Abstract
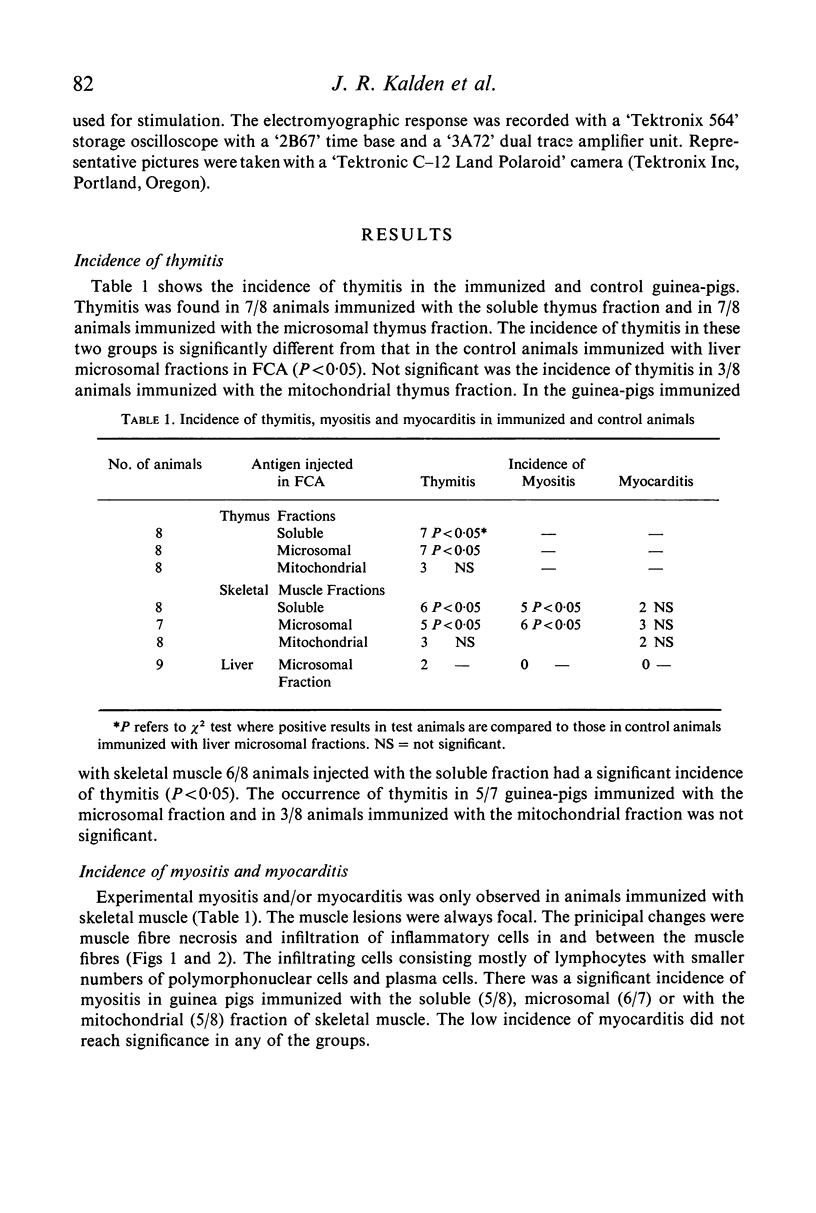
