Abstract
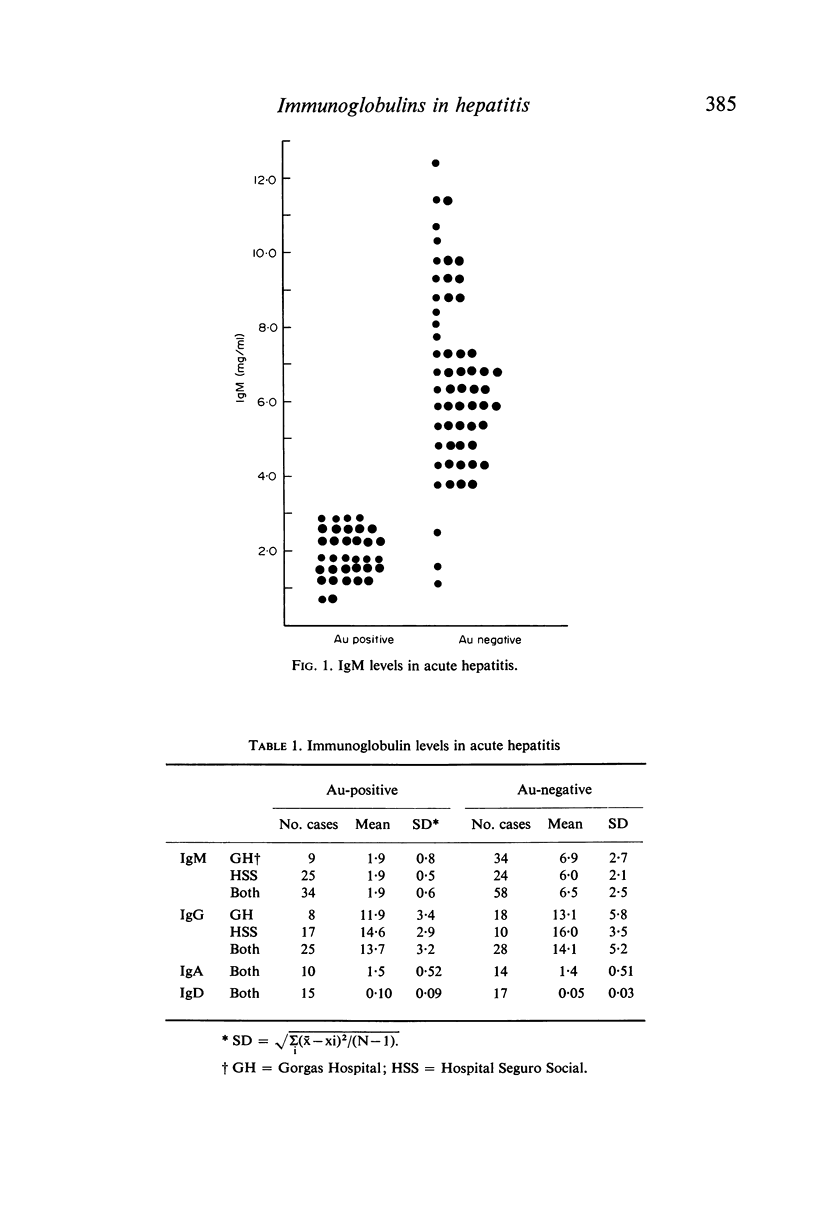
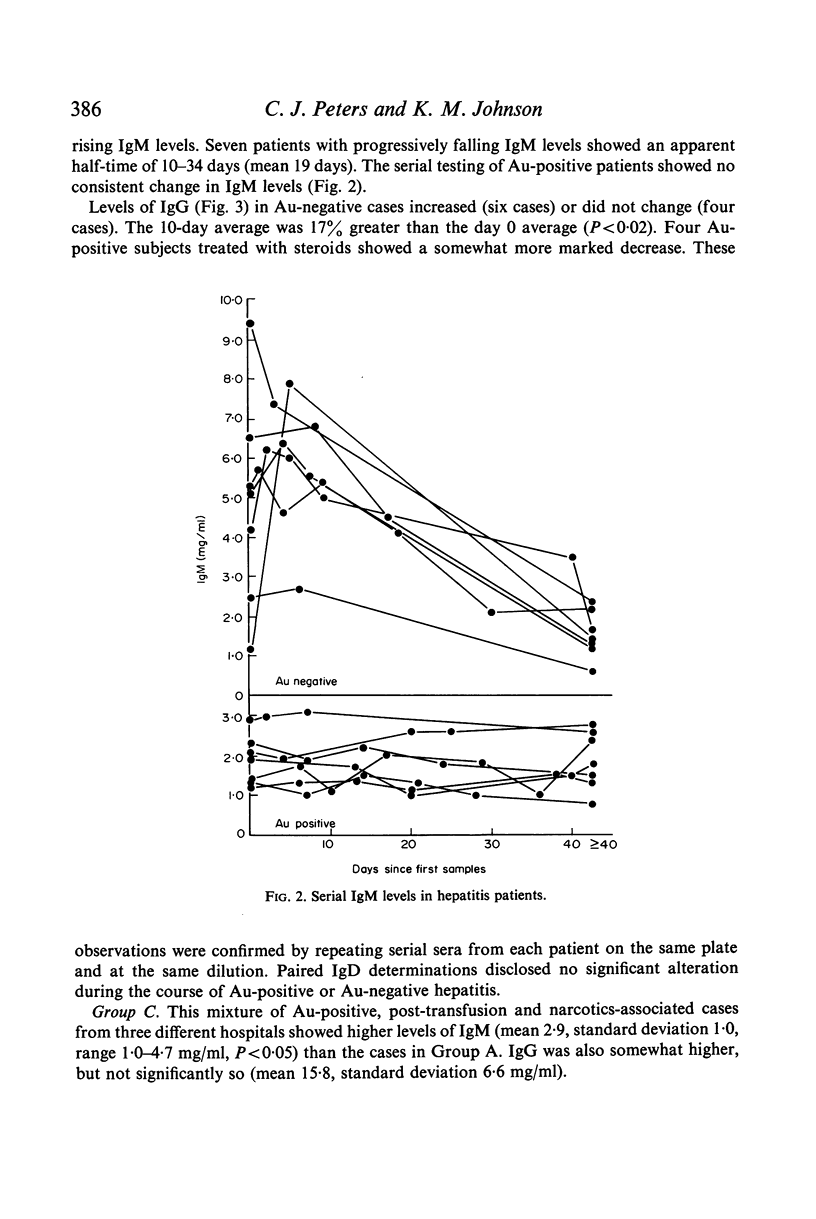
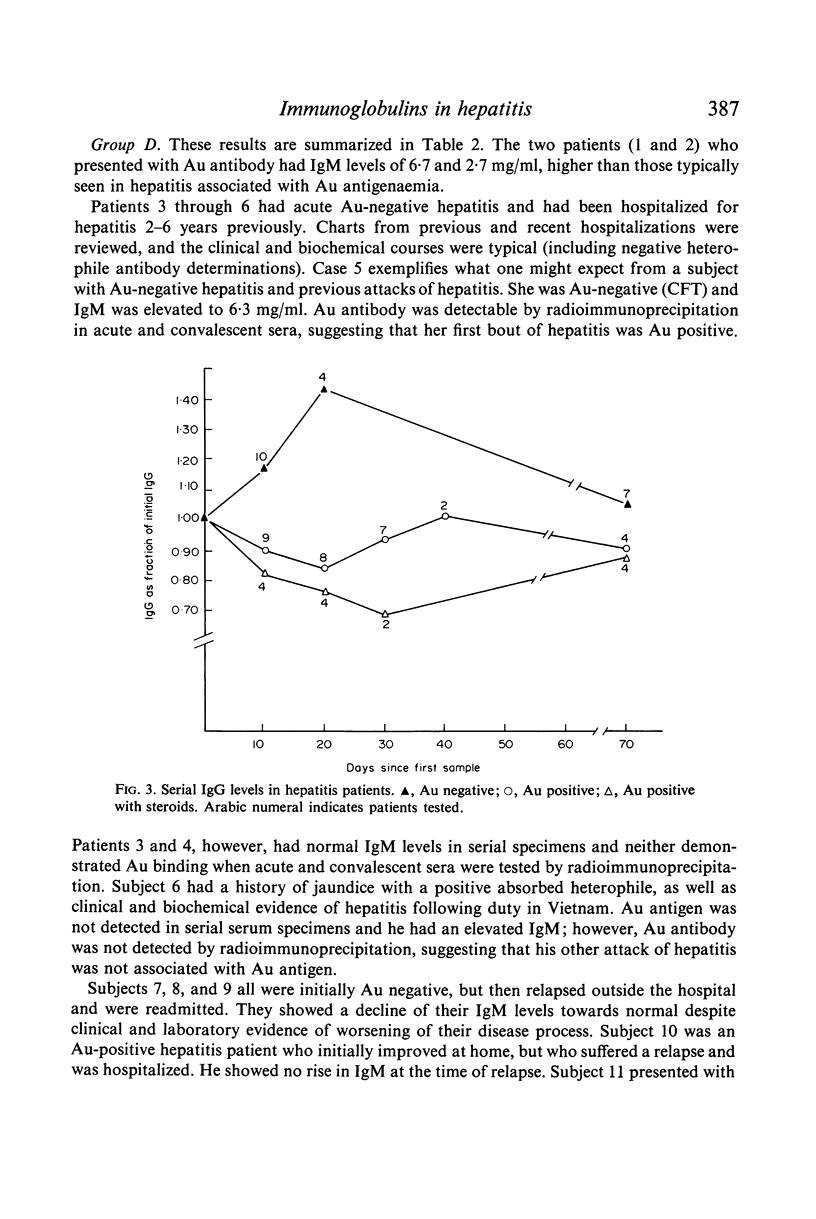
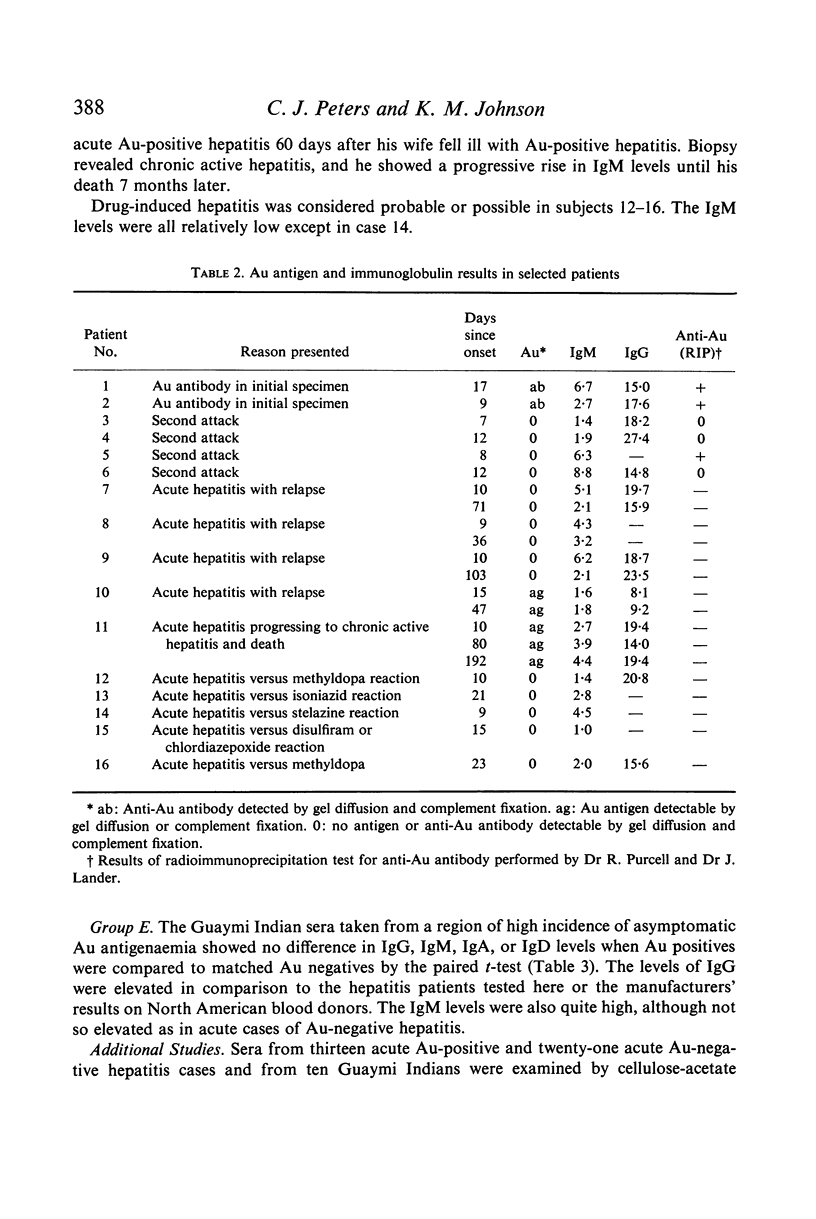
Ig levels were determined by radial immunodiffusion in uncomplicated cases of acute hepatitis with or without Australia antigenaemia. Initial sera from Australia antigen negative cases showed a striking elevation in IgM levels when compared to Australia antigen positive cases (6·5 versus 1·9 mg/ml). None of twenty-four Australia antigen positive cases exceeded 3 mg/ml IgM, and only 3/58 Australia antigen negative cases exhibited values below 3 mg/ml. Intial sera from Australia antigen positive and Australia antigen negative subjects did not differ in concentration of IgG, IgA, or IgD. Serial determinations of IgG revealed a transient fall in patients with Australia antigen positive hepatitis, and a rise in Australia antigen negative cases. Asymptomatic, Australia antigen positive, Guaymi Indian subjects were compared to matched Australia antigen negative controls from the same indigenous group and no differences in the concentration of IgG, IgM, IgA or IgD were found, although elevations of IgG and IgM were common in both groups. No evidence of abnormal proteins was found when sera were tested by cellulose acetate electrophoresis or by immunoelectrophoresis versus immunoglobulin-specific antisera. Ultracentrifugal analysis failed to detect `7S' IgM.