Abstract
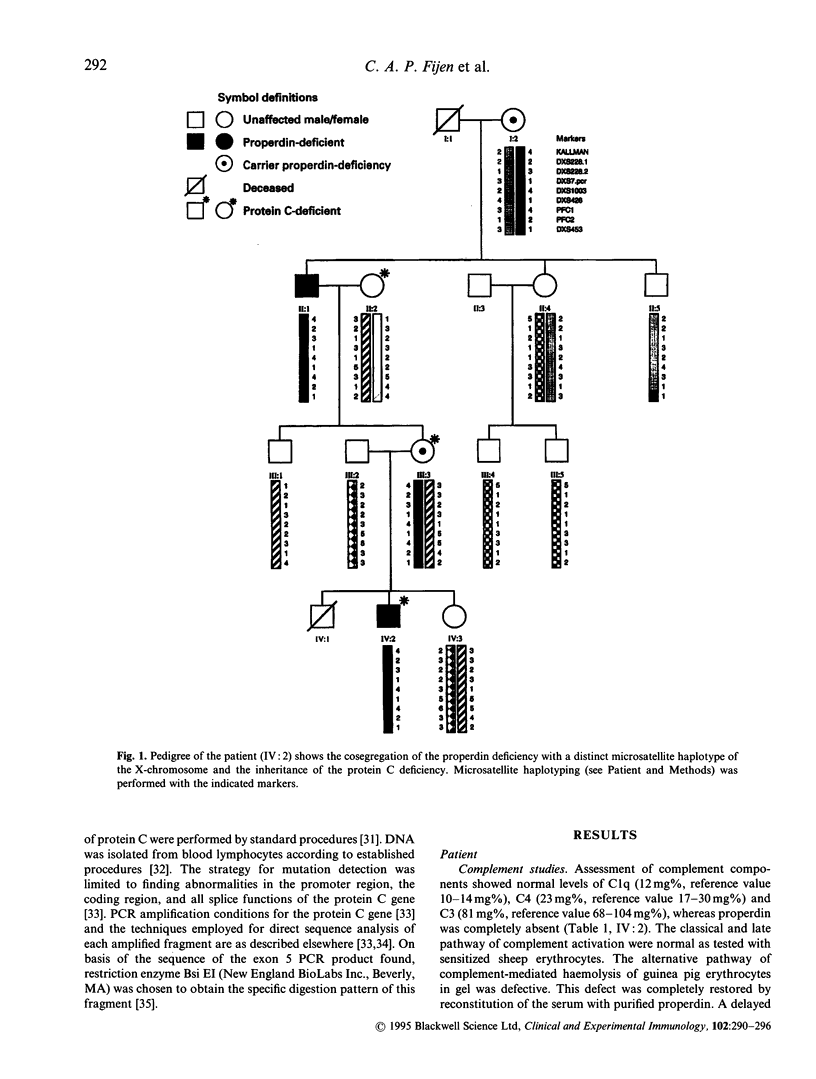
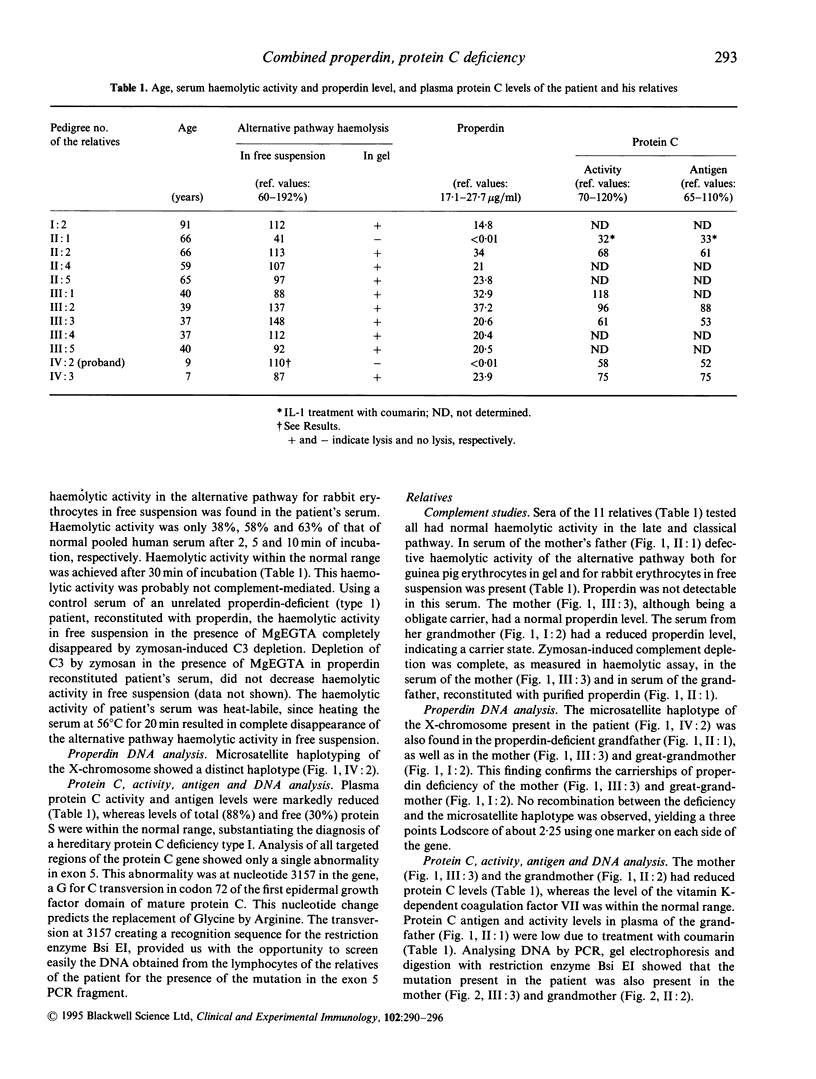
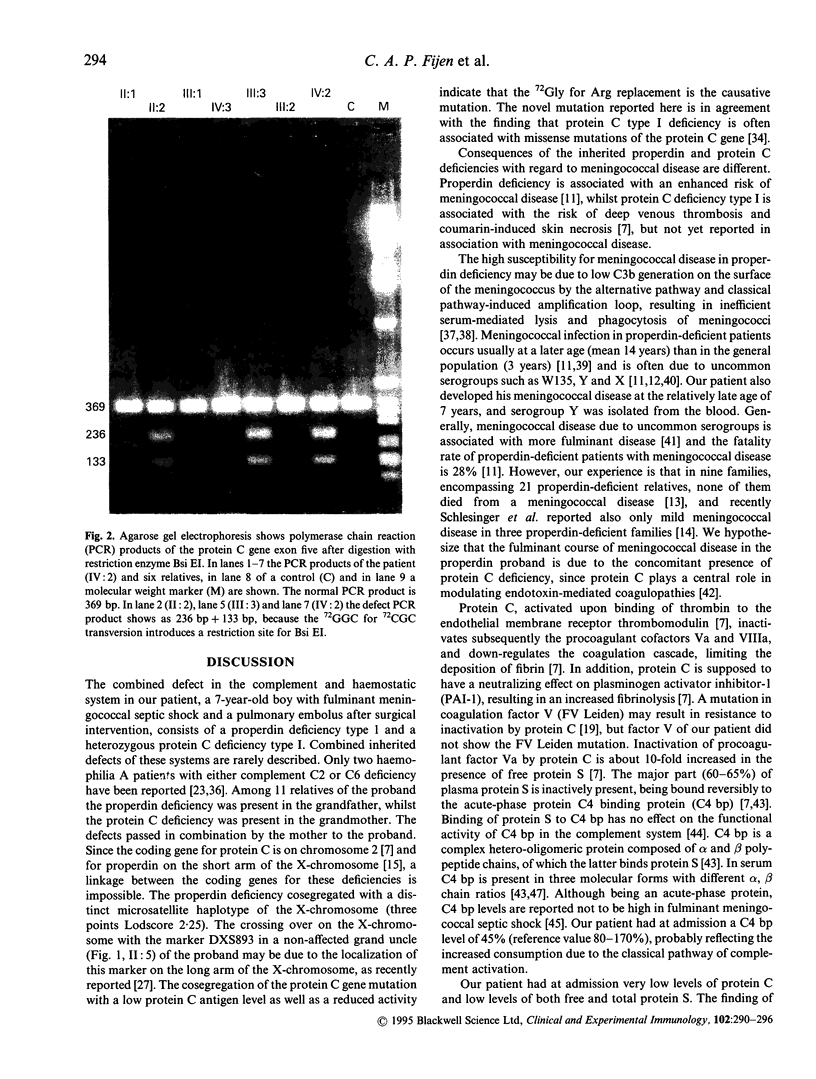
A 7-year-old patient with fulminant septic shock due to Neisseria meningitidis of the uncommon serogroup Y developed extensive gangrene of the limbs. Multiple amputations were necessary and a pulmonary embolism occurred within 2 days post-operatively. Complement and haemostatic system studies, done after recovery, showed a complete absence of properdin antigen and a low protein C antigen and activity level in plasma. Defective haemolytic activity in gel by the alternative pathway of complement activation could be restored with purified properdin, indicating a properdin deficiency type 1. Protein C antigen level as well as activity were in agreement with a protein C deficiency type I. The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) product of exon five of the protein C gene showed a substitution of 72Gly by Arg. Both deficiencies were traced among relatives of the patient. Serum of the father of the patient's mother was also properdin-deficient. Microsatellite haplotyping of the X-chromosome of the patient and his relatives showed that a distinct haplotype cosegregated with the properdin deficiency (Lodscore 2.25; four informative meioses). The protein C type I deficiency was present in the patient's mother and her mother and cosegregated with the mutation found. So far as is known, this is the first patient described with combined inherited properdin deficiency and protein C deficiency.
