Abstract
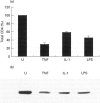
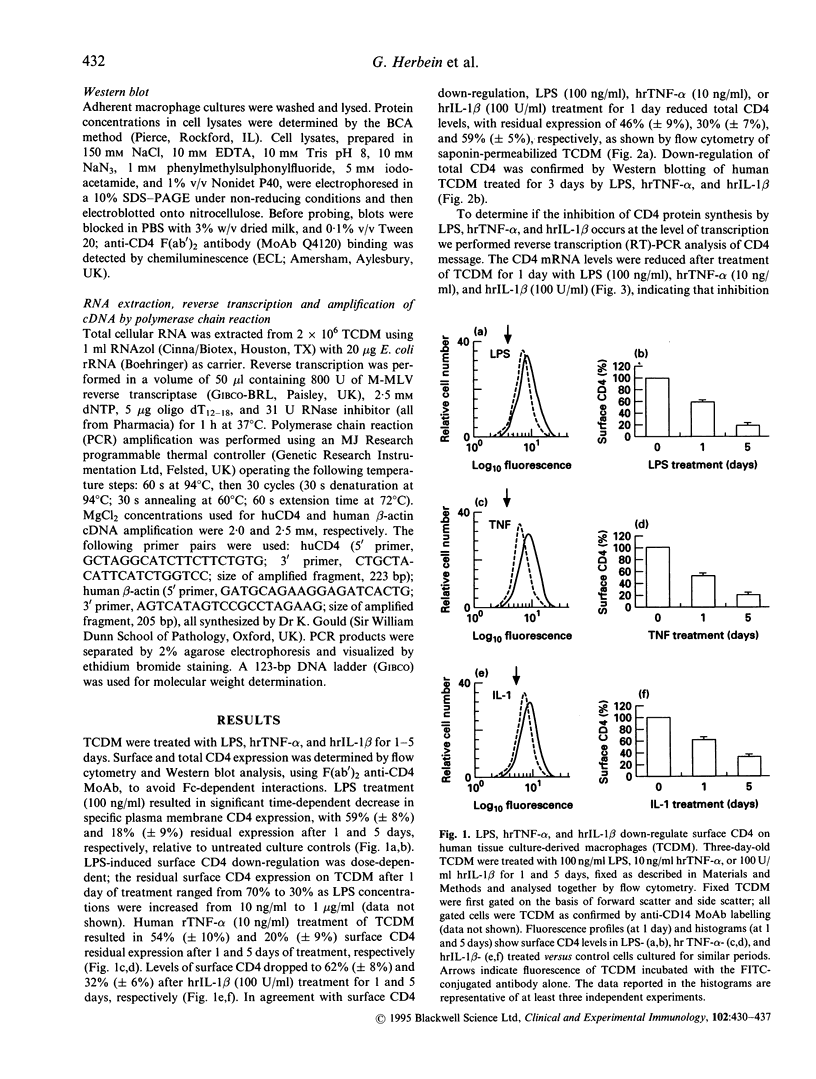
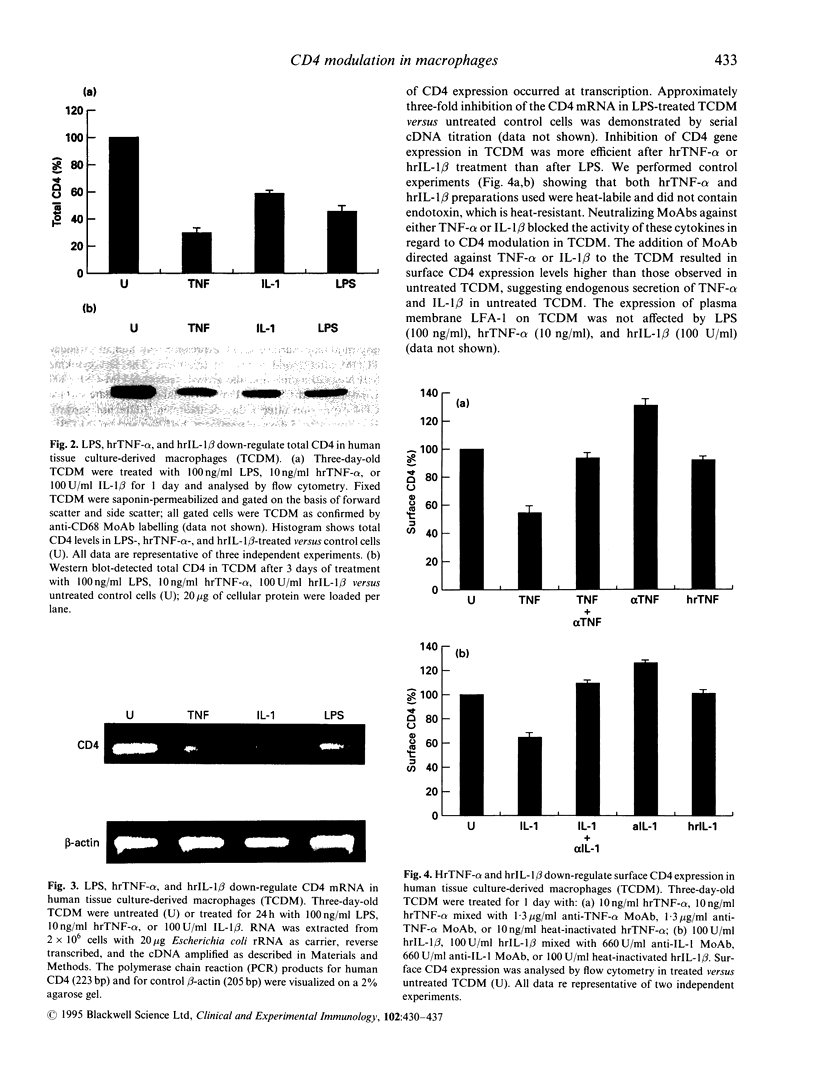
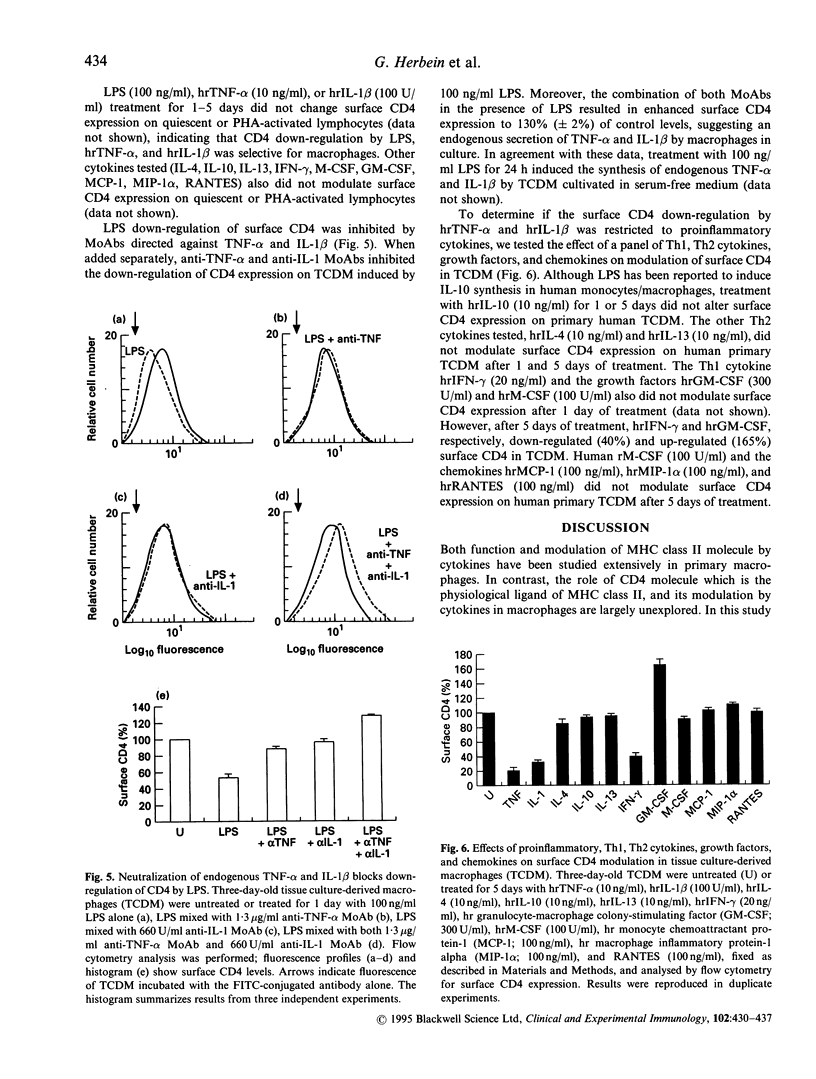
The regulation of CD4 expression on macrophages and its role in immune cell interactions remain obscure. In contrast with primary lymphocytes, primary macrophages express only low amounts of surface CD4, which is regulated differentially for example by adherence in vitro. We report that addition of LPS for 1-5 days to human blood monocyte tissue culture-derived macrophages (TCDM) down-regulates both surface CD4 expression and total cellular CD4 antigen content as measured by flow cytometry and Western blot analysis. TNF-alpha and IL-1 beta, proinflammatory cytokines which are both induced by LPS, also down-regulate surface and total CD4 expression in TCDM. This down-regulation of CD4 expression by LPS, TNF-alpha, and IL-1 beta occurs at the level of transcription. The decreased macrophage CD4 expression induced by LPS was blocked by MoAbs directed against human TNF-alpha and IL-1 beta, demonstrating that LPS acts on CD4 expression through induction of endogenous TNF-alpha and IL-1 beta. Conversely, neither LPS nor TNF-alpha and IL-1 beta were able to modulate surface CD4 expression on quiescent or phytohaemagglutinin (PHA)-activated lymphocytes. Of other cytokines and growth factors tested, Th2 cytokines (IL-4, IL-10, IL-13), chemokines (MCP-1, MIP-1 alpha, RANTES), and macrophage colony-stimulating factor did not alter CD4 expression in primary macrophages; granulocyte-monocyte colony-stimulating factor and the prototypal Th1 cytokine interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) modulated surface CD4 expression only after prolonged treatment (5 days). Our results show that LPS, TNF-alpha and IL-1 beta selectively down-regulate CD4 expression in primary human macrophages, and that decreased CD4 expression induced by LPS results from endogenous secretion of TNF-alpha and IL-1 beta by the macrophages.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blum M. D., Wong G. T., Higgins K. M., Sunshine M. J., Lacy E. Reconstitution of the subclass-specific expression of CD4 in thymocytes and peripheral T cells of transgenic mice: identification of a human CD4 enhancer. J Exp Med. 1993 May 1;177(5):1343–1358. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.5.1343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady H. J., Pennington D. J., Miles C. G., Dzierzak E. A. CD4 cell surface downregulation in HIV-1 Nef transgenic mice is a consequence of intracellular sequestration. EMBO J. 1993 Dec 15;12(13):4923–4932. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06186.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buonocore L., Rose J. K. Blockade of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 production in CD4+ T cells by an intracellular CD4 expressed under control of the viral long terminal repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2695–2699. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clapham P. R., Weiss R. A., Dalgleish A. G., Exley M., Whitby D., Hogg N. Human immunodeficiency virus infection of monocytic and T-lymphocytic cells: receptor modulation and differentiation induced by phorbol ester. Virology. 1987 May;158(1):44–51. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90236-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collman R., Godfrey B., Cutilli J., Rhodes A., Hassan N. F., Sweet R., Douglas S. D., Friedman H., Nathanson N., Gonzalez-Scarano F. Macrophage-tropic strains of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 utilize the CD4 receptor. