Abstract
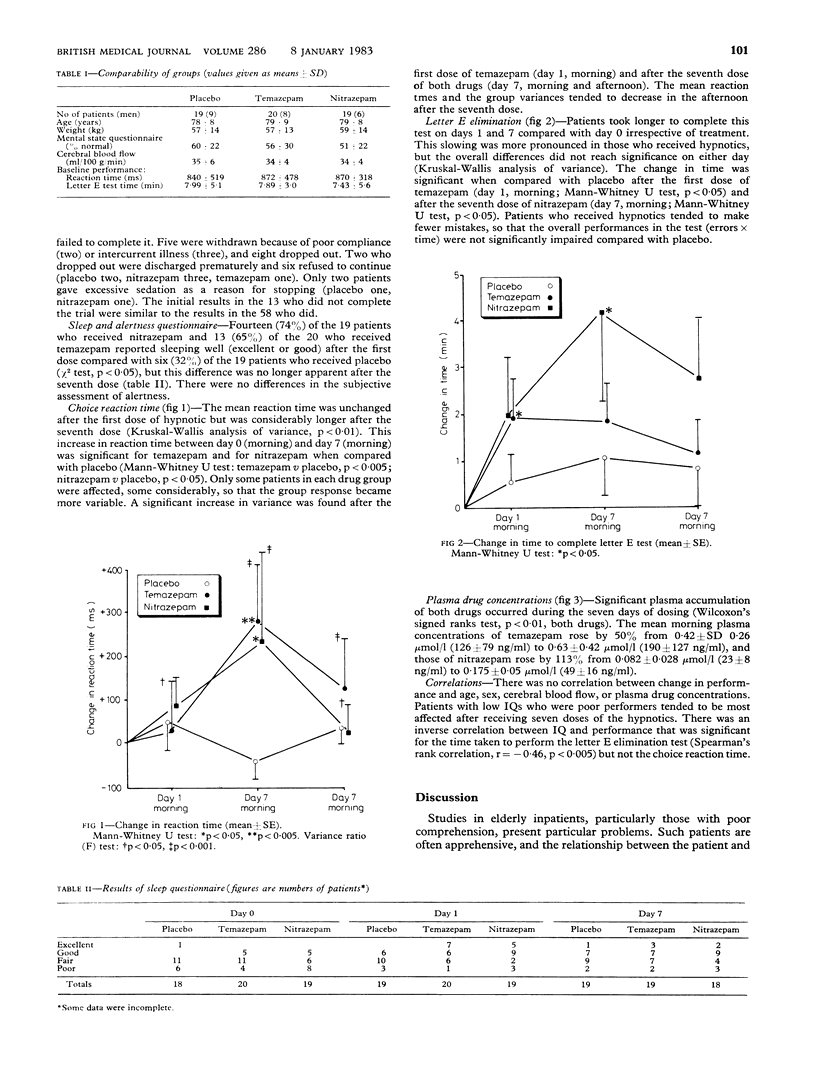
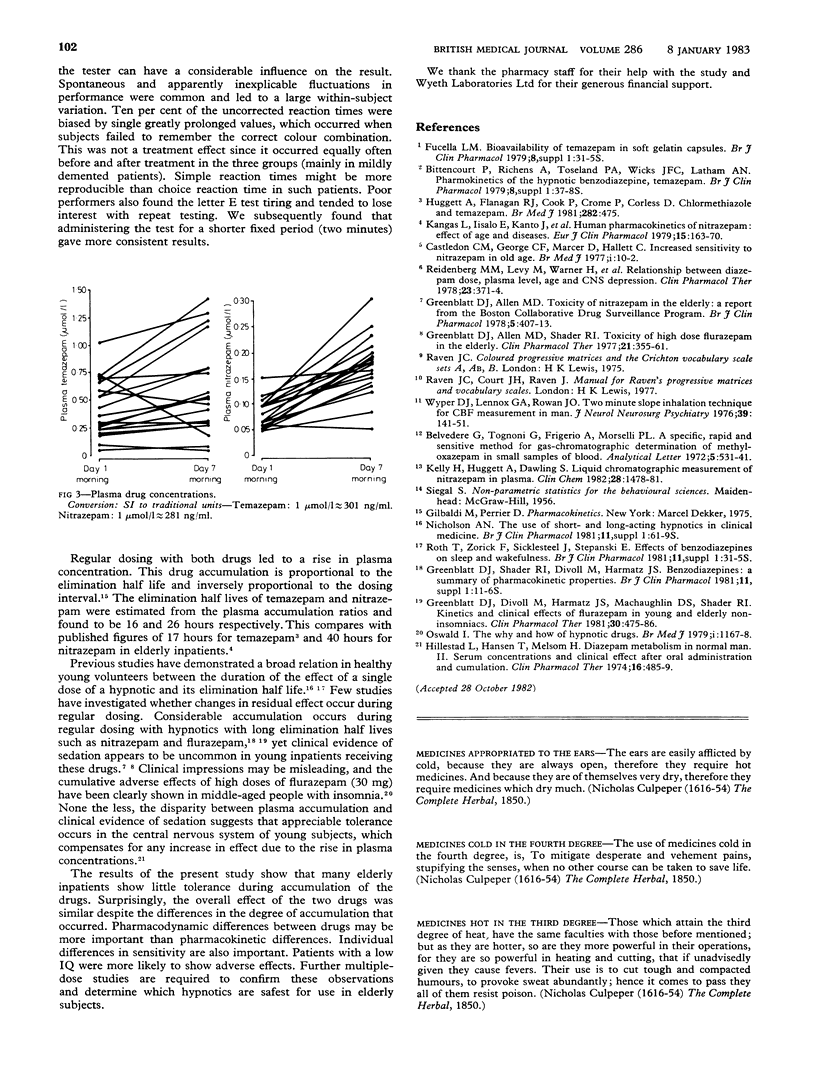
The hypnotic and residual sedative effects of the first and seventh of seven regular night-time doses of nitrazepam 5 mg, temazepam 20 mg, and placebo were studied in 58 elderly inpatients. Plasma temazepam and nitrazepam concentrations rose by about 50% and 113% respectively between the mornings of day 1 and day 7. Patients reported sleeping well more often after the first dose of either hypnotic (p less than 0.05), but there was no difference after the seventh dose. Reaction time was unchanged on the morning after the first dose but was significantly prolonged after the seventh dose of both hypnotics (p less than 0.01). The time taken to eliminate the letter E from a page of prose tended to be prolonged after the first dose of both drugs (temazepam v placebo, p less than 0.05; nitrazepam v placebo, not significant) and was further prolonged on the morning after the seventh dose of nitrazepam (nitrazepam v placebo, p less than 0.05). Thus plasma accumulation of the drug was associated with a deterioration in daytime performance. This change in performance did not correlate with age, cerebral blood flow, or plasma concentration, but patients of low intelligence tended to be more severely affected.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Castleden C. M., George C. F., Marcer D., Hallett C. Increased sensitivity to nitrazepam in old age. Br Med J. 1977 Jan 1;1(6052):10–12. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6052.10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt D. J., Allen M. D., Shader R. I. Toxicity of high-dose flurazepam in the elderly. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1977 Mar;21(3):355–361. doi: 10.1002/cpt1977213355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt D. J., Allen M. D. Toxicity of nitrazepam in the elderly: a report from the Boston Collaborative Drug Surveillance Program. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1978 May;5(5):407–413. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1978.tb01646.