Full text
PDF



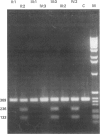
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allaart C. F., Poort S. R., Rosendaal F. R., Reitsma P. H., Bertina R. M., Briët E. Increased risk of venous thrombosis in carriers of hereditary protein C deficiency defect. Lancet. 1993 Jan 16;341(8838):134–138. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)90003-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnum S. R. C4b-binding protein, a regulatory protein of complement. Immunol Res. 1991;10(1):28–42. doi: 10.1007/BF02918165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertina R. M., Koeleman B. P., Koster T., Rosendaal F. R., Dirven R. J., de Ronde H., van der Velden P. A., Reitsma P. H. Mutation in blood coagulation factor V associated with resistance to activated protein C. Nature. 1994 May 5;369(6475):64–67. doi: 10.1038/369064a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouloux P. M., Hardelin J. P., Munroe P., Kirk J. M., Legouis R., Levilliers J., Hazan J., Weissenbach J., Petit C. A dinucleotide repeat polymorphism at the Kallmann locus (Xp22.3). Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 11;19(19):5453–5453. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.19.5453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P., Kierulf P., Gaustad P., Skulberg A., Bruun J. N., Halvorsen S., Sørensen E. Plasma endotoxin as a predictor of multiple organ failure and death in systemic meningococcal disease. J Infect Dis. 1989 Feb;159(2):195–204. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.2.195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P., Mollnes T. E., Kierulf P. Complement activation and endotoxin levels in systemic meningococcal disease. J Infect Dis. 1989 Jul;160(1):58–65. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.1.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daha M. R., Bertina R. M., Thompson J., Kauffmann R. H., Nicholson-Weller A., Veltkamp J. J., Briët E. Combined hereditary deficiency of the sixth component of complement and factor VIII coagulant activity in a Dutch family. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Jun;48(3):733–738. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B., Hildebrand B. Degradation of human complement component C4b in the presence of the C4b-binding protein-protein S complex. Biochem J. 1983 Mar 1;209(3):857–863. doi: 10.1042/bj2090857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeVoe I. W. The meningococcus and mechanisms of pathogenicity. Microbiol Rev. 1982 Jun;46(2):162–190. doi: 10.1128/mr.46.2.162-190.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolan G., Ball J., Preston F. E. Protein C and protein S. Baillieres Clin Haematol. 1989 Oct;2(4):999–1042. doi: 10.1016/s0950-3536(89)80055-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly A., Kozman H., Gedeon A. K., Webb S., Lynch M., Sutherland G. R., Richards R. I., Mulley J. C. A linkage map of microsatellite markers on the human X chromosome. Genomics. 1994 Apr;20(3):363–370. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T., Austen K. F., Ruddy S. Properdin factor D. II. Activation to D by properdin. J Exp Med. 1974 Aug 1;140(2):426–436. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.2.426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figueroa J., Andreoni J., Densen P. Complement deficiency states and meningococcal disease. Immunol Res. 1993;12(3):295–311. doi: 10.1007/BF02918259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fijen C. A., Kuijper E. J., Hannema A. J., Sjöholm A. G., van Putten J. P. Complement deficiencies in patients over ten years old with meningococcal disease due to uncommon serogroups. Lancet. 1989 Sep 9;2(8663):585–588. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90712-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fijnvandraat K., Derkx B., Peters M., Bijlmer R., Sturk A., Prins M. H., van Deventer S. J., ten Cate J. W. Coagulation activation and tissue necrosis in meningococcal septic shock: severely reduced protein C levels predict a high mortality. Thromb Haemost. 1995 Jan;73(1):15–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fourrier F., Lestavel P., Chopin C., Marey A., Goudemand J., Rime A., Mangalaboyi J. Meningococcemia and purpura fulminans in adults: acute deficiencies of proteins C and S and early treatment with antithrombin III concentrates. Intensive Care Med. 1990;16(2):121–124. doi: 10.1007/BF02575306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerson W. T., Dickerman J. D., Bovill E. G., Golden E. Severe acquired protein C deficiency in purpura fulminans associated with disseminated intravascular coagulation: treatment with protein C concentrate. Pediatrics. 