Abstract
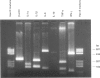
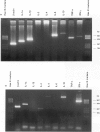
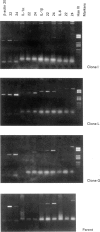
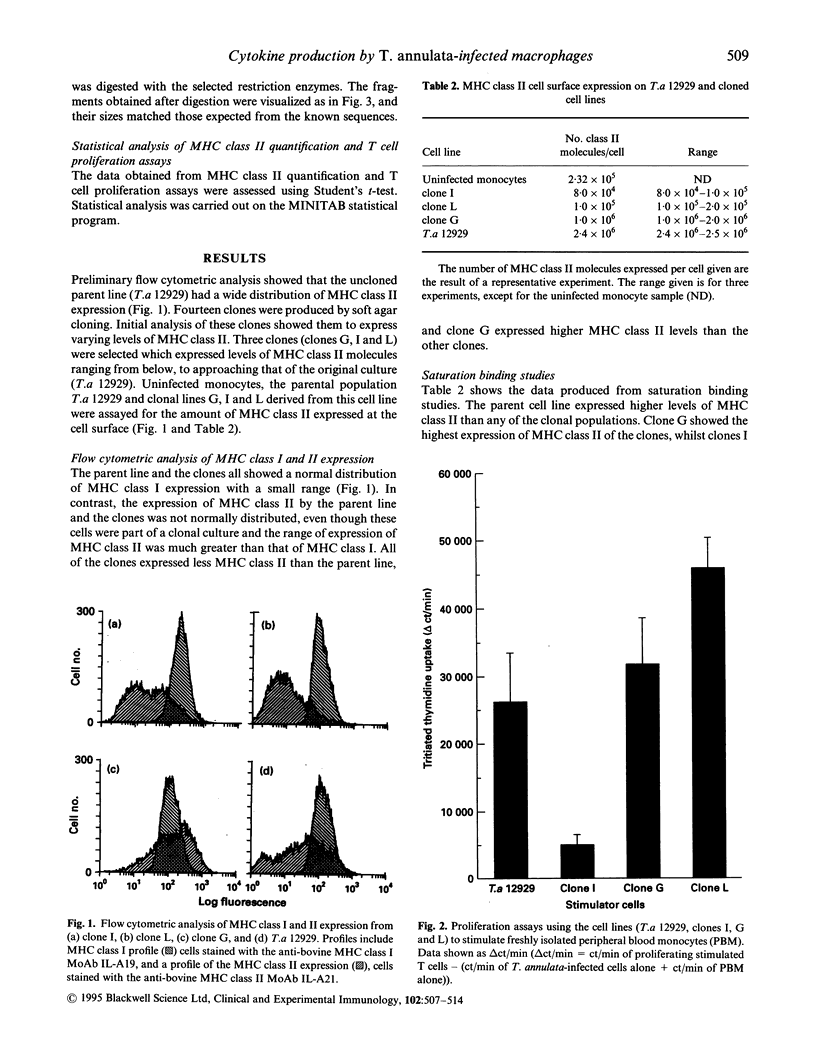
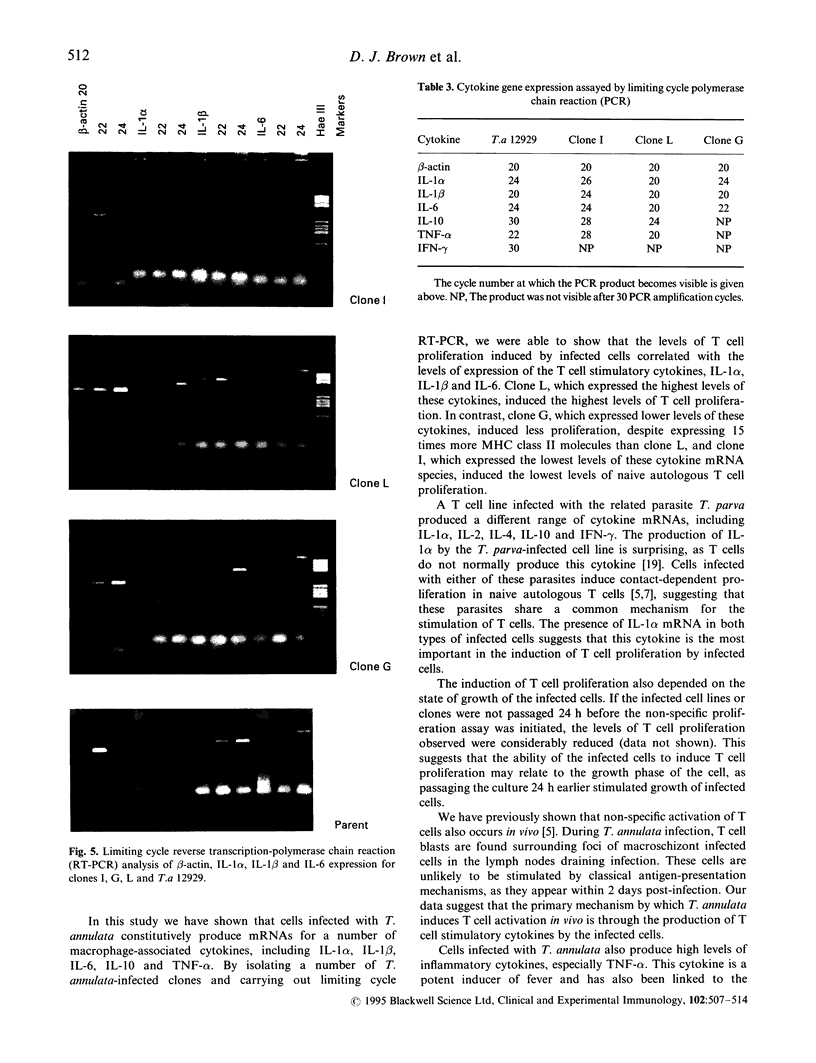
A major feature of the pathology induced by Theileria annulata is acute lymphocytic proliferation, and this study investigates the mechanisms underlying the intrinsic ability of T. annulata-infected monocytes to induce naive autologous T cells to proliferate. Different T. annulata-infected clones expressed different but constant levels of MHC class II, varying from < 1.0 x 10(5) to 1.5 x 10(6) molecules/cell, as measured by saturation binding. However, no correlation was found between the level of MHC class II expression and levels of induced T cell proliferation. Theileria annulata-infected cell lines and clones were assayed for cytokine mRNA expression by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). The infected cells assayed produced mRNA specific for IL-1 alpha, IL-1 beta, IL-6, IL-10 and tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), but not IL-2 or IL-4. One clone (clone G) did not produce mRNA for TNF-alpha. The degree of T cell proliferation induced by infected cells was directly correlated with the amount of mRNA produced for the T cell stimulatory cytokines IL-1 alpha and IL-6, as assessed by a semiquantitative technique. In contrast, cells infected with the related parasite T. parva produced mRNA for IL-1 alpha, IL-2, IL-4, IL-10 and interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma). Since T. parva-infected cells also induce naive autologous T cell proliferation, it seems likely that the production of IL-1 alpha by cells infected with either parasite is a major signal for the induction of non-specific T cell proliferation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bensaid A., Naessens J., Kemp S. J., Black S. J., Shapiro S. Z., Teale A. J. An immunochemical analysis of class I (BoLA) molecules on the surface of bovine cells. Immunogenetics. 1988;27(2):139–144. doi: 10.1007/BF00351089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell J. D., Brown D. J., Glass E. J., Hall F. R., Spooner R. L. Theileria annulata sporozoite targets. Parasite Immunol. 1994 Sep;16(9):501–505. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1994.tb00378.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell J. D., Howie S. E., Odling K. A., Glass E. J. Theileria annulata induces abberrant T cell activation in vitro and in vivo. Clin Exp Immunol. 1995 Feb;99(2):203–210. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1995.tb05533.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakkalath H. R., Titus R. G. Leishmania major-parasitized macrophages augment Th2-type T cell activation. J Immunol. 