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4468–4476. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4468-4476.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding A. H., Sanchez E., Srimal S., Nathan C. F. Macrophages rapidly internalize their tumor necrosis factor receptors in response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 5;264(7):3924–3929. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle A. G., Herbein G., Montaner L. J., Minty A. J., Caput D., Ferrara P., Gordon S. Interleukin-13 alters the activation state of murine macrophages in vitro: comparison with interleukin-4 and interferon-gamma. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Jun;24(6):1441–1445. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830240630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle C., Strominger J. L. Interaction between CD4 and class II MHC molecules mediates cell adhesion. Nature. 1987 Nov 19;330(6145):256–259. doi: 10.1038/330256a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faltynek C. R., Finch L. R., Miller P., Overton W. R. Treatment with recombinant IFN-gamma decreases cell surface CD4 levels on peripheral blood monocytes and on myelomonocyte cell lines. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 15;142(2):500–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleury S., Lamarre D., Meloche S., Ryu S. E., Cantin C., Hendrickson W. A., Sekaly R. P. Mutational analysis of the interaction between CD4 and class II MHC: class II antigens contact CD4 on a surface opposite the gp120-binding site. Cell. 1991 Sep 6;66(5):1037–1049. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90447-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia J. V., Miller A. D. Serine phosphorylation-independent downregulation of cell-surface CD4 by nef. Nature. 1991 Apr 11;350(6318):508–511. doi: 10.1038/350508a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassan N. F., Campbell D. E., Douglas S. D. Purification of human monocytes on gelatin-coated surfaces. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Dec 24;95(2):273–276. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90415-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbein G., Keshav S., Collin M., Montaner L. J., Gordon S. HIV-1 induces tumour necrosis factor and IL-1 gene expression in primary human macrophages independent of productive infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1994 Mar;95(3):442–449. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1994.tb07016.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoxie J. A., Matthews D. M., Callahan K. J., Cassel D. L., Cooper R. A. Transient modulation and internalization of T4 antigen induced by phorbol esters. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 15;137(4):1194–1201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura I., Koga Y., Oh-Hori N., Onodera K., Kimura G., Nomoto K. Depletion of the surface CD4 molecule by the envelope protein of human immunodeficiency virus expressed in a human CD4+ monocytoid cell line. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3748–3754. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3748-3754.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazazi F., Mathijs J. M., Foley P., Cunningham A. L. Variations in CD4 expression by human monocytes and macrophages and their relationships to infection with the human immunodeficiency virus. J Gen Virol. 1989 Oct;70(Pt 10):2661–2672. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-10-2661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornbluth R. S., Oh P. S., Munis J. R., Cleveland P. H., Richman D. D. Interferons and bacterial lipopolysaccharide protect macrophages from productive infection by human immunodeficiency virus in vitro. J Exp Med. 1989 Mar 1;169(3):1137–1151. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.3.1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyanagi Y., O'Brien W. A., Zhao J. Q., Golde D. W., Gasson J. C., Chen I. S. Cytokines alter production of HIV-1 from primary mononuclear phagocytes. Science. 1988 Sep 23;241(4873):1673–1675. doi: 10.1126/science.241.4873.1673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krakauer T., Oppenheim J. J. IL-1 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha each up-regulate both the expression of IFN-gamma receptors and enhance IFN-gamma-induced HLA-DR expression on human monocytes and a human monocytic cell line (THP-1). J Immunol. 1993 Feb 15;150(4):1205–1211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamarre D., Capon D. J., Karp D. R., Gregory T., Long E. O., Sékaly R. P. Class II MHC molecules and the HIV gp 120 envelope protein interact with functionally distinct regions of the CD4 molecule. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3271–3277. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08487.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenburg M. E., Landau N. R. Vpu-induced degradation of CD4: requirement for specific amino acid residues in the cytoplasmic domain of CD4. J Virol. 1993 Dec;67(12):7238–7245. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.12.7238-7245.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lähdevirta J., Maury C. P., Teppo A. M., Repo H. Elevated levels of circulating cachectin/tumor necrosis factor in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am J Med. 1988 Sep;85(3):289–291. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(88)90576-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariani R., Skowronski J. CD4 down-regulation by nef alleles isolated from human immunodeficiency virus type 1-infected individuals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5549–5553. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melendez-Guerrero L. M., Nicholson J. K., McDougal J. S. In vitro infection of monocytes with HIVBa-L. Effect on cell surface expression of CD4, CD14, HLA-DR, and HLA-DQ. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1990 Jun;6(6):731–741. doi: 10.1089/aid.1990.6.731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill J. E., Koyanagi Y., Chen I. S. Interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor alpha can be induced from mononuclear phagocytes by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 binding to the CD4 receptor. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4404–4408. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4404-4408.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miceli M. C., von Hoegen P., Parnes J. R. Adhesion versus coreceptor function of CD4 and CD8: role of the cytoplasmic tail in coreceptor activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2623–2627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montaner L. J., Doyle A. G., Collin M., Herbein G., Illei P., James W., Minty A., Caput D., Ferrara P., Gordon S. Interleukin 13 inhibits human immunodeficiency virus type 1 production in primary blood-derived human macrophages in vitro. J Exp Med. 1993 Aug 1;178(2):743–747. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.2.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montaner L. J., Griffin P., Gordon S. Interleukin-10 inhibits initial reverse transcription of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 and mediates a virostatic latent state in primary blood-derived human macrophages in vitro. J Gen Virol. 