1993 Feb;91(2):418–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hach-Wunderle V., Scharrer I. Prävalenz des hereditären Mangels an Antithrombin III, Protein C und Protein S. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1993 Feb 12;118(6):187–190. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1059317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart C. A., Rogers T. R. Meningococcal disease. J Med Microbiol. 1993 Jul;39(1):3–25. doi: 10.1099/00222615-39-1-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiemstra P. S., Langeler E., Compier B., Keepers Y., Leijh P. C., van den Barselaar M. T., Overbosch D., Daha M. R. Complete and partial deficiencies of complement factor D in a Dutch family. J Clin Invest. 1989 Dec;84(6):1957–1961. doi: 10.1172/JCI114384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson D. M., Stafford C. T., Maloney M. J., Lutcher C. L. Desensitization to factor VIII in a patient with classic hemophilia and C2 deficiency. Ann Allergy. 1987 Mar;58(3):215–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazatchkine M. D., Fearon D. T., Silbert J. E., Austen K. F. Surface-associated heparin inhibits zymosan-induced activation of the human alternative complement pathway by augmenting the regulatory action of the control proteins on particle-bound C3b. J Exp Med. 1979 Nov 1;150(5):1202–1215. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.5.1202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kölble K., Cant A. J., Fay A. C., Whaley K., Schlesinger M., Reid K. B. Carrier detection in families with properdin deficiency by microsatellite haplotyping. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jan;91(1):99–102. doi: 10.1172/JCI116207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannens M., Slater R. M., Heyting C., Geurts van Kessel A., Goedde-Salz E., Frants R. R., Van Ommen G. J., Pearson P. L. Regional localization of DNA probes on the short arm of chromosome 11 using aniridia-Wilms' tumor-associated deletions. Hum Genet. 1987 Feb;75(2):180–187. doi: 10.1007/BF00591083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marlar R. A., Montgomery R. R., Broekmans A. W. Diagnosis and treatment of homozygous protein C deficiency. Report of the Working Party on Homozygous Protein C Deficiency of the Subcommittee on Protein C and Protein S, International Committee on Thrombosis and Haemostasis. J Pediatr. 1989 Apr;114(4 Pt 1):528–534. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(89)80688-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miletich J., Sherman L., Broze G., Jr Absence of thrombosis in subjects with heterozygous protein C deficiency. N Engl J Med. 1987 Oct 15;317(16):991–996. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198710153171604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson U. R., Nilsson B. Simplified assays of hemolytic activity of the classical and alternative complement pathways. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Aug 3;72(1):49–59. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90432-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poort S. R., Pabinger-Fasching I., Mannhalter C., Reitsma P. H., Bertina R. M. Twelve novel and two recurrent mutations in 14 Austrian families with hereditary protein C deficiency. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1993 Apr;4(2):273–280. doi: 10.1097/00001721-199304000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powars D., Larsen R., Johnson J., Hulbert T., Sun T., Patch M. J., Francis R., Chan L. Epidemic meningococcemia and purpura fulminans with induced protein C deficiency. Clin Infect Dis. 1993 Aug;17(2):254–261. doi: 10.1093/clinids/17.2.254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitsma P. H., Poort S. R., Allaart C. F., Briët E., Bertina R. M. The spectrum of genetic defects in a panel of 40 Dutch families with symptomatic protein C deficiency type I: heterogeneity and founder effects. Blood. 1991 Aug 15;78(4):890–894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitsma P. H., Poort S. R., Bernardi F., Gandrille S., Long G. L., Sala N., Cooper D. N. Protein C deficiency: a database of mutations. For the Protein C & S Subcommittee of the Scientific and Standardization Committee of the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis. Thromb Haemost. 