Abstract
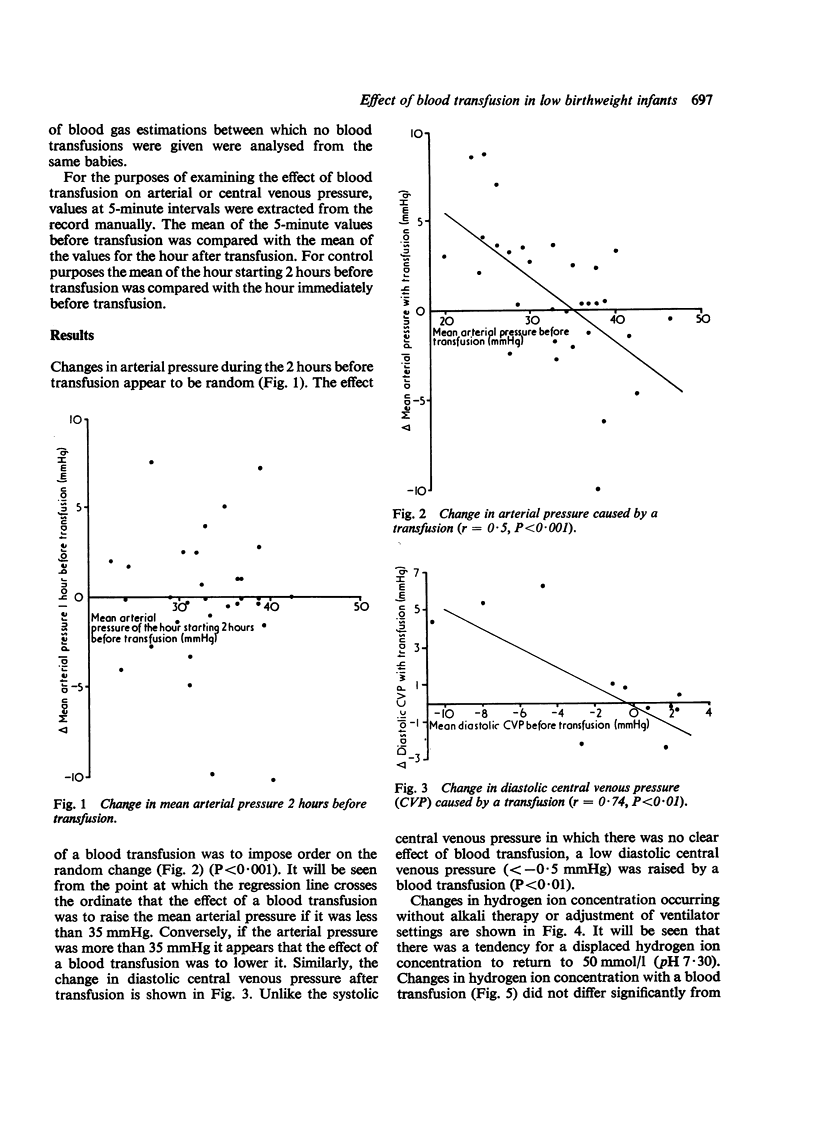
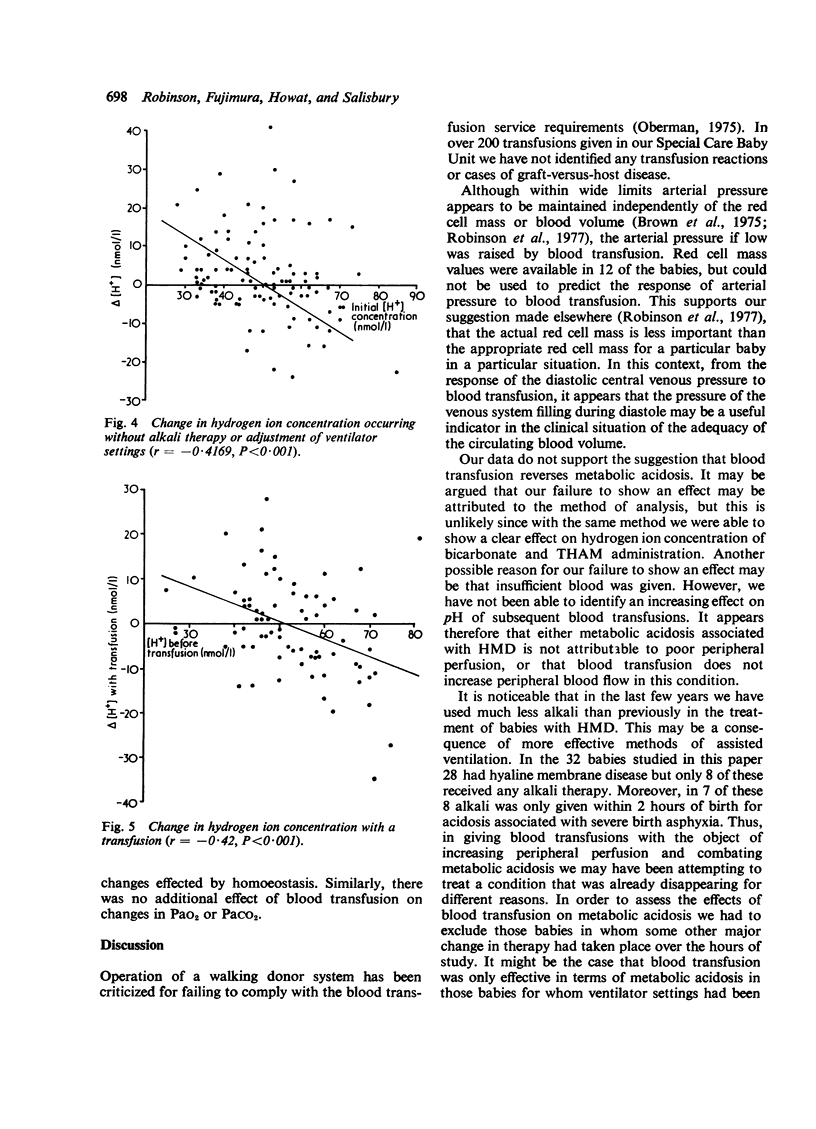
143 fresh blood transfusions were given to 32 low birthweight babies, 28 of whom had hyaline membrane disease. The arterial or central venous pressure was raised by a blood transfusion if before transfusion the mean arterial pressure was less than 35 mmHg or if the diastolic central venous pressure was less than -- 0-5 mmHg. There was no effect of blood transfusion on pH. It therefore appears either that metabolic acidosis in hyaline membrane disease is not caused by poor peripheral perfusion or that blood transfusion does not increase peripheral blood flow in this condition. The safety of the procedure is assessed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown E. G., Krouskop R. W., McDonnell F. E., Sweet A. Y. Blood volume and blood pressure in infants with respiratory distress. J Pediatr. 1975 Dec;87(6 Pt 2):1133–1138. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(75)80127-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassady G. Plasma volume studies in low birth weight infants. Pediatrics. 1966 Dec;38(6):1020–1027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inall J. A., Bluhm M. M., Kerr M. M., Douglas T. A., Hope C. S., Hutchison J. H. Blood volume and haematocrit studies in respiratory distress syndrome of the newborn. Arch Dis Child. 1965 Oct;40(213):480–484. doi: 10.1136/adc.40.213.480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberman H. A. Replacement transfusion in the newborn infant: a commentary. J Pediatr. 1975 Apr;86(4):586–587. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(75)80157-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usher R. H., Saigal S., O'Neil A., Surainder Y., Chua L-B Estimation of red blood cell volume in premature infants with and without respiratory distress syndrome. Biol Neonate. 1975;26(3-4):241–248. doi: 10.1159/000240735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


