Abstract
The pressure and volume changes associated with the first breath were measured in 17 healthy term babies, using oesophageal balloons and a reverse plethysmograph. 5 babies expanded their lungs with less than --20 cmH2O (--2 kPa). The characteristic opening pressure pattern previously described was seen in only one baby, whose initial volume change was an expiratory one. It is concluded that opening pressures greater than 10 cmH2O (0.96 kPa) are rarely seen in term healthy infants.
Full text
PDF
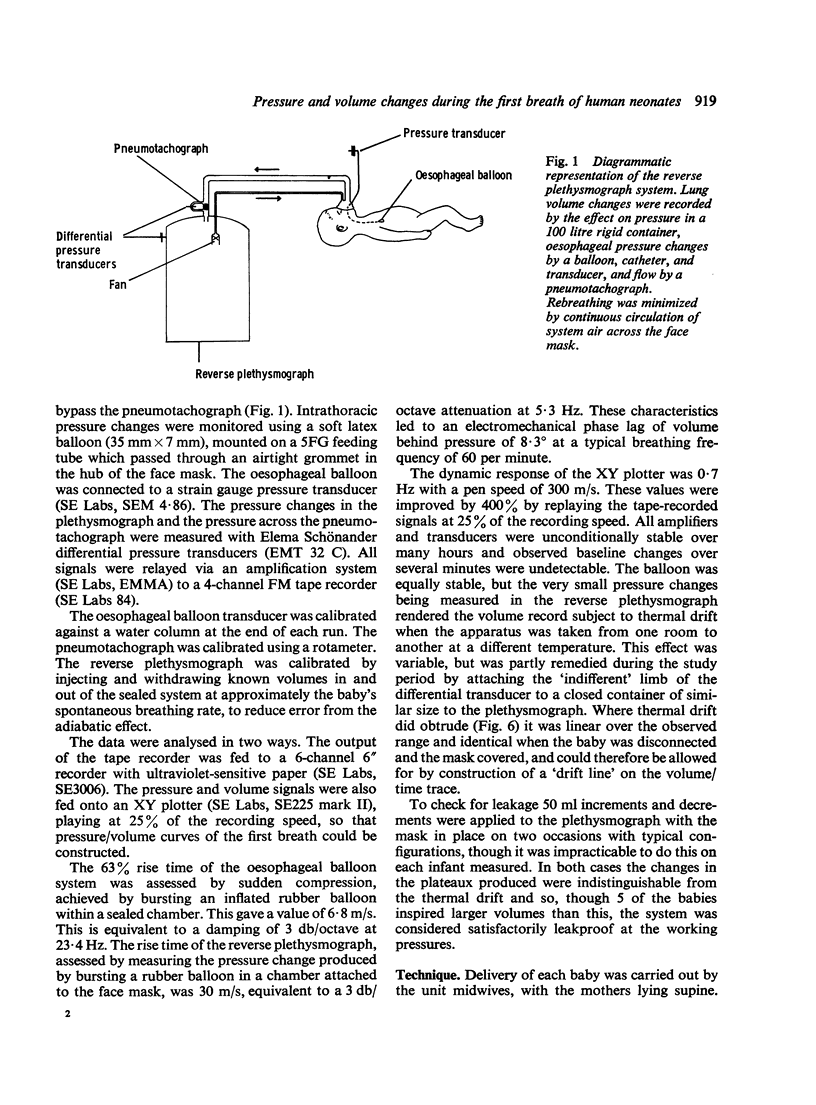

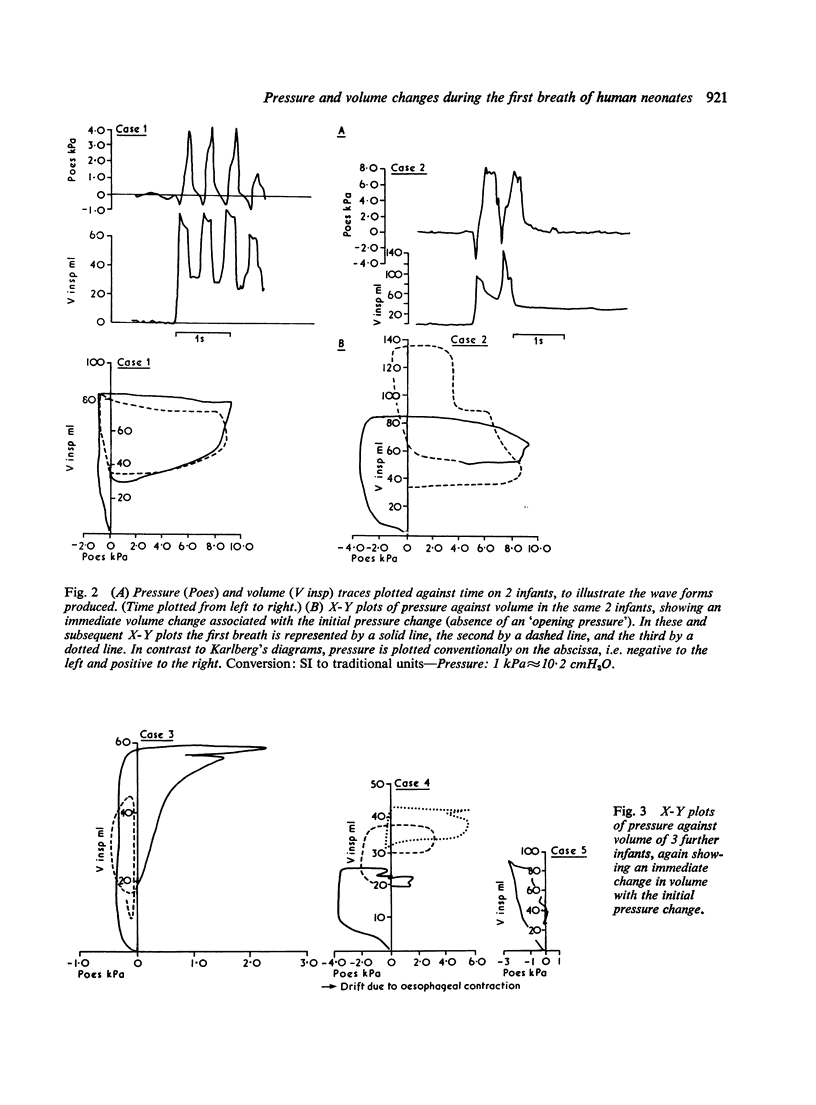

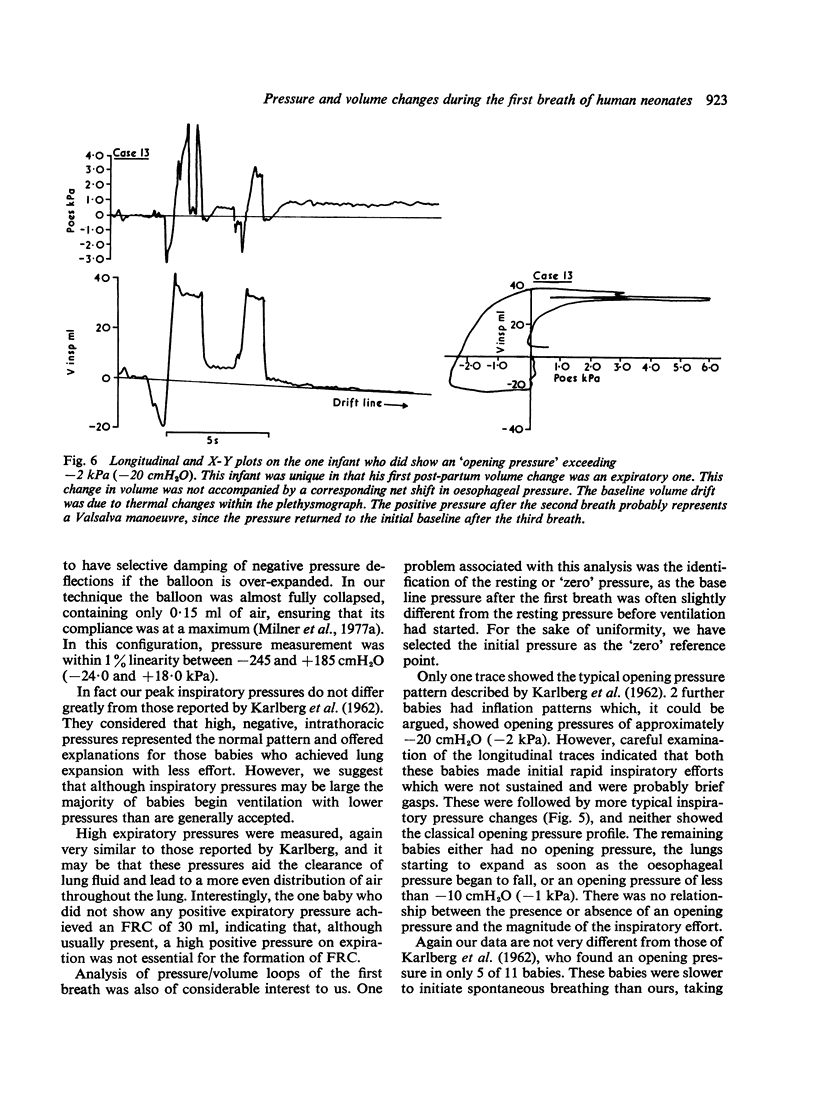

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AGOSTONI E. Volume-pressure relationships of the thorax and lung in the newborn. J Appl Physiol. 1959 Nov;14:909–913. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1959.14.6.909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AVERY M. E., FRANK N. R., GRIBETZ I. The inflationary force produced by pulmonary vascular distention in excised lungs; the possible relation of this force to that needed to inflate the lungs at birth. J Clin Invest. 1959 Mar;38(3):456–462. doi: 10.1172/JCI103821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AVERY M. E., MEAD J. Surface properties in relation to atelectasis and hyaline membrane disease. AMA J Dis Child. 1959 May;97(5 Pt 1):517–523. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1959.02070010519001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOK C. D., SUTHERLAND J. M., SEGAL S., CHERRY R. B., MEAD J., MCILROY M. B., SMITH C. A. Studies of respiratory physiology in the newborn infant. III. Measurements of mechanics of respiration. J Clin Invest. 1957 Mar;36(3):440–448. doi: 10.1172/JCI103441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWES G. S., MOTT J. C., WIDDICOMBE J. G., WYATT D. G. Changes in the lungs of the new-born lamb. J Physiol. 1953 Jul;121(1):141–162. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahms B. B., Krauss A. N., Auld P. A. Pulmonary function in dysmature infants. J Pediatr. 1974 Mar;84(3):434–437. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(74)80734-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enhörning G., Adams F. H., Norman A. Effect of lung expansion on the fetal lamb circulation. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1966 Sep;55(5):441–451. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1966.tb15234.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEUBELLE F., KARLBERG P., KOCH G., LIND J., WALLGREN G., WEGELIUS C. [Aeration of the lung in the newborn infant]. Biol Neonat. 1959 Oct;1:169–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRIBETZ I., FRANK N. R., AVERY M. E. Static volume-pressure relations of excised lungs of infants with hyaline membrane disease, newborn and stillborn infants. J Clin Invest. 1959 Dec;38:2168–2175. doi: 10.1172/JCI103996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRUENWOLD P. Normal and abnormal expansion of the lungs of newborn infants obtained at autopsy. III. Opening presure, maximal volume, and stability of expansion. Lab Invest. 1963 May;12:563–576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARLBERG P., KOCH G. Respiratory studies in newborn infants. III. Development of mechanics of breathing during the first week of life. A longitudinal study. Acta Paediatr Suppl. 1962 Jun;135:121–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1962.tb08666.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner A. D., Saunders R. A., Hopkin I. E. Effects of continuous distending pressure on lung volumes and lung mechanics in the immediate neonatal period. Biol Neonate. 1977;31(1-2):111–115. doi: 10.1159/000240950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen M., Laurence K. M. Expansion pressures and rupture pressures in the newborn lung. Lancet. 1965 Oct 9;2(7415):721–722. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)90458-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWYER P. R., REIMAN R. C., WRIGHT J. J. Ventilation and ventilatory mechanics in the newborn: methods and results in 15 resting infants. J Pediatr. 1960 May;56:612–622. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(60)80334-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders R. A., Milner A. D., Hopkin I. E. The effects of continuous positive airway pressure on lung mechanics and lung volumes in the neonate. Biol Neonate. 1976;29(3-4):178–186. doi: 10.1159/000240862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