1994 Nov 15;153(10):4378–4387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies C. J., Joosten I., Andersson L., Arriens M. A., Bernoco D., Bissumbhar B., Byrns G., van Eijk M. J., Kristensen B., Lewin H. A. Polymorphism of bovine MHC class II genes. Joint report of the Fifth International Bovine Lymphocyte Antigen (BoLA) Workshop, Interlaken, Switzerland, 1 August 1992. Eur J Immunogenet. 1994 Aug;21(4):259–289. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-313x.1994.tb00198.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiorentino D. F., Zlotnik A., Mosmann T. R., Howard M., O'Garra A. IL-10 inhibits cytokine production by activated macrophages. J Immunol. 1991 Dec 1;147(11):3815–3822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass E. J., Innes E. A., Spooner R. L., Brown C. G. Infection of bovine monocyte/macrophage populations with Theileria annulata and Theileria parva. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1989 Nov 15;22(4):355–368. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(89)90171-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass E. J., Spooner R. L. Parasite-accessory cell interactions in theileriosis. Antigen presentation by Theileria annulata-infected macrophages and production of continuously growing antigen-presenting cell lines. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Nov;20(11):2491–2497. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830201120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goddeeris B. M., Morrison W. I. The bovine autologous Theileria mixed leucocyte reaction: influence of monocytes and phenotype of the parasitized stimulator cell on proliferation and parasite specificity. Immunology. 1987 Jan;60(1):63–69. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HULLIGER L., WILDE K. H., BROWN C. G., TURNER L. MODE OF MULTIPLICATION OF THEILERIA IN CULTURES OF BOVINE LYMPHOCYTIC CELLS. Nature. 1964 Aug 15;203:728–730. doi: 10.1038/203728a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins J., Dutia B. M., Bujdoso R., McConnell I. In vivo modulation of CD1 and MHC class II expression by sheep afferent lymph dendritic cells. Comparison of primary and secondary immune responses. J Exp Med. 1989 Oct 1;170(4):1303–1318. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.4.1303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins J., Dutia B. M., McConnell I. Monoclonal antibodies to sheep lymphocytes. I. Identification of MHC class II molecules on lymphoid tissue and changes in the level of class II expression on lymph-borne cells following antigen stimulation in vivo. Immunology. 1986 Nov;59(3):433–438. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles G., Dutia B. M., Glass E. J., MacCarthy-Morrogh L., Spooner R. L., Hopkins J. Improved discrimination of bovine class II DR beta-chains polymorphisms using immunoblotting. Anim Genet. 1994 Jun;25(3):129–131. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2052.1994.tb00100.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. S., Griffiths B. W. Comparative studies of Iodo-bead and chloramine-T methods for the radioiodination of human alpha-fetoprotein. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Nov 16;74(1):181–189. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90379-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison W. I., Goddeeris B. M., Brown W. C., Baldwin C. L., Teale A. J. Theileria parva in cattle: characterization of infected lymphocytes and the immune responses they provoke. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1989 Feb;20(3):213–237. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(89)90003-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. R., Coffman R. L. TH1 and TH2 cells: different patterns of lymphokine secretion lead to different functional properties. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:145–173. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.001045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiner S. L., Zheng S., Wang Z. E., Stowring L., Locksley R. M. Leishmania promastigotes evade interleukin 12 (IL-12) induction by macrophages and stimulate a broad range of cytokines from CD4+ T cells during initiation of infection. J Exp Med. 1994 Feb 1;179(2):447–456. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.2.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schein E. On the life cycle of Theileria annulata (Dschunkowsky and Luhs, 1904) in the midgut and hemolymph of Hyalomma anatolicum excavatum (Koch, 1844). Z Parasitenkd. 1975 Sep 12;47(2):165–167. doi: 10.1007/BF00382639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sileghem M., Flynn J. N., Logan-Henfrey L., Ellis J. Tumour necrosis factor production by monocytes from cattle infected with Trypanosoma (Duttonella) vivax and Trypanosoma (Nannomonas) congolense: possible association with severity of anaemia associated with the disease. Parasite Immunol. 1994 Jan;16(1):51–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1994.tb00304.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spooner R. L., Innes E. A., Glass E. J., Brown C. G. Theileria annulata and T. parva infect and transform different bovine mononuclear cells. Immunology. 1989 Feb;66(2):284–288. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Lierop M. J., Nilsson P. R., Wagenaar J. P., Van Noort J. M., Campbell J. D., Glass E. J., Joosten I., Hensen E. J. The influence of MHC polymorphism on the selection of T-cell determinants of FMDV in cattle. Immunology. 1995 Jan;84(1):79–85. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilde J. K. East Coast fever. Adv Vet Sci. 1967;11:207–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Waal Malefyt R., Abrams J., Bennett B., Figdor C. G., de Vries J. E. Interleukin 10(IL-10) inhibits cytokine synthesis by human monocytes: an autoregulatory role of IL-10 produced by monocytes. J Exp Med. 1991 Nov 1;174(5):1209–1220. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.5.1209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]