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bevan G., Taswell H. F., Gleich G. J. Serum immunoglobulin levels in blood donors implicated in transmission of hepatitis. JAMA. 1968 Jan 1;203(1):38–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giles J. P., Krugman S. Viral hepatitis. Immunoglobulin response during the course of the disease. JAMA. 1969 Apr 21;208(3):497–503. doi: 10.1001/jama.208.3.497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giles J. P., McCollum R. W., Berndtson L. W., Jr, Krugman S. Relation of Australia-SH antigen to the willowbrook MS-2 strain. N Engl J Med. 1969 Jul 17;281(3):119–122. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196907172810302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havens W. P., Jr, Williams T. L. THE CHANGES IN THE SERUM PROTEINS IN PATIENTS WITH EXPERIMENTALLY INDUCED INFECTIOUS HEPATITIS. J Clin Invest. 1948 May;27(3 Pt 1):340–345. doi: 10.1172/JCI101964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs J. R. Serum proteins in liver disease. Proc R Soc Med. 1967 Dec;60(12):1250–1254. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee F. I. Immunoglobulins in viral hepatitis and active alcoholic liver-disease. Lancet. 1965 Nov 20;2(7421):1043–1046. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)90571-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LoGrippo G. A., Hayashi H., Sharpless N. Immunoglobulins and interferon responses in infectious and transfusion associated hepatitis. Henry Ford Hosp Med J. 1967 Mar;15(1):57–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LoGrippo G. A., Hayashi H., Sharpless N., Wolfrom B., Jaslow R. Effect of infectious hepatitis on the immunoglobulins in mentally retarded children. JAMA. 1966 Mar 14;195(11):939–942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSSERMAN E. F., TAKATSUKI K. The plasma proteins in liver disease. Med Clin North Am. 1963 May;47:679–710. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)33572-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters R. L., Ashcavai M. Immunoglobulin levels in detection of viral hepatitis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1970 Jul;54(1):102–109. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/54.1.102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purcell R. H., Holland P. V., Walsh J. H., Wong D. C., Morrow A. G., Chanock R. M. A complement-fixation test for measuring Australia antigen and antibody. J Infect Dis. 1969 Sep;120(3):383–386. doi: 10.1093/infdis/120.3.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. S., Anderson S. G., Grab B. A research standard for human serum immunoglobulins IgG, IgA and IgM. Bull World Health Organ. 1970;42(4):535–552. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt P. M., Hofstetter J. R. La gammaM-globuline dans l'hépatite virale. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1968 Feb 10;98(6):184–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon A., McLaughlin C. L. Biosynthesis of low molecular weight (7S) and high molecular weight (19S) immunoglobulin M. J Clin Invest. 1970 Jan;49(1):150–160. doi: 10.1172/JCI106214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOMASI T. B., Jr, TISDALE W. A. SERUM GAMMA-GLOBULINS IN ACUTE AND CHRONIC LIVER DISEASES. Nature. 1964 Feb 22;201:834–835. doi: 10.1038/201834a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim F. A. Immunoglobulins in the course of viral hepatitis and in cholestatic and obstructive jaundice. Acta Med Scand. 1968 May;183(5):473–479. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1968.tb10510.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


