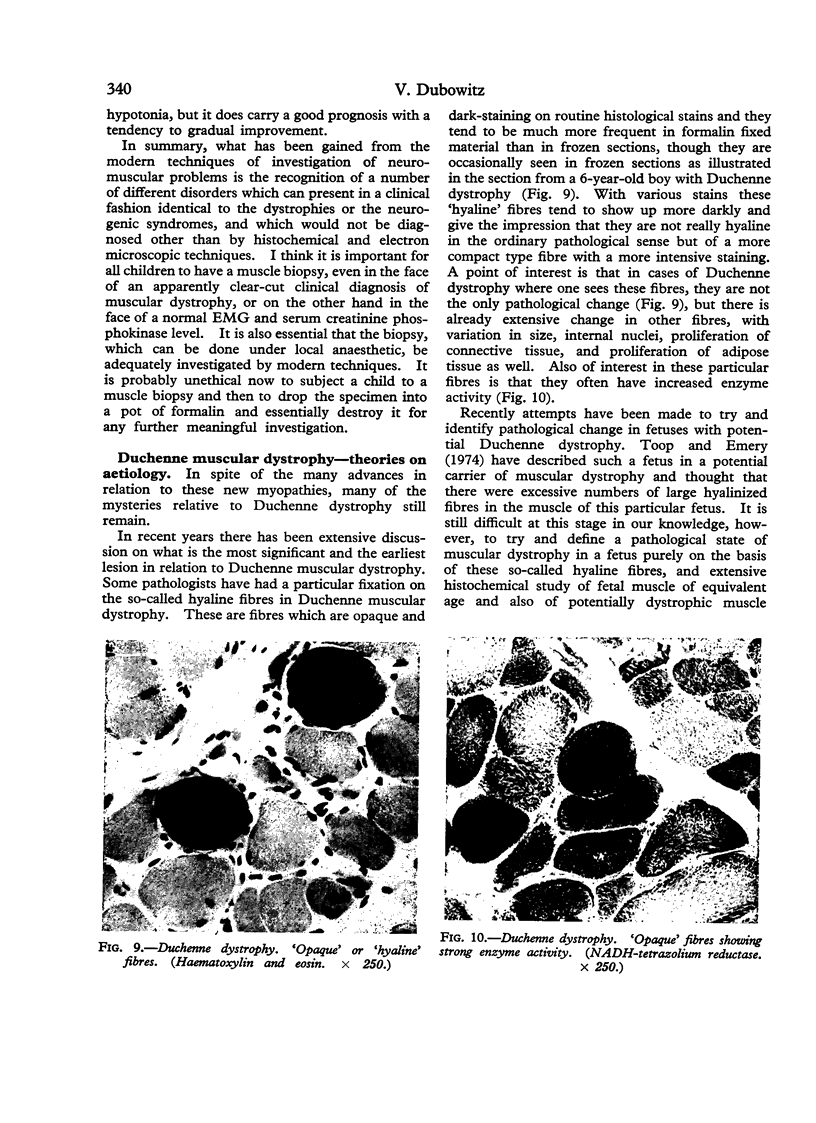
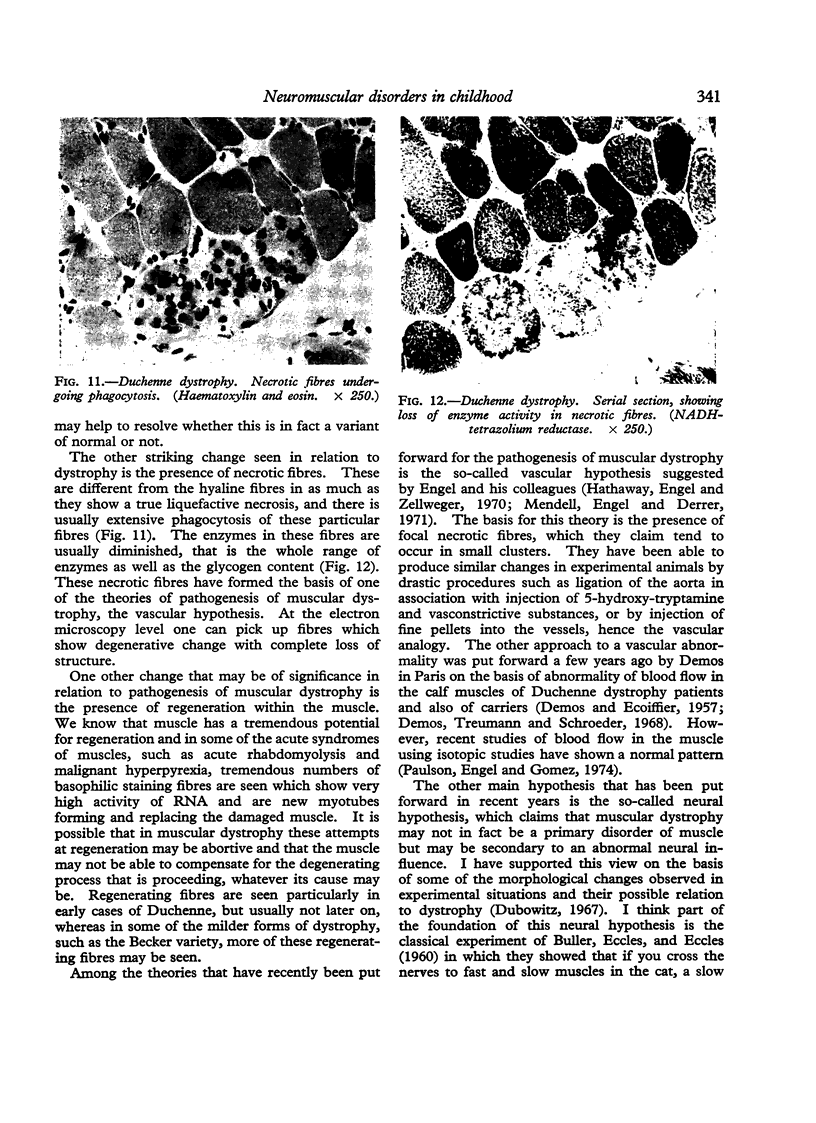
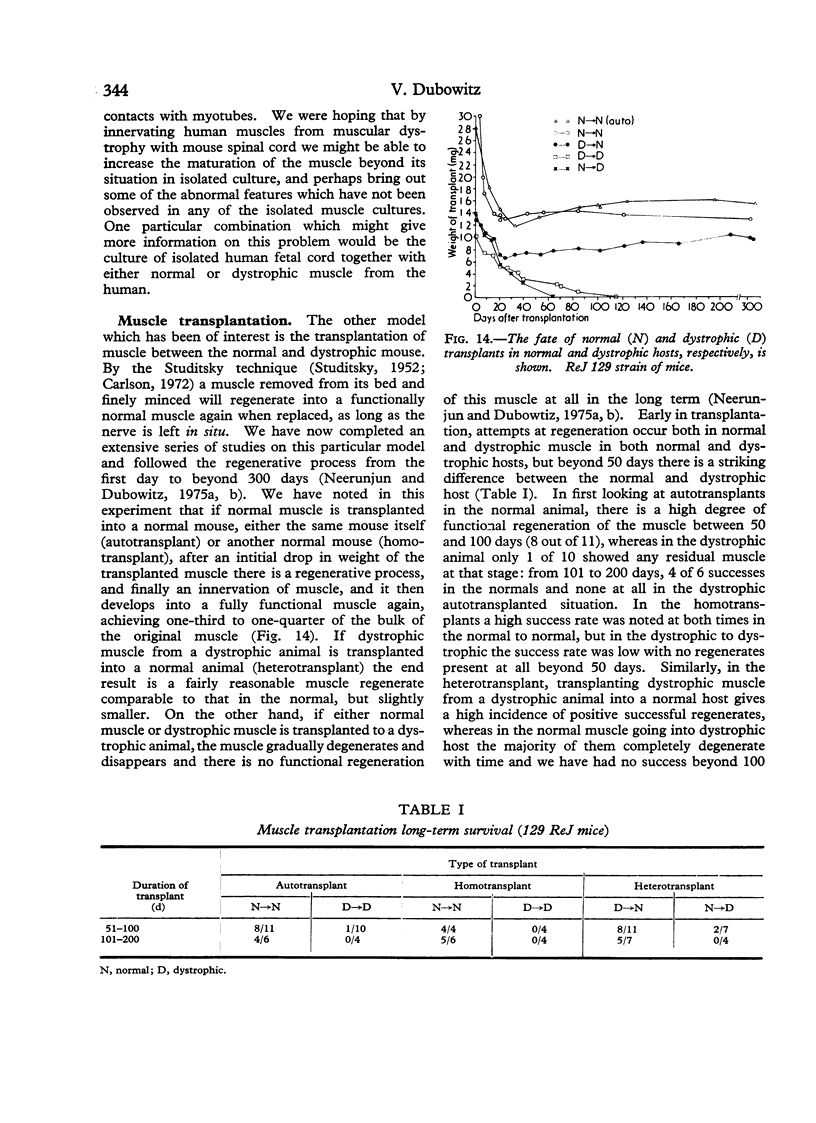
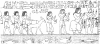Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BULLER A. J., ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M. Interactions between motoneurones and muscles in respect of the characteristic speeds of their responses. J Physiol. 1960 Feb;150:417–439. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballantyne J. P., Hansen S. A new method for the estimation of the number of motor units in a muscle. I. Control subjects and patients with myasthenia gravis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1974 Aug;37(8):907–915. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.37.8.907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop A., Gallup B., Skeate Y., Dubowitz V. Morphological studies on normal and diseased human muscle in culture. J Neurol Sci. 1971 Jul;13(3):333–350. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(71)90037-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEMOS J., ECOIFFIER J. Troubles circulatoires au cours de la myopathie; études artériographiques. Rev Fr Etud Clin Biol. 1957 May;2(5):489–494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOWITZ V., PEARSE A. G. A comparative histochemical study of oxidative enzyme and phosphorylase activity in skeletal muscle. Z Zellforch Microsk Anat Histochem. 1960;2:105–117. doi: 10.1007/BF00744575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOWITZ V., PEARSE A. G. Reciprocal relationship of phosphorylase and oxidative enzymes in skeletal muscle. Nature. 