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt D. J., Divoll M., Harmatz J. S., MacLaughlin D. S., Shader R. I. Kinetics and clinical effects of flurazepam in young and elderly noninsomniacs. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1981 Oct;30(4):475–486. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1981.191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillestad L., Hansen T., Melsom H. Diazepam metabolism in normal man. II. Serum concentration and clinical effect after oral administration and cumulation. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1974 Sep;16(3):485–489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huggett A., Flanagan R. J., Cook P., Crome P., Corless D. Chlormethiazole and temazepam. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Feb 7;282(6262):475–475. doi: 10.1136/bmj.282.6262.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kangas L., Iisalo E., Kanto J., Lehtinen V., Pynnönen S., Ruikka I., Salminen J., Sillanpä M., Syvälahti E. Human pharmacokinetics of nitrazepam: effect of age and diseases. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1979 Apr 17;15(3):163–170. doi: 10.1007/BF00563100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly H., Huggett A., Dawling S. Liquid-chromatographic measurement of nitrazepam in plasma. Clin Chem. 1982 Jul;28(7):1478–1481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oswald I. The why and how of hypnotic drugs. Br Med J. 1979 May 5;1(6172):1167–1168. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6172.1167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reidenberg M. M., Levy M., Warner H., Coutinho C. B., Schwartz M. A., Yu G., Cheripko J. Relationship between diazepam dose, plasma level, age, and central nervous system depression. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1978 Apr;23(4):371–374. doi: 10.1002/cpt1978234371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyper D. J., Lennox G. A., Rowan J. O. Two minute slope inhalation technique for cerebral blood flow measurement in man. 1. Method. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1976 Feb;39(2):141–146. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.39.2.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


