Abstract
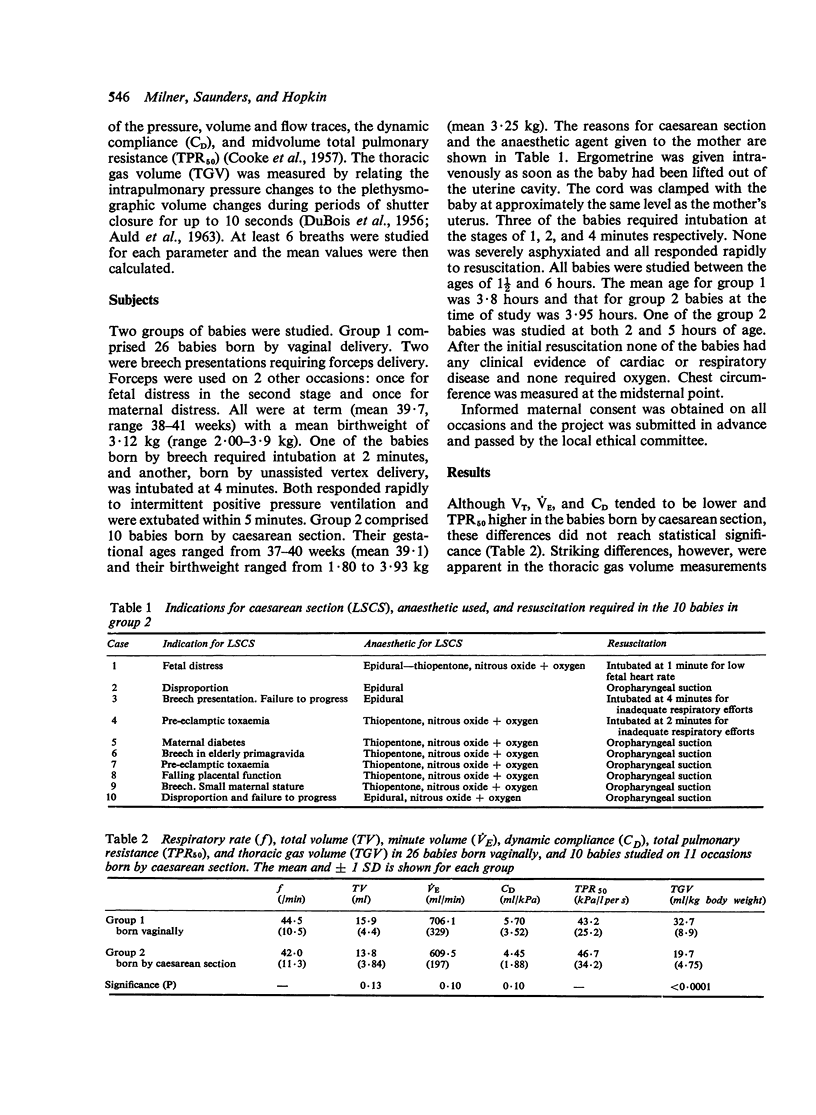
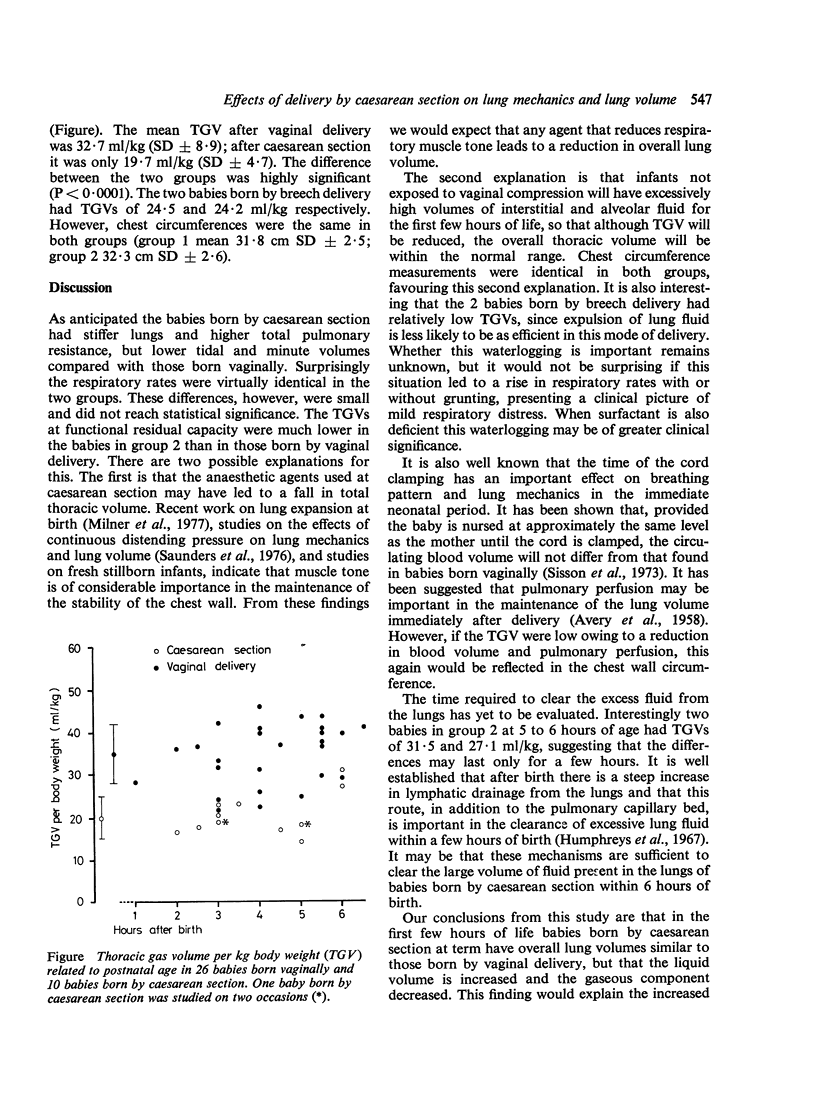
Lung function tests were carried out in the first 6 hours of life on 26 babies born by vaginal delivery and 10 born by caesarean section. The babies born by caesarean section had a mean thoracic gas volume of only 19.7 ml/kg body weight compared with 32.7 ml/kg for the babies born vaginally. We conclude that this is owing to an excess of lung fluid in the babies born by caesarean section.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AULD P. A., NELSON N. M., CHERRY R. B., RUDOLPH A. J., SMITH C. A. Measurement of thoracic gas volume in the newborn infant. J Clin Invest. 1963 Apr;42:476–483. doi: 10.1172/JCI104736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson R. C., Berendes H., Weiss W. Fetal compromise during elective cesarean section. II. A report from the Colloborative Project. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1969 Oct 15;105(4):579–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brice J. E., Walker C. H. Changing pattern of respiratory distress in newborn. Lancet. 1977 Oct 8;2(8041):752–754. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90249-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOK C. D., SUTHERLAND J. M., SEGAL S., CHERRY R. B., MEAD J., MCILROY M. B., SMITH C. A. Studies of respiratory physiology in the newborn infant. III. Measurements of mechanics of respiration. J Clin Invest. 1957 Mar;36(3):440–448. doi: 10.1172/JCI103441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiswick M. L., Milner R. D. Crying vital capacity. Measurement of neonatal lung function. Arch Dis Child. 1976 Jan;51(1):22–27. doi: 10.1136/adc.51.1.22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOIS A. B., BOTELHO S. Y., BEDELL G. N., MARSHALL R., COMROE J. H., Jr A rapid plethysmographic method for measuring thoracic gas volume: a comparison with a nitrogen washout method for measuring functional residual capacity in normal subjects. J Clin Invest. 1956 Mar;35(3):322–326. doi: 10.1172/JCI103281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hack M., Fanaroff A. A., Klaus M. H., Mendelawitz B. D., Merkatz I. R. Neonatal respiratory distress following elective delivery. A preventable disease? Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1976 Sep 1;126(1):43–47. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(76)90462-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphreys P. W., Normand I. C., Reynolds E. O., Strang L. B. Pulmonary lymph flow and the uptake of liquid from the lungs of the lamb at the start of breathing. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(1):1–29. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjellmer I., Magno R., Karlsson K. Anesthesia for Cesarean section. I. Effects on the respiratory adaptation of the newborn in elective Cesarean section. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1974;18(1):48–57. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.1974.tb00699.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magno R., Karlsson K., Selstam U., Wickström I. Anesthesia for cesarean section V: effects of enflurane anesthesia on the respiratory adaptation of the newborn in elective cesarean section. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1976;20(2):147–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.1976.tb05021.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magno R., Selstam U., Karlsson K. Anesthesia for cesarean section II: effects of the induction-delivery interval on the respiratory adaptation of the newborn in elective cesarean section. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1975;19(4):250–259. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.1975.tb05181.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner A. D., Saunders R. A., Hopkin I. E. Effects of continuous distending pressure on lung volumes and lung mechanics in the immediate neonatal period. Biol Neonate. 1977;31(1-2):111–115. doi: 10.1159/000240950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reis R. A., Gerbie A. B., Gerbie M. V. Reducing hazards to the newborn during cesarean section. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1970 Jan;130(1):124–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders R. A., Milner A. D., Hopkin I. E. The effects of continuous positive airway pressure on lung mechanics and lung volumes in the neonate. Biol Neonate. 1976;29(3-4):178–186. doi: 10.1159/000240862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sisson T. R., Knutson S., Kendall N. The blood volume of infants. IV. Infants born by cesarean section. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1973 Oct 1;117(3):351–357. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(73)90037-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usher R. H., Allen A. C., McLean F. H. Risk of respiratory distress syndrome related to gestational age, route of delivery, and maternal diabetes. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1971 Nov;111(6):826–832. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(71)90495-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


