Abstract
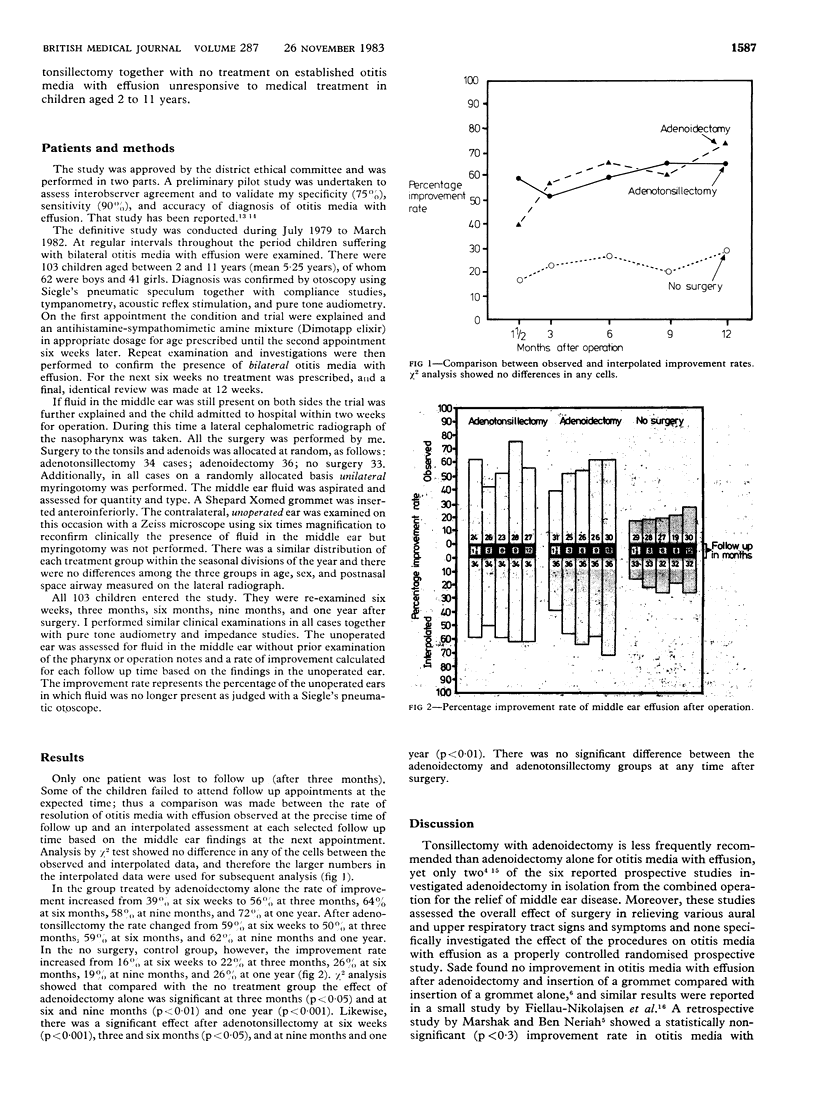
A prospective study was conducted of the effects of adenoidectomy and adenotonsillectomy on established otitis media with effusion unresponsive to medical treatment. The operations were performed at random with a controlled no surgery group on a cohort of 103 children with the condition and the results assessed six weeks, three months, six months, nine months, and one year later. After adenoidectomy the rate of resolution of the condition increased from 39% at six weeks to 72% at one year; and after adenotonsillectomy the rate increased from 59% at six weeks to 62% at one year. In the no surgery group the rate increased from 16% at six weeks to 26% at one year. Compared with the no surgery group the effect of adenoidectomy alone at one year was highly significant (p less than 0.001), and similarly the effect of adenotonsillectomy was significant (p less than 0.01). There was, however, no increased benefit from the addition of tonsillectomy compared with adenoidectomy alone. Thus there was resolution of 36-46% of chronic effusions as a result of adenoidectomy.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BATEMAN G. H. Secretory otitis media. J Laryngol Otol. 1957 Apr;71(4):261-70; discussion, 289-93. doi: 10.1017/s002221510005177x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birck H. G., Mravec J. J. Myringostomy for middle ear effusions. Results of a two-year study. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1976 Mar-Apr;85(2 Suppl 25 Pt 2):263–267. doi: 10.1177/00034894760850S249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bluestone C. D., Cantekin E. I., Beery Q. C. Certain effects of adenoidectomy of Eustachian tube ventilatory function. Laryngoscope. 1975 Jan;85(1):113–127. doi: 10.1288/00005537-197501000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawes J. D. The aetiology and sequelae of exudative otitis media. J Laryngol Otol. 1970 Jun;84(6):583–610. doi: 10.1017/s0022215100072297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiellau-Nikolajsen M., Falbe-Hansen J., Knudstrup P. Adenoidectomy for middle ear disorders: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci. 1980 Oct;5(5):323–327. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2273.1980.tb00898.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerwat J. The structure and function of the nasopharyngeal lymphoid tissue with special reference to the aetiology of secretory otitis. J Laryngol Otol. 1975 Feb;89(2):169–174. doi: 10.1017/s0022215100080221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschalk G. H. Serous otitis. A conservative approach to treatment. Arch Otolaryngol. 1972 Aug;96(2):110–112. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1972.00770090184003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbert J., Stell P. M. The role of enlarged adenoids in the aetiology of serous otitis media. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci. 1982 Aug;7(4):253–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2273.1982.tb01392.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeans W. D., Fernando D. C., Maw A. R., Leighton B. C. A longitudinal study of the growth of the nasopharynx and its contents in normal children. Br J Radiol. 1981 Feb;54(638):117–121. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-54-638-117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCKEE W. J. THE PART PLAYED BY ADENOIDECTOMY IN THE COMBINED OPERATION OF TONSILLECTOMY WITH ADENOIDECTOMY. SECOND PART OF A CONTROLLED STUDY IN CHILDREN. Br J Prev Soc Med. 1963 Jul;17:133–140. doi: 10.1136/jech.17.3.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshak G., Neriah Z. B. Adenoidectomy versus tympanostomy in chronic secretory otitis media. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Suppl. 1980 May-Jun;89(3 Pt 2):316–318. doi: 10.1177/00034894800890s374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maw A. R., Jeans W. D., Cable H. R. Adenoidectomy. A prospective study to show clinical and radiological changes two years after operation. J Laryngol Otol. 1983 Jun;97(6):511–518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maw A. R., Jeans W. D., Fernando D. C. Inter-observer variability in the clinical and radiological assessment of adenoid size, and the correlation with adenoid volume. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci. 1981 Oct;6(5):317–322. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2273.1981.tb01805.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mawson S. R., Adlington P., Evans M. A controlled study evaluation of adeno-tonsillectomy in children. J Laryngol Otol. 1967 Jul;81(7):777–790. doi: 10.1017/s0022215100067694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mawson S. R., Brennand J. Long-term follow up of 129 glue ears. Proc R Soc Med. 1969 May;62(5):460–464. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paradise J. L., Bluestone C. D., Rogers K. D., Taylor F. H. Efficacy of adenoidectomy in recurrent otitis media. Historical overview and preliminary results from a randomized, controlled trial. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Suppl. 1980 May-Jun;89(3 Pt 2):319–321. doi: 10.1177/00034894800890s375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roydhouse N. Adenoidectomy for otitis media with mucoid effusion. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Suppl. 1980 May-Jun;89(3 Pt 2):312–315. doi: 10.1177/00034894800890s373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rynnel-Dagö B., Ahlbom A., Schiratzki H. Effects of adenoidectomy: a controlled two-year follow-up. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1978 Mar-Apr;87(2 Pt 1):272–278. doi: 10.1177/000348947808700223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