1993 Jan 11;69(1):77–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross S. C., Densen P. Complement deficiency states and infection: epidemiology, pathogenesis and consequences of neisserial and other infections in an immune deficiency. Medicine (Baltimore) 1984 Sep;63(5):243–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger M., Mashal U., Levy J., Fishelson Z. Hereditary properdin deficiency in three families of Tunisian Jews. Acta Paediatr. 1993 Sep;82(9):744–747. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1993.tb12550.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholten R. J., Bijlmer H. A., Poolman J. T., Kuipers B., Caugant D. A., Van Alphen L., Dankert J., Valkenburg H. A. Meningococcal disease in The Netherlands, 1958-1990: a steady increase in the incidence since 1982 partially caused by new serotypes and subtypes of Neisseria meningitidis. Clin Infect Dis. 1993 Feb;16(2):237–246. doi: 10.1093/clind/16.2.237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schramm W., Spannagl M., Bauer K. A., Rosenberg R. D., Birkner B., Linnau Y., Schwarz H. P. Treatment of coumarin-induced skin necrosis with a monoclonal antibody purified protein C concentrate. Arch Dermatol. 1993 Jun;129(6):753–756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spanjaard L., Bol P., de Marie S., Zanen H. C. Association of meningococcal serogroups with the course of disease in the Netherlands, 1959-83. Bull World Health Organ. 1987;65(6):861–868. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturk A., Morrien-Salomons W. M., Huisman M. V., Borm J. J., Büller H. R., ten Cate J. W. Analytical and clinical evaluation of commercial protein C assays. Clin Chim Acta. 1987 Jun 15;165(2-3):263–270. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(87)90170-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson P. J., Dahlbäck B. Resistance to activated protein C as a basis for venous thrombosis. N Engl J Med. 1994 Feb 24;330(8):517–522. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199402243300801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderström C., Braconier J. H., Christensen K. K., Christensen P., Sjöholm A. G. Opsonization of group B streptococci in properdin deficient serum. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand C. 1985 Dec;93(6):251–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1985.tb02953.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderström C., Braconier J. H., Käyhty H., Sjöholm A. G., Thuresson B. Immune response to tetravalent meningococcal vaccine: opsonic and bactericidal functions of normal and properdin deficient sera. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1989 Mar;8(3):220–224. doi: 10.1007/BF01965264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor F. B., Jr, Chang A., Esmon C. T., D'Angelo A., Vigano-D'Angelo S., Blick K. E. Protein C prevents the coagulopathic and lethal effects of Escherichia coli infusion in the baboon. J Clin Invest. 1987 Mar;79(3):918–925. doi: 10.1172/JCI112902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truedsson L., Sjöholm A. G., Laurell A. B. Screening for deficiencies in the classical and alternative pathways of complement by hemolysis in gel. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1981 Jun;89(3):161–166. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1981.tb02680.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinazzer H., Pangraz U. Protein C: comparison of different assays in normal and abnormal plasma samples. Thromb Res. 1987 Apr 1;46(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(87)90201-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waage A., Brandtzaeg P., Halstensen A., Kierulf P., Espevik T. The complex pattern of cytokines in serum from patients with meningococcal septic shock. Association between interleukin 6, interleukin 1, and fatal outcome. J Exp Med. 1989 Jan 1;169(1):333–338. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.1.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadelius C., Pigg M., Sundvall M., Sjöholm A. G., Goonewardena P., Kuijper E. J., Tijssen C. C., Jansz A., Späth P. J., Schaad U. B. Linkage analysis in properdin deficiency families: refined location in proximal Xp. Clin Genet. 1992 Jul;42(1):8–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1992.tb03126.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Hinsbergh V. W., Bertina R. M., van Wijngaarden A., van Tilburg N. H., Emeis J. J., Haverkate F. Activated protein C decreases plasminogen activator-inhibitor activity in endothelial cell-conditioned medium. Blood. 1985 Feb;65(2):444–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]