Abstract
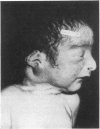
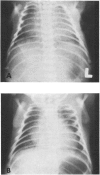
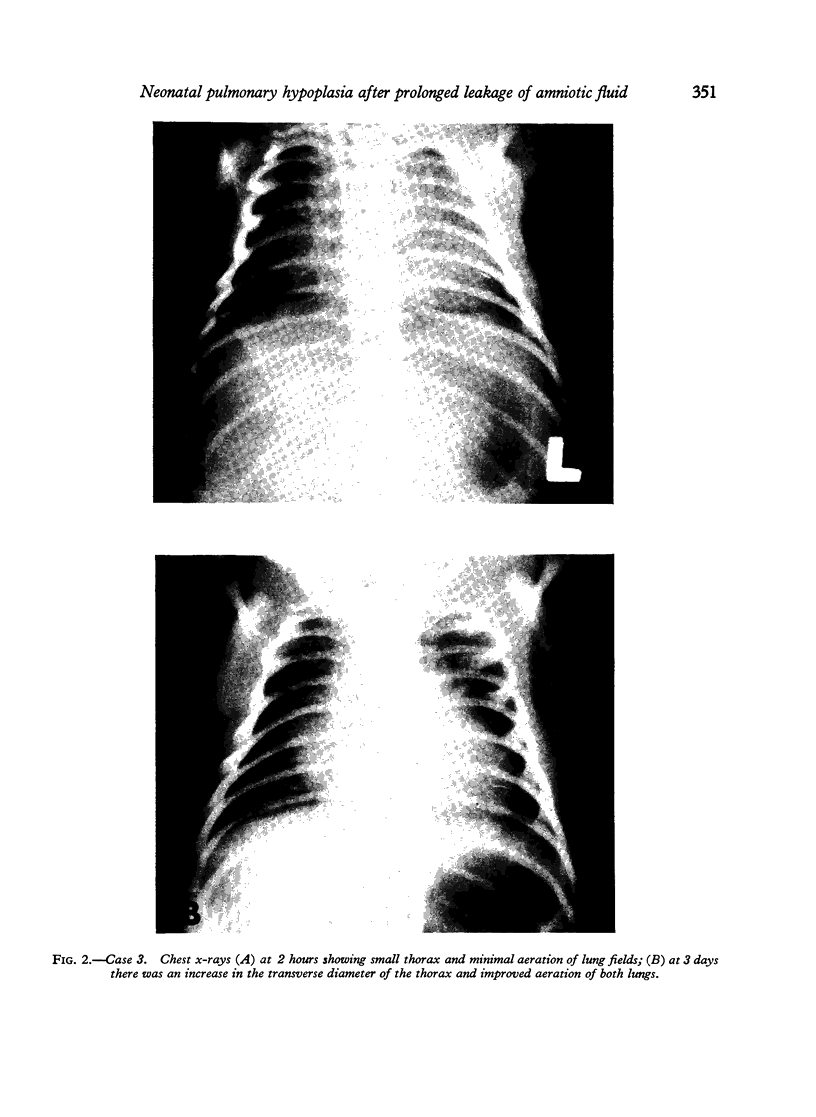
The clinical, radiological, and pathological features of the 'oligohydramnios tetrad' (Potter's facies, limb malpositions, pulmonary hypoplasia, and growth retardation) resulting from chronic amniotic fluid leakage are described in 2 infants who died of respiratory failure within 12 hours of delivery. A third infant with a partial form of the syndrome had prolonged respiratory symptoms and survived the neonatal period: the course of the disease and the radiological findings were compatible with a hypothetical diagnosis of partial pulmonary hypoplasia. Pulmonary hypoplasia should be recognized as a cause of chronic respiratory symptoms in viable infants.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAIN A. D., SMITH I. I., GAULD I. K. NEWBORN AFTER PROLONGED LEAKAGE OF LIQUOR AMNII. Br Med J. 1964 Sep 5;2(5409):598–599. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5409.598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLANC W. A., APPERSON J. W., McNALLY J. Pathology of the newborn and of the placenta in oligohydramnios. Bull Sloane Hosp Women Columbia Presbyt Med. 1962;8:51–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMyer W., Baird I. Mortality and skeletal malformations from amniocentesis and oligohydramnios in rats: cleft palate, clubfoot, microstomia, and adactyly. Teratology. 1969 Feb;2(1):33–37. doi: 10.1002/tera.1420020105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EMERY J. L., MITHAL A. The number of alveoli in the terminal respiratory unit of man during late intrauterine life and childhood. Arch Dis Child. 1960 Dec;35:544–547. doi: 10.1136/adc.35.184.544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finegold M. J., Katzew H., Genieser N. B., Becker M. H. Lung structure in thoracic dystrophy. Am J Dis Child. 1971 Aug;122(2):153–159. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1971.02110020087013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendrick F. J., Feild L. E. Congenital anomalies induced in normal and adrenalectomized rats by amniocentesis. Anat Rec. 1967 Dec;159(4):353–356. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091590403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler H. G., Peel K. R., Hoar R. A. Extramembraneous pregnancy and amniorrhoea. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Commonw. 1970 Sep;77(9):809–812. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1970.tb04404.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liberman M. M., Abraham J. M., France N. E. Association between pneumomediastinum and renal anomalies. Arch Dis Child. 1969 Aug;44(236):471–475. doi: 10.1136/adc.44.236.471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman M. Letter: More on the "oligohydraminios syndrome". J Pediatr. 1975 Mar;86(3):481–481. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(75)81000-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman M., Levin M. Fetal pulmonary hypoplasia, anuria, and oligohydramnios: clinicopathologic observations and review of the literature. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1974 Apr 15;118(8):1119–1123. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(74)90692-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reale F. R., Esterly J. R. Pulmonary hypoplasia: a morphometric study of the lungs of infants with diaphragmatic hernia, anencephaly, and renal malformations. Pediatrics. 1973 Jan;51(1):91–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simnett J. D. Stimulation of cell division following unilateral collapse of the lung. Anat Rec. 1974 Dec;180(4):681–686. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091800412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas I. T., Smith D. W. Oligohydramnios, cause of the nonrenal features of Potter's syndrome, including pulmonary hypoplasia. J Pediatr. 1974 Jun;84(6):811–815. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(74)80753-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]