Abstract
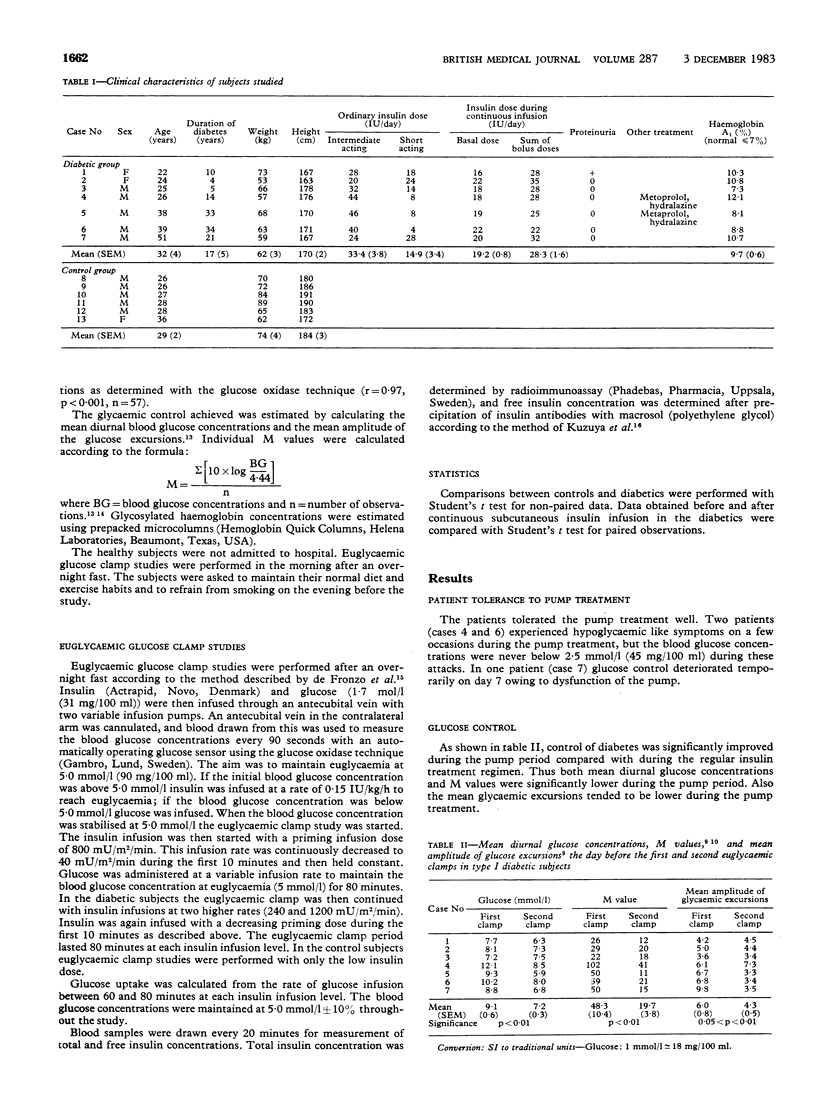
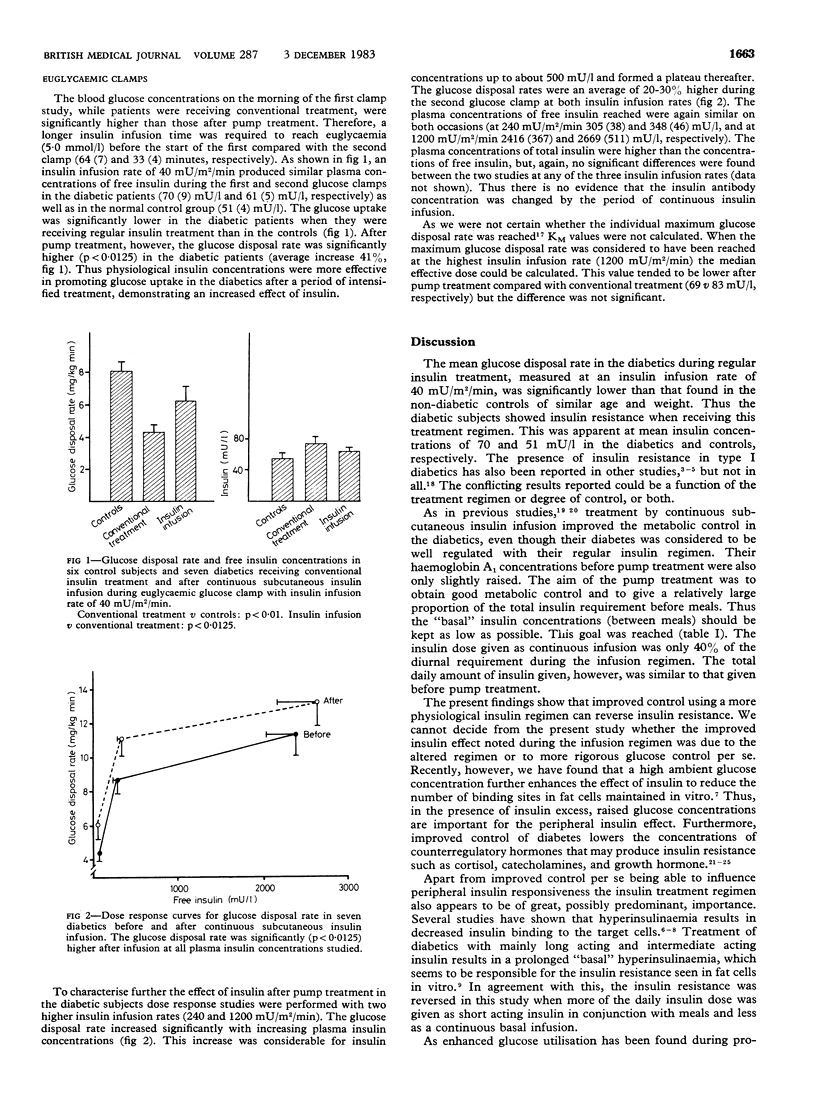
Insulin responsiveness was studied with the euglycaemic glucose clamp technique in seven patients with type I diabetes and in six control subjects matched for age and weight. The glucose disposal rate was significantly reduced in the diabetic subjects when they were receiving conventional insulin treatment compared with the control group, showing insulin resistance in the diabetics. The diabetic patients were again studied after eight days of intensified metabolic control achieved with continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion. During the infusion a more physiological insulin regimen was used compared with their regular treatment, less of the total insulin dose being given as continuous infusion and more as bolus doses before meals. The insulin resistance in the diabetics was largely reversed after this improved metabolic control. Dose response studies showed an increased glucose disposal rate at all plasma insulin concentrations, including the maximum insulin concentration, indicating a predominant effect of the continuous infusion regimen at the postreceptor level. The improved insulin effect seen with continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion could be due to the improved metabolic control achieved as well as the more physiological regimen.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amatruda J. M., Newmeyer H. W., Chang C. L. Insulin-induced alterations in insulin binding and insulin action in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes. Diabetes. 1982 Feb;31(2):145–148. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.2.145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cigolini M., Smith U. Human adipose tissue in culture. VIII. Studies on the insulin-antagonistic effect of glucocorticoids. Metabolism. 1979 May;28(5):502–510. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(79)90189-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Hendler R., Simonson D. Insulin resistance is a prominent feature of insulin-dependent diabetes. Diabetes. 1982 Sep;31(9):795–801. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.9.795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Tobin J. D., Andres R. Glucose clamp technique: a method for quantifying insulin secretion and resistance. Am J Physiol. 1979 Sep;237(3):E214–E223. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.237.3.E214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deibert D. C., DeFronzo R. A. Epinephrine-induced insulin resistance in man. J Clin Invest. 1980 Mar;65(3):717–721. doi: 10.1172/JCI109718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doberne L., Greenfield M. S., Schulz B., Reaven G. M. Enhanced glucose utilization during prolonged glucose clamp studies. Diabetes. 1981 Oct;30(10):829–835. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.10.829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavin J. R., 3rd, Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr, de Meyts P., Buell D. N. Insulin-dependent regulation of insulin receptor concentrations: a direct demonstration in cell culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):84–88. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg H. N. Investigation of insulin sensitivity in treated subjects with ketosis-prone diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1977 Apr;26(4):278–283. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.4.278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harano Y., Ohgaku S., Hidaka H., Haneda K., Kikkawa R., Shigeta Y., Abe H. Glucose, insulin and somatostatin infusion for the determination of insulin sensitivity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1977 Nov;45(5):1124–1127. doi: 10.1210/jcem-45-5-1124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison L. C., Martin F. I., Melick R. A. Correlation between insulin receptor binding in isolated fat cells and insulin sensitivity in obese human subjects. J Clin Invest. 1976 Dec;58(6):1435–1441. doi: 10.1172/JCI108599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hockaday T. D. Diabetic maculopathy. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Mar 19;286(6369):915–916. doi: 10.1136/bmj.286.6369.915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R. Insulin resistance, insulin insensitivity, and insulin unresponsiveness: a necessary distinction. Metabolism. 1978 Dec;27(12 Suppl 2):1893–1902. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(78)80007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolterman O. G., Insel J., Saekow M., Olefsky J. M. Mechanisms of insulin resistance in human obesity: evidence for receptor and postreceptor defects. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jun;65(6):1272–1284. doi: 10.1172/JCI109790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kono T., Barham F. W. The relationship between the insulin-binding capacity of fat cells and the cellular response to insulin. Studies with intact and trypsin-treated fat cells. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6210–6216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konturek S. J., Tasler J., Obtulowicz W., Coy D. H., Schally A. V. Effect of growth hormone-release inhibiting hormone on hormones stimulating exocrine pancreatic secretion. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jul;58(1):1–6. doi: 10.1172/JCI108438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuzuya H., Blix P. M., Horwitz D. L., Steiner D. F., Rubenstein A. H. Determination of free and total insulin and C-peptide in insulin-treated diabetics. Diabetes. 1977 Jan;26(1):22–29. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.1.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lönnroth P., DiGirolamo M., Smith U. Influence of ambient glucose and insulin concentrations on adipocyte insulin binding. Metabolism. 1983 Jun;32(6):609–614. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(83)90032-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lönnroth P., Smith U. beta-Adrenergic dependent downregulation of insulin binding in rat adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 May 16;112(3):972–979. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91713-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maneschi F., Mashiter K., Kohner E. M. Insulin resistance and insulin deficiency in diabetic retinopathy of non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Diabetes. 