1960 Mar 5;185:701–702. doi: 10.1038/185701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demos J., Treumann F., Schroeder W. Anomalies de régulation de la micro-circulation musculaire chez les enfants atteints de dystrophie musculaire progressive par rapport a des enfants normaux du même age. Rev Fr Etud Clin Biol. 1968 May;13(5):467–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallup B., Bishop A., Dubowitz V. Autoradiographic studies of RNA and DNA synthesis during myogenesis in cultures of human, chick and rat muscle. J Neurol Sci. 1972 Oct;17(2):127–140. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(72)90135-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallup B., Dubowitz V. Letter: Failure of "dystrophic" neurones to support functional regeneration of normal or dystrophic muscle in culture. Nature. 1973 Jun 1;243(5405):287–289. doi: 10.1038/243287a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallup B., Strugalska-Cynowska H., Dubowitz V. Histochemical studies on normal and diseased human and chick muscle in tissue culture. J Neurol Sci. 1972 Oct;17(2):109–125. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(72)90134-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathaway P. W., Engel W. K., Zellweger H. Experimental myopathy after microarterial embolization; comparison with childhood x-linked pseudohypertrophic muscular dystrophy. Arch Neurol. 1970 Apr;22(4):365–378. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1970.00480220079011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunze D., Reichmann G., Egger E., Leuschner G., Eckhardt H. Erythrozytenlipide bei Progressiver Muskeldystrophie. Clin Chim Acta. 1973 Feb 12;43(3):333–341. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(73)90471-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matheson D. W., Howland J. L. Erythrocyte deformation in human muscular dystrophy. Science. 1974 Apr 12;184(4133):165–166. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4133.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McComas A. J., Sica R. E., Campbell M. J. "Sick" motoneurones. A unifying concept of muscle disease. Lancet. 1971 Feb 13;1(7694):321–326. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91045-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendell J. R., Engel W. K., Derrer E. C. Duchenne muscular dystrophy: functional ischemia reproduces its characteristic lesions. Science. 1971 Jun 11;172(3988):1143–1145. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3988.1143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POCH H., BECKER P. E. Eine Muskeldystrophie auf einem altägyptischen Relief. Nervenarzt. 1955 Dec 20;26(12):528–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panayiotopoulos C. P., Scarpalezos S., Papapetropoulos T. Electrophysiological estimation of motor units in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. J Neurol Sci. 1974 Sep;23(1):89–98. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(74)90145-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulson O. B., Engel A. G., Gomez M. R. Muscle blood flow in Duchenne type muscular dystrophy, limb-girdle dystrophy, polymyositis, and in normal controls. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1974 Jun;37(6):685–690. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.37.6.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toop J., Emery A. E. Muscle histology in fetuses at risk for Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Clin Genet. 1974;5(3):230–233. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1974.tb01687.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]