Abstract
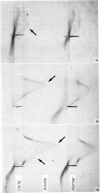
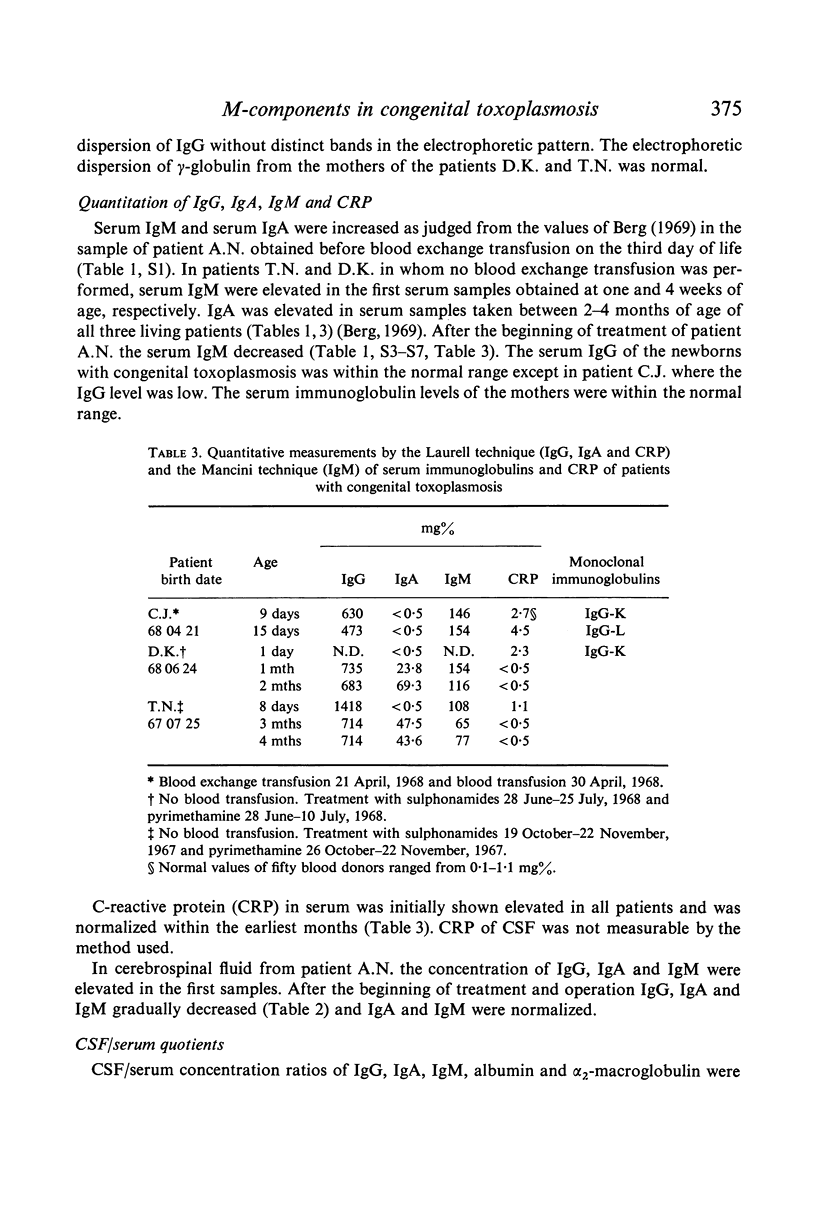
Monoclonal immunoglobulins in serum and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) were found in newborns with congenital toxoplasmosis. The M-components were of IgG-class and of both κ and λ type. The monoclonal proteins were found in the serum of newborns but not in the serum of their mothers. The monoclonal immunoglobulins were therefore selectively transferred or synthesized by the newborn. There was a local production or selective local accumulation of immunoglobulins in the cerebrospinal fluid. The M-components disappeared and the IgM level in serum and cerebrospinal fluid decreased after therapy. IgA was found to be elevated between 2–4 months of age. CRP was elevated in the first weeks after birth but afterwards returned to normal. The Dye test localized antibody activity to the site of the M-components in the electrophoresis of both serum and cerebrospinal fluid. The Dye test antibodies of mothers' sera also showed restricted heterogeneity with about the same electrophoretic localization as in the children's sera. Rheumatoid factors were found in serum and CSF of newborns with congenital toxoplasmosis, but not in serum of their mothers.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLLEN J. C., KUNKEL H. G., KABAT E. A. STUDIES ON HUMAN ANTIBODIES. II. DISTRIBUTION OF GENETIC FACTORS. J Exp Med. 1964 Mar 1;119:453–465. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.3.453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aiuti F., Ungari S., Turbessi G., Serra G. B. Immunologic aspects of congenital syphilis. Helv Paediatr Acta. 1966 Apr;21(1):66–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelsson U., Bachmann R., Hällén J. Frequency of pathological proteins (M-components) om 6,995 sera from an adult population. Acta Med Scand. 1966 Feb;179(2):235–247. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1966.tb05453.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BACHMANN R., LAURELL C. B. STUDIES ON THE SERUM GAMMA 1A-GLOBULIN LEVEL. I. HEALTHY SUBJECTS AND HYPERGAMMAGLOBULINEMIC PATIENTS. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1965;17:39–45. doi: 10.3109/00365516509077281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartfeld H. Distribution of rheumatoid factor activity in nonrheumatoid states. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1969 Dec 10;168(1):30–40. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1969.tb43092.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg T., Nilsson B. A. The foetal development of serum levels of IgG and IgM. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1969 Nov;58(6):577–583. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1969.tb04765.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg T. The immunoglobulin development during the first year of life. A longitudinal study. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1969 May;58(3):229–236. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1969.tb04711.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DALLOZ J. C., CASTAING N., NEZELOF C., SELIGMANN M. PARAPROT'EIN'EMIE TRANSITOIRE DE TYPE GAMMA. OBSERVATION CHEZ UN NOURRISSON ATTEINT DU SYNDROME D'ALDRICH. Presse Med. 1965 May 26;73:1541–1546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDELMAN G. M., KABAT E. A. STUDIES ON HUMAN ANTIBODIES. I. STARCH GEL ELECTROPHORESIS OF THE DISSOCIATED POLYPEPTIDE CHAINS. J Exp Med. 1964 Mar 1;119:443–452. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.3.