1983 Jan;32(1):82–87. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.1.82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mecklenburg R. S., Benson J. W., Jr, Becker N. M., Brazel P. L., Fredlund P. N., Metz R. J., Nielsen R. L., Sannar C. A., Steenrod W. J., Jr Clinical use of the insulin infusion pump in 100 patients with type I diabetes. N Engl J Med. 1982 Aug 26;307(9):513–518. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198208263070901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M., Saekow M. The effects of dietary carbohydrate content on insulin binding and glucose metabolism by isolated rat adipocytes. Endocrinology. 1978 Dec;103(6):2252–2263. doi: 10.1210/endo-103-6-2252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen O., Beck-Nielsen H., Heding L. Increased insulin receptors after exercise in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1980 Apr 17;302(16):886–892. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198004173021603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen O., Hjøllund E. Insulin receptor binding to fat and blood cells and insulin action in fat cells from insulin-dependent diabetics. Diabetes. 1982 Aug;31(8 Pt 1):706–715. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.8.706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickup J. C., Keen H., Parsons J. A., Alberti K. G., Rowe A. S. Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion: improved blood-glucose and intermediary-metabolite control in diabetics. Lancet. 1979 Jun 16;1(8129):1255–1257. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)92225-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizza R. A., Mandarino L. J., Gerich J. E. Cortisol-induced insulin resistance in man: impaired suppression of glucose production and stimulation of glucose utilization due to a postreceptor detect of insulin action. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Jan;54(1):131–138. doi: 10.1210/jcem-54-1-131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizza R. A., Mandarino L. J., Gerich J. E. Effects of growth hormone on insulin action in man. Mechanisms of insulin resistance, impaired suppression of glucose production, and impaired stimulation of glucose utilization. Diabetes. 1982 Aug;31(8 Pt 1):663–669. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.8.663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHLICHTKRULL J., MUNCK O., JERSILD M. THE M-VALVE, AN INDEX OF BLOOD-SUGAR CONTROL IN DIABETICS. Acta Med Scand. 1965 Jan;177:95–102. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1965.tb01810.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Service F. J., Molnar G. D., Rosevear J. W., Ackerman E., Gatewood L. C., Taylor W. F. Mean amplitude of glycemic excursions, a measure of diabetic instability. Diabetes. 1970 Sep;19(9):644–655. doi: 10.2337/diab.19.9.644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamborlane W. V., Sherwin R. S., Genel M., Felig P. Restoration of normal lipid and aminoacid metabolism in diabetic patients treated with a portable insulin-infusion pump. Lancet. 1979 Jun 16;1(8129):1258–1261. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)92226-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


