Abstract
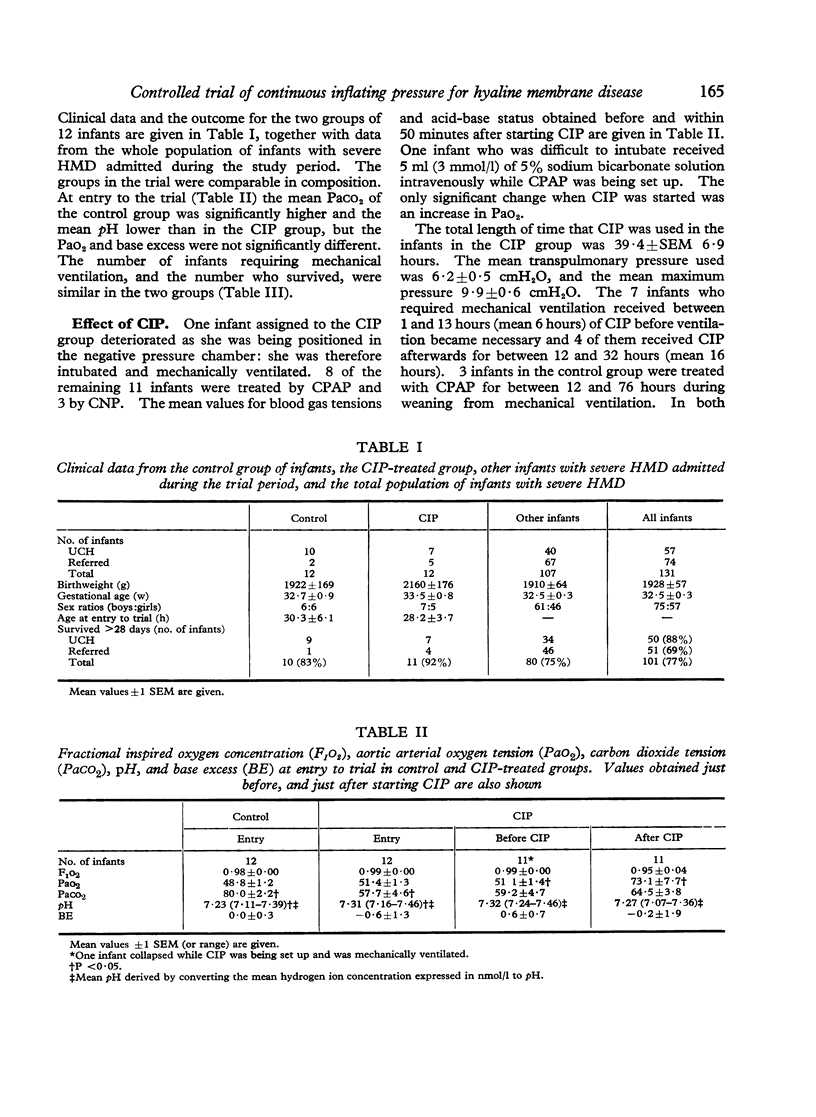
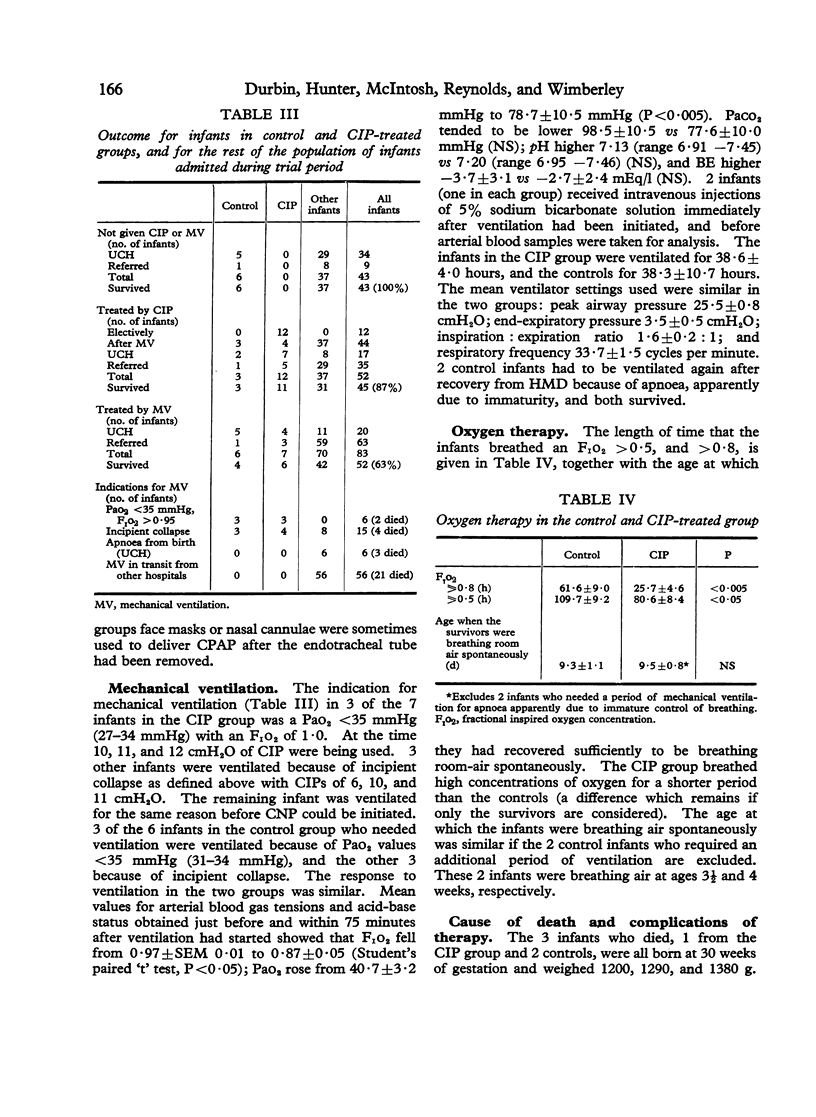
A controlled trial of elective intervention with continuous inflating pressure (CIP) was performed in infants with severe hyaline membrane disease who weighed more than 1000 g at birth. Infants entered the trial if their arterial oxygen tension (PaO2) fell below 60 mmHg while breathing a fractional inspired oxygen concentration (F1O2) greater than 0-95. 11 out of 12 infants in the CIP-treated group and 10 out of 12 in the control group survived. 7 treated and 6 control infants required mechanical ventilation. When CIP was started the Pao2 of the treated infants increased, and they breathed high concentrations of oxygen for a significantly shorter period than the control infants. During the 31-month duration of the trial 107 other infants with severe hyaline membrane disease were admitted who did not meet the criteria for entry to the trial. 37 survived after breathing high concentrations of oxygen (F1O2 greater than 0-60) spontaneously without any ventilatory assistance, and the remaining 70 infants were already being ventilated on their arrival in the unit, usually because they had required mechanical ventilation during transfer from other hospitals. The neonatal survival rate for those infants born in this hospital during the study period was 88% (50 out of 57 infants) and for those referred from other hospitals it was 69% (51 out of 74 infants). The maximum further increase in overall survival rate that might have been achieved in our population of infants if CIP had been initiated very early in the course of the illness was 5%--i.e. from 77% (101/131) to 82% (107/131).
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamson T. M., Hawker J. M., Reynolds E. O., Shaw J. L. Hypoxemia during recovery from severe hyaline membrane disease. Pediatrics. 1969 Aug;44(2):168–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrie H. Letter: Continuous positive airway pressure for respiratory-distress syndrome. Lancet. 1973 Oct 13;2(7833):851–851. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90898-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum J. D., Roberton N. R. Distending pressure in infants with respiratory distress syndrome. Arch Dis Child. 1974 Oct;49(10):771–781. doi: 10.1136/adc.49.10.771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake A. M., Durbin G. M., MacNab A. J., Collins L. M., Hunter N. J., Reynolds E. O., Sellens G. Simplified mechanical ventilation for hyaline-membrane disease. Lancet. 1973 Nov 24;2(7839):1176–1178. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92941-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caliumi-Pellegrini G., Agostino R., Orzalesi M., Nodari S., Marzetti G., Savignoni P. G., Bucci G. Twin nasal cannula for administration of continuous positive airway pressure to newborn infants. Arch Dis Child. 1974 Mar;49(3):228–230. doi: 10.1136/adc.49.3.228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chernick V. Hyaline-membrane disease: therapy with constant lung-distending pressure. N Engl J Med. 1973 Aug 9;289(6):302–304. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197308092890606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chernick V., Vidyasagar D. Continuous negative chest wall pressure in hyaline membrane disease: one year experience. Pediatrics. 1972 May;49(5):753–760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole V. A., Normand I. C., Reynolds E. O., Rivers R. P. Pathogenesis of hemorrhagic pulmonary edema and massive pulmonary hemorrhage in the newborn. Pediatrics. 1973 Feb;51(2):175–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumarasamy N., Nüssli R., Vischer D., Dangel P. H., Duc G. V. Artificial ventilation in hyaline membrane disease: the use of positive end-expiratory pressure and continuous positive airway pressure. Pediatrics. 1973 Apr;51(4):629–640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn P. M. Respiratory distress syndrome. Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) using the Gregory box. Proc R Soc Med. 1974 Apr;67(4):245–247. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanaroff A. A., Cha C. C., Sosa R., Crumrine R. S., Klaus M. H. Controlled trial of continuous negative external pressure in the treatment of severe respiratory distress syndrome. J Pediatr. 1973 Jun;82(6):921–928. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80418-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory G. A., Kitterman J. A., Phibbs R. H., Tooley W. H., Hamilton W. K. Treatment of the idiopathic respiratory-distress syndrome with continuous positive airway pressure. N Engl J Med. 1971 Jun 17;284(24):1333–1340. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197106172842401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman S., Reynolds E. O. Methods for improving oxygenation in infants mechanically ventilated for severe hyaline membrane disease. Arch Dis Child. 1973 Aug;48(8):612–617. doi: 10.1136/adc.48.8.612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kattwinkel J., Fleming D., Cha C. C., Fanaroff A. A., Klaus M. H. A device for administration of continuous positive airway pressure by the nasal route. Pediatrics. 1973 Jul;52(1):131–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds E. O. Indications for mechanical ventilation in infants with hyaline membrane disease. Pediatrics. 1970 Aug;46(2):193–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds E. O. Management of hyaline membrane disease. Br Med Bull. 1975 Jan;31(1):18–24. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds E. O. Pressure waveform and ventilator settings for mechanical ventilation in severe hyaline membrane disease. Int Anesthesiol Clin. 1974 Winter;12(4):259–280. doi: 10.1097/00004311-197412040-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds E. O., Taghizadeh A. Improved prognosis of infants mechanically ventilated for hyaline membrane disease. Arch Dis Child. 1974 Jul;49(7):505–515. doi: 10.1136/adc.49.7.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes P. G., Hall R. T. Continuous positive airway pressure delivered by face mask in infants with the idiopathic respiratory distress syndrome: a controlled study. Pediatrics. 1973 Jul;52(1):1–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