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLEISCHMAN J. B., PAIN R. H., PORTER R. R. Reduction of gamma-globulins. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1962 Sep;Suppl 1:174–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUDENBERG H. H. GM GENES AND GAMMA-G-GLOBULIN SYNTHESIS IN THE HUMAN FETUS. J Immunol. 1965 Apr;94:514–520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALLEN J. Frequency of "abnormal" serum globulins (M-components) in the aged. Acta Med Scand. 1963 Jun;173:737–744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOKAMA Y., RILEY R. F. Purification of C-reactive protein, an acute phase protein of human serum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Jul 16;74:305–308. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91371-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harboe M., Pande H., Brandtzaeg P., Tveter K. J., Hjort P. F. Synthesis of donor type gamma-G-globulin following thymus transplantation in hypo-gamma-globulinaemia with severe lymphocytopenia. Scand J Haematol. 1966;3(5):351–374. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1966.tb02379.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hällén J. Discrete gammaglobulin (M-)components in serum. Clinical study of 150 subjects without myelomatosis. Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1966;462:1–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPPELER R., SPENGLER G. A., ROULET D. L., RIVA G. [On B2A-paraproteinoses]. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1961 Sep 30;91:1151–1153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURELL C. B. ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY CROSSED ELECTROPHORESIS. Anal Biochem. 1965 Feb;10:358–361. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURELL C. B., LAURELL H., WALDENSTROM J. Glycoproteins in serum from patients with myeloma, macroglobulinemia and related conditions. Am J Med. 1957 Jan;22(1):24–36. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(57)90335-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Quantitative estimation of proteins by electrophoresis in agarose gel containing antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodinova R., Jouja V., Lanc A. Influence of the intestinal flora on the development of immune reactions in infants. J Bacteriol. 1967 Mar;93(3):797–800. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.3.797-800.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANNIK M., KUNKEL H. G. LOCALIZATION OF ANTIBODIES IN GROUP I AND GROUP II GAMMA-GLOBULINS. J Exp Med. 1963 Nov 1;118:817–826. doi: 10.1084/jem.118.5.817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOLLER G. ANTIBODY-INDUCED DEPRESSION OF THE IMMUNE RESPONSE: A STUDY OF THE MECHANISM IN VARIOUS IMMUNOLOGICAL SYSTEMS. Transplantation. 1964 May;2:405–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaux J. L., Heremans J. F. Thirty cases of monoclonal immunoglobulin disorders other than myeloma or macroglobulinemia. A classification of diseases associated with the production of monoclonal-type immunoglobulins. Am J Med. 1969 Apr;46(4):562–579. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(69)90075-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSSERMAN E. F. Natural history of multiple myeloma before radiological evidence of disease. Radiology. 1958 Aug;71(2):157–174. doi: 10.1148/71.2.