manderino G. L., Marasco W., Kaercher K., Hirata A. A., Ward P. A. A specific enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for the determination of human C5a antigen. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Sep 16;62(3):305–314. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma D., Sessler M. J., Meyer T. F., Schrod L., Hänsch G. M., Burger R. Expression of polypeptide segments of the human complement component C3 in E. coli: genetic and immunological characterization of cDNA clones specific for the alpha-chain of C3. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3398–3402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S., Ecker U., Hadding U., Bitter-Suermann D. Platelet-serotonin release by C3a and C5a: two independent pathways of activation. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1506–1509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldo J. E., Rogers R. M. Adult respiratory-distress syndrome: changing concepts of lung injury and repair. N Engl J Med. 1982 Apr 15;306(15):900–909. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198204153061504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rother K. Leucocyte mobilizing factor: a new biological activity derived from the third component of complement. Eur J Immunol. 1972 Dec;2(6):550–558. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830020615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruppel A., Diesfeld H. J., Rother U. Immunoblot analysis of Schistosoma mansoni antigens with sera of schistosomiasis patients: diagnostic potential of an adult schistosome polypeptide. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Dec;62(3):499–506. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigle W. O., Goodman M. G., Morgan E. L., Hugli T. E. Regulation of immune response by components of the complement cascade and their activated fragments. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1983;6(2-3):173–194. doi: 10.1007/BF00205872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



