Abstract
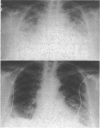
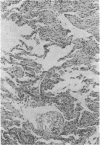
Amiodarone was administered to 80 patients with recurrent cardiac tachyarrhythmias previously resistant to drug treatment. Forty nine patients were treated for ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation and 31 for supra-ventricular arrhythmias. The mean (range six days to 51 months), permitting a total of 100 patient years of observation. Adverse reactions were observed in 69 patients. Severe side effects were encountered in 13: four patients developed interstitial pneumonitis, four patients developed incessant ventricular tachycardia, three patients taking amiodarone and digoxin sustained sinus node arrest with depression of escape foci, one patient developed hepatitis, and one patient developed hypercalcaemia with renal failure. Furthermore, a rise in the serum concentration of digoxin and potentiation of warfarin anticoagulation occurred in cases in which these agents were combined with amiodarone. Amiodarone was stopped in 14 patients because of side effects. Although amiodarone is effective in suppressing arrhythmias in most patients in whom extensive use of antiarrhythmic drugs has been unsuccessful, it is associated with diverse and serious toxicity. These observations suggest that at present the use of amiodarone should be reserved for patients with life threatening or seriously disabling arrhythmias in whom longer established drugs have been ineffective or are contraindicated.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alboni P., Fischer D. M. Blocco seno-atriale in corso di terapia con amiodarone. G Ital Cardiol. 1973;3(2):288–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bashour T., Jokhadar M., Cheng T. O. Effective management of the long q-t syndrome with amiodarone. Chest. 1981 Jun;79(6):704–706. doi: 10.1378/chest.79.6.704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodine W. N., DeSantis J. Sinus arrest during treatment with amiodarone. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Oct 9;285(6347):1047–1047. doi: 10.1136/bmj.285.6347.1047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. K., Primhak R. A., Newton P. Use of amiodarone in bradycardia-tachycardia syndrome. Br Heart J. 1978 Oct;40(10):1149–1152. doi: 10.1136/hrt.40.10.1149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Amico D. J., Kenyon K. R., Ruskin J. N. Amiodarone keratopathy: drug-induced lipid storage disease. Arch Ophthalmol. 1981 Feb;99(2):257–261. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1981.03930010259007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamer A., Peter T., Mandel W. J., Scheinman M. M., Weiss D. The potentiation of warfarin anticoagulation by amiodarone. Circulation. 1982 May;65(5):1025–1029. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.65.5.1025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heger J. J., Prystowsky E. N., Jackman W. M., Naccarelli G. V., Warfel K. A., Rinkenberger R. L., Zipes D. P. Clinical efficacy and electrophysiology during long-term therapy for recurrent ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 1981 Sep 3;305(10):539–545. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198109033051002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaski J. C., Girotti L. A., Messuti H., Rutitzky B., Rosenbaum M. B. Long-term management of sustained, recurrent, symptomatic ventricular tachycardia with amiodarone. Circulation. 1981 Aug;64(2):273–279. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.64.2.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchlinski F. E., Gansler T. S., Waxman H. L., Josephson M. E. Amiodarone pulmonary toxicity. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Dec;97(6):839–845. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-6-839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus F. I., Fontaine G. H., Frank R., Grosgogeat Y. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutic applications of the antiarrhythmic agent amiodarone. Am Heart J. 1981 Apr;101(4):480–493. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(81)90140-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McComb J. M., Logan K. R., Khan M. M., Geddes J. S., Adgey A. A. Amiodarone-induced ventricular fibrillation. Eur J Cardiol. 1980;11(5):381–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGovern B., Garan H., Ruskin J. N. Sinus arrest during treatment with amiodarone. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Jan 16;284(6310):160–161. doi: 10.1136/bmj.284.6310.160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier C., Kauer B., Müller U., Ludin H. P. Neuromyopathy during chronic amiodarone treatment. A case report. J Neurol. 1979 Jan 5;220(4):231–239. doi: 10.1007/BF00314147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melmed S., Nademanee K., Reed A. W., Hendrickson J. A., Singh B. N., Hershman J. M. Hyperthyroxinemia with bradycardia and normal thyrotropin secretion after chronic amiodarone administration. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Nov;53(5):997–1001. doi: 10.1210/jcem-53-5-997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moysey J. O., Jaggarao N. S., Grundy E. N., Chamberlain D. A. Amiodarone increases plasma digoxin concentrations. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Jan 24;282(6260):272–272. doi: 10.1136/bmj.282.6260.272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nademanee K., Hendrickson J. A., Cannom D. S., Goldreyer B. N., Singh B. N. Control of refractory life-threatening ventricular tachyarrhythmias by amiodarone. Am Heart J. 1981 Jun;101(6):759–768. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(81)90613-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petty T. L. Editorial: What else can injure the lungs? N Engl J Med. 1976 Apr 22;294(17):954–954. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197604222941714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees A., Dalal J. J., Reid P. G., Henderson A. H., Lewis M. J. Dangers of amiodarone and anticoagulant treatment. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 May 30;282(6278):1756–1757. doi: 10.1136/bmj.282.6278.1756-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley S. A., Williams S. E., Cooke N. J. Alveolitis after treatment with amiodarone. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Jan 16;284(6310):161–162. doi: 10.1136/bmj.284.6310.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotmensch H. H., Liron M., Tupilski M., Laniado S. Possible association of pneumonitis with amiodarone therapy. Am Heart J. 1980 Sep;100(3):412–413. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(80)90165-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. W., Haber E. Digoxin intoxication: the relationship of clinical presentation to serum digoxin concentration. J Clin Invest. 1970 Dec;49(12):2377–2386. doi: 10.1172/JCI106457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobol S. M., Rakita L. Pneumonitis and pulmonary fibrosis associated with amiodarone treatment: a possible complication of a new antiarrhythmic drug. Circulation. 1982 Apr;65(4):819–824. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.65.4.819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartini R., Kappenberger L., Steinbrunn W., Meyer U. A. Dangerous interaction between amiodarone and quinidine. Lancet. 1982 Jun 12;1(8285):1327–1329. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92400-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veglia L., Scandiffio T., Guerricchio G. "Torsioni di punta" e amiodarone. G Ital Cardiol. 1978;8(9):1025–1029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velebit V., Podrid P., Lown B., Cohen B. H., Graboys T. B. Aggravation and provocation of ventricular arrhythmias by antiarrhythmic drugs. Circulation. 1982 May;65(5):886–894. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.65.5.886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vos A. K., van Ramshorst A. G., Grosfeld J. C., Goossens J. P. A peculiar cutaneous pigmentation from cordarone. Dermatologica. 1972;145(5):297–303. doi: 10.1159/000252057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westveer D. C., Gadowski G. A., Gordon S., Timmis G. C. Amiodarone-induced ventricular tachycardia. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Oct;97(4):561–562. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-4-561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright A. J., Brackenridge R. G. Pulmonary infiltration and bone marrow depression complicating treatment with amiodarone. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 May 1;284(6325):1303–1303. doi: 10.1136/bmj.284.6325.1303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]