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OUDIN J. B. Specific precipitation in gels and its application to immunochemical analysis. Methods Med Res. 1952;5:335–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterland C. K., Miller E. J., Karakawa W. W., Krause R. M. Characteristics of streptococcal group-specific antibody isolated from hyperimmune rabbits. J Exp Med. 1966 Apr 1;123(4):599–614. doi: 10.1084/jem.123.4.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxelius V. A., Rorsman H., Laurell A. B. Immunoglobulins of cerebrospinal fluid in syphilis. Br J Vener Dis. 1969 Jun;45(2):121–125. doi: 10.1136/sti.45.2.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PLAYFAIR J. H., WOLFENDALE M. R., KAY H. E. The leucocytes of peripheral blood in the human foetus. Br J Haematol. 1963 Jul;9:336–344. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1963.tb06558.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PLOTZ C. M., SINGER J. M. The latex fixation test. I. Application to the serologic diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Med. 1956 Dec;21(6):888–892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTER D. D., DIXON F. J., LARSEN A. E. THE DEVELOPMENT OF A MYELOMA-LIKE CONDITION IN MINK WITH ALEUTIAN DISEASE. Blood. 1965 May;25:736–742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIVA G. IDIOPATHISCHE UND BEGLEITPARAPROTEINAEMIEN. Helv Med Acta. 1964 Nov;31:285–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington J. S., Miller M. J. 19S and 7S anti-toxoplasma antibodies in diagnosis of acute congenital and acquired toxoplasmosis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Feb;121(2):357–363. doi: 10.3181/00379727-121-30778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington J. S., Miller M. J., Brownlee I. IgM antibodies in acute toxoplasmosis. I. Diagnostic significance in congenital cases and a method for their rapid demonstration. Pediatrics. 1968 Jun;41(6):1082–1091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEIDEGGER J. J. Une micro-méthode de l'immuno-electrophorèse. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1955;7(2):103–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SILVERSTEIN A. M., LUKES R. J. Fetal response to antigenic stimulus. I. Plasmacellular and lymphoid reactions in the human fetus to intrauterine infection. Lab Invest. 1962 Nov;11:918–932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabin A. B., Feldman H. A. Dyes as Microchemical Indicators of a New Immunity Phenomenon Affecting a Protozoon Parasite (Toxoplasma). Science. 1948 Dec 10;108(2815):660–663. doi: 10.1126/science.108.2815.660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soothill J. F., Hayes K., Dudgeon J. A. The immunoglobulins in congenital rubella. Lancet. 1966 Jun 25;1(7452):1385–1388. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)90299-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiehm E. R., Ammann A. J., Cherry J. D. Elevated cord macroglobulins in the diagnosis of intrauterine infections. N Engl J Med. 1966 Nov 3;275(18):971–977. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196611032751801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yount W. J., Dorner M. M., Kunkel H. G., Kabat E. A. Studies on human antibodies. VI. Selective variations in subgroup composition and genetic markers. J Exp Med. 1968 Mar 1;127(3):633–646. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.3.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Furth R., Schuit H. R., Hijmans W. The immunological development of the human fetus. J Exp Med. 1965 Dec 1;122(6):1173–1188. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.6.1173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]