1994 Dec;75(Pt 12):3393–3400. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-75-12-3393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscicki R. A., Amento E. P., Krane S. M., Kurnick J. T., Colvin R. B. Modulation of surface antigens of a human monocyte cell line, U937, during incubation with T lymphocyte-conditioned medium: detection of T4 antigen and its presence on normal blood monocytes. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):743–748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama T., Wiest D. L., Abraham K. M., Munitz T. I., Perlmutter R. M., Singer A. Decreased signaling competence as a result of receptor overexpression: overexpression of CD4 reduces its ability to activate p56lck tyrosine kinase and to regulate T-cell antigen receptor expression in immature CD4+CD8+ thymocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 15;90(22):10534–10538. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.22.10534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neudorf S., Jones M., Parker S., Papes R., Lattier D. Phorbol esters down-regulate transcription and translation of the CD4 gene. J Immunol. 1991 Apr 15;146(8):2836–2840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn L., Kunkel S., Nabel G. J. Tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 1 stimulate the human immunodeficiency virus enhancer by activation of the nuclear factor kappa B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2336–2340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paillard F., Sterkers G., Vaquero C. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of TcR, CD4 and CD8 gene expression during activation of normal human T lymphocytes. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1867–1872. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08312.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauwels R., Balzarini J., Baba M., Snoeck R., Schols D., Herdewijn P., Desmyter J., De Clercq E. Rapid and automated tetrazolium-based colorimetric assay for the detection of anti-HIV compounds. J Virol Methods. 1988 Aug;20(4):309–321. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(88)90134-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelchen-Matthews A., Boulet I., Littman D. R., Fagard R., Marsh M. The protein tyrosine kinase p56lck inhibits CD4 endocytosis by preventing entry of CD4 into coated pits. J Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;117(2):279–290. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.2.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieber P., Riethmüller G. Loss of circulating T4+ monocytes in patients infected with HTLV-III. Lancet. 1986 Feb 1;1(8475):270–270. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90801-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robey E., Axel R. CD4: collaborator in immune recognition and HIV infection. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):697–700. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90082-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux-Lombard P., Modoux C., Cruchaud A., Dayer J. M. Purified blood monocytes from HIV 1-infected patients produce high levels of TNF alpha and IL-1. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1989 Mar;50(3):374–384. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(89)90144-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon P., Giovane A., Wasylyk B., Klatzmann D. Characterization of the human CD4 gene promoter: transcription from the CD4 gene core promoter is tissue-specific and is activated by Ets proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 15;90(16):7739–7743. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.16.7739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon P., Olivier R., Riviere Y., Brisson E., Gluckman J. C., Kieny M. P., Montagnier L., Klatzmann D. Loss of CD4 membrane expression and CD4 mRNA during acute human immunodeficiency virus replication. J Exp Med. 1988 Dec 1;168(6):1953–1969. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.6.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada S., Scarborough J. D., Killeen N., Littman D. R. A lineage-specific transcriptional silencer regulates CD4 gene expression during T lymphocyte development. Cell. 1994 Jun 17;77(6):917–929. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90140-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siu G., Wurster A. L., Duncan D. D., Soliman T. M., Hedrick S. M. A transcriptional silencer controls the developmental expression of the CD4 gene. EMBO J. 1994 Aug 1;13(15):3570–3579. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06664.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleckman B. P., Shin J., Igras V. E., Collins T. L., Strominger J. L., Burakoff S. J. Disruption of the CD4-p56lck complex is required for rapid internalization of CD4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7566–7570. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart S. J., Fujimoto J., Levy R. Human T lymphocytes and monocytes bear the same Leu-3(T4) antigen. J Immunol. 1986 May 15;136(10):3773–3778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teppler H., Lee S. H., Rieber E. P., Gordon S. Murine immunoglobulin G anti-CD4 monoclonal antibodies bind to primary human monocytes and macrophages through Fc receptors as well as authentic CD4. AIDS. 1990 Jul;4(7):627–632. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199007000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wassmer P., Chan C., Lögdberg L., Shevach E. M. Role of the L3T4-antigen in T cell activation. II. Inhibition of T cell activation by monoclonal anti-L3T4 antibodies in the absence of accessory cells. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2237–2242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weyand C. M., Goronzy J., Fathman C. G. Modulation of CD4 by antigenic activation. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 1;138(5):1351–1354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willey R. L., Maldarelli F., Martin M. A., Strebel K. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Vpu protein induces rapid degradation of CD4. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):7193–7200. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.7193-7200.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood G. S., Warner N. L., Warnke R. A. Anti-Leu-3/T4 antibodies react with cells of monocyte/macrophage and Langerhans lineage. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):212–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zúiga-Pflücker J. C., Jones L. A., Chin L. T., Kruisbeek A. M. CD4 and CD8 act as co-receptors during thymic selection of the T cell repertoire. Semin Immunol. 1991 May;3(3):167–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Waal Malefyt R., Abrams J., Bennett B., Figdor C. G., de Vries J. E. Interleukin 10(IL-10) inhibits cytokine synthesis by human monocytes: an autoregulatory role of IL-10 produced by monocytes. J Exp Med. 1991 Nov 1;174(5):1209–1220. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.5.1209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]