Abstract
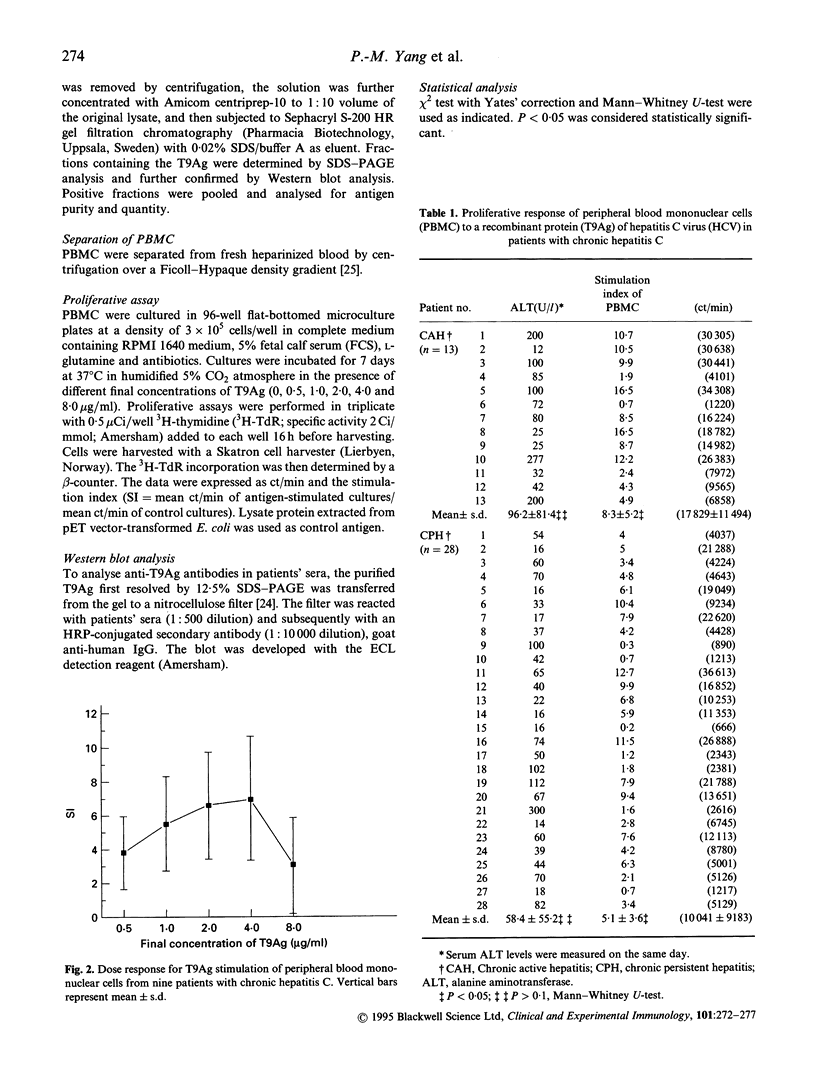
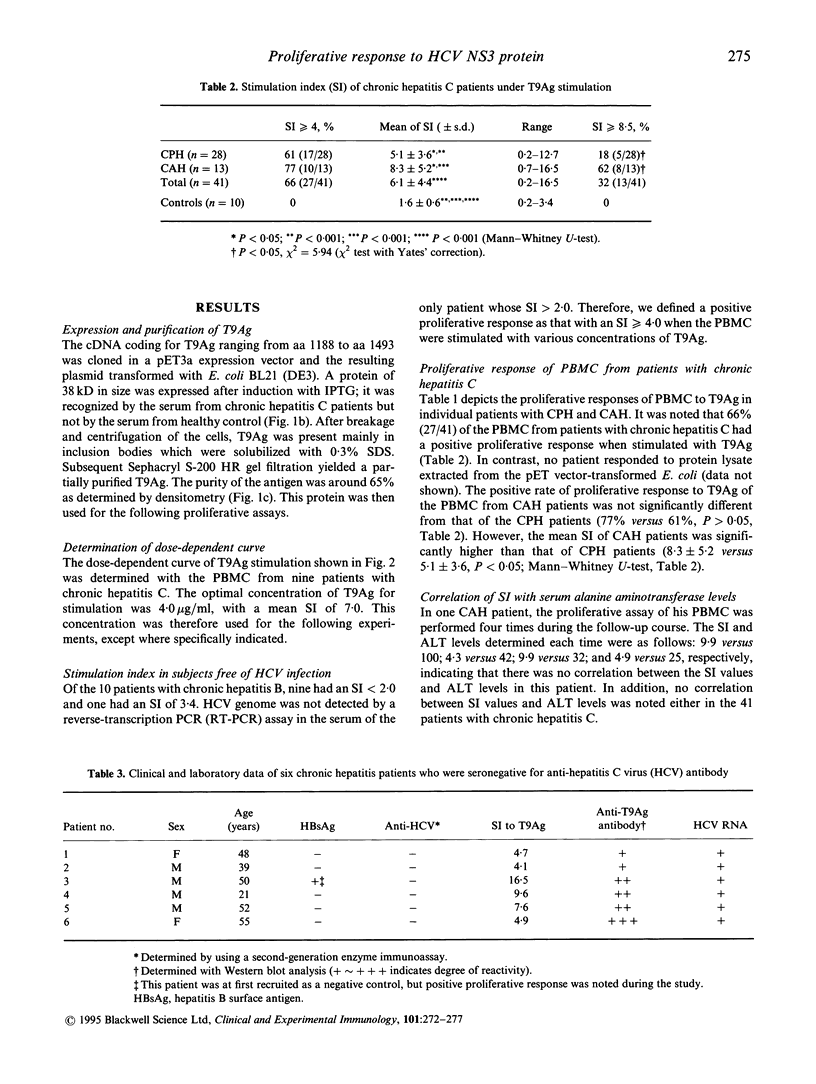
The proliferative response of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) to a recombinant non-structural (NS3) protein of hepatitis C virus (HCV) was studied in 41 patients with chronic hepatitis C. Of them, 28 had chronic persistent hepatitis (CPH) and 13 chronic active hepatitis (CAH). The positive proliferation rate of PBMC to the recombinant NS3 protein, T9Ag, was 66% in the 41 patients (77% in CAH versus 61% in CPH; P > 0.05) when stimulation index (SI) = 4 was set as the cut-off value. However, mean SI of CAH patients was significantly higher than that of CPH patients (8.3 +/- 5.2 versus 5.1 +/- 3.6; P < 0.05). Six other chronic hepatitis patients who were repeatedly negative for anti-HCV antibody but positive for serum HCV RNA also had an SI of > or = 4.0. The frequency of cellular immune response to the T9Ag is among the highest results obtained by using HCV antigens tested so far. Our studies thus indicate that NS3 is an immunologically important region of HCV for T cells. Moreover, the proliferative response to T9Ag may help to establish hepatitis C etiology in chronic hepatitis patients who are seronegative with currently available anti-HCV assays.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberti A. Diagnosis of hepatitis C. Facts and perspectives. J Hepatol. 1991 May;12(3):279–282. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(91)90827-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alter H. J., Purcell R. H., Shih J. W., Melpolder J. C., Houghton M., Choo Q. L., Kuo G. Detection of antibody to hepatitis C virus in prospectively followed transfusion recipients with acute and chronic non-A, non-B hepatitis. N Engl J Med. 1989 Nov 30;321(22):1494–1500. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198911303212202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alter H. J. The hepatitis C virus and its relationship to the clinical spectrum of NANB hepatitis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1990;5 (Suppl 1):78–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.1990.tb01783.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bortolotti F., Tagger A., Cadrobbi P., Crivellaro C., Pregliasco F., Ribero M. L., Alberti A. Antibodies to hepatitis C virus in community-acquired acute non-A, non-B hepatitis. J Hepatol. 1991 Mar;12(2):176–180. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(91)90935-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botarelli P., Brunetto M. R., Minutello M. A., Calvo P., Unutmaz D., Weiner A. J., Choo Q. L., Shuster J. R., Kuo G., Bonino F. T-lymphocyte response to hepatitis C virus in different clinical courses of infection. Gastroenterology. 1993 Feb;104(2):580–587. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90430-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen D. S., Kuo G. C., Sung J. L., Lai M. Y., Sheu J. C., Chen P. J., Yang P. M., Hsu H. M., Chang M. H., Chen C. J. Hepatitis C virus infection in an area hyperendemic for hepatitis B and chronic liver disease: the Taiwan experience. J Infect Dis. 1990 Oct;162(4):817–822. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.4.817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. J., Lin M. H., Tai K. F., Liu P. C., Lin C. J., Chen D. S. The Taiwanese hepatitis C virus genome: sequence determination and mapping the 5' termini of viral genomic and antigenomic RNA. Virology. 1992 May;188(1):102–113. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90739-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dienes H. P., Hütteroth T., Hess G., Meuer S. C. Immunoelectron microscopic observations on the inflammatory infiltrates and HLA antigens in hepatitis B and non-A, non-B. Hepatology. 1987 Nov-Dec;7(6):1317–1325. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840070623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari C., Valli A., Galati L., Penna A., Scaccaglia P., Giuberti T., Schianchi C., Missale G., Marin M. G., Fiaccadori F. T-cell response to structural and nonstructural hepatitis C virus antigens in persistent and self-limited hepatitis C virus infections. Hepatology. 1994 Feb;19(2):286–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genesca J., Esteban J. I., Alter H. J. Blood-borne non-A, non-B hepatitis: hepatitis C. Semin Liver Dis. 1991 May;11(2):147–164. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1040432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung M. C., Spengler U., Schraut W., Hoffmann R., Zachoval R., Eisenburg J., Eichenlaub D., Riethmüller G., Paumgartner G., Ziegler-Heitbrock H. W. Hepatitis B virus antigen-specific T-cell activation in patients with acute and chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol. 1991 Nov;13(3):310–317. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(91)90074-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao J. H., Chen P. J., Lai M. Y., Yang P. M., Sheu J. C., Wang T. H., Chen D. S. Mixed infections of hepatitis C virus as a factor in acute exacerbations of chronic type C hepatitis. J Infect Dis. 1994 Nov;170(5):1128–1133. doi: 10.1093/infdis/170.5.1128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koskinas J., McFarlane B. M., Nouri-Aria K. T., Tibbs C. J., Mizokami M., Donaldson P. T., McFarlane I. G., Williams R. Cellular and humoral immune reactions against autoantigens and hepatitis C viral antigens in chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology. 1994 Nov;107(5):1436–1442. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90547-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koziel M. J., Dudley D., Afdhal N., Choo Q. L., Houghton M., Ralston R., Walker B. D. Hepatitis C virus (HCV)-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes recognize epitopes in the core and envelope proteins of HCV. J Virol. 1993 Dec;67(12):7522–7532. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.12.7522-7532.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo G., Choo Q. L., Alter H. J., Gitnick G. L., Redeker A. G., Purcell R. H., Miyamura T., Dienstag J. L., Alter M. J., Stevens C. E. An assay for circulating antibodies to a major etiologic virus of human non-A, non-B hepatitis. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):362–364. doi: 10.1126/science.2496467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosley J. W., Aach R. D., Hollinger F. B., Stevens C. E., Barbosa L. H., Nemo G. J., Holland P. V., Bancroft W. H., Zimmerman H. J., Kuo G. Non-A, non-B hepatitis and antibody to hepatitis C virus. JAMA. 1990 Jan 5;263(1):77–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakatsuji Y., Matsumoto A., Tanaka E., Ogata H., Kiyosawa K. Detection of chronic hepatitis C virus infection by four diagnostic systems: first-generation and second-generation enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, second-generation recombinant immunoblot assay and nested polymerase chain reaction analysis. Hepatology. 1992 Aug;16(2):300–305. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840160204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schupper H., Hayashi P., Scheffel J., Aceituno S., Paglieroni T., Holland P. V., Zeldis J. B. Peripheral-blood mononuclear cell responses to recombinant hepatitis C virus antigens in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 1993 Nov;18(5):1055–1060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. L., Chen P. J., Hwang L. H., Kao J. H., Huang J. H., Chang T. H., Chen D. S. Immune response to a hepatitis C virus nonstructural protein in chronic hepatitis C virus infection. J Hepatol. 1994 Sep;21(3):403–411. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(05)80320-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. L., Chen P. J., Lai M. Y., Yang P. M., Sung J. L., Huang J. H., Hwang L. H., Chang T. H., Chen D. S. Acute exacerbations of chronic type B hepatitis are accompanied by increased T cell responses to hepatitis B core and e antigens. Implications for hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jan;89(1):87–96. doi: 10.1172/JCI115590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. J., Geysen H. M., Christopherson C., Hall J. E., Mason T. J., Saracco G., Bonino F., Crawford K., Marion C. D., Crawford K. A. Evidence for immune selection of hepatitis C virus (HCV) putative envelope glycoprotein variants: potential role in chronic HCV infections. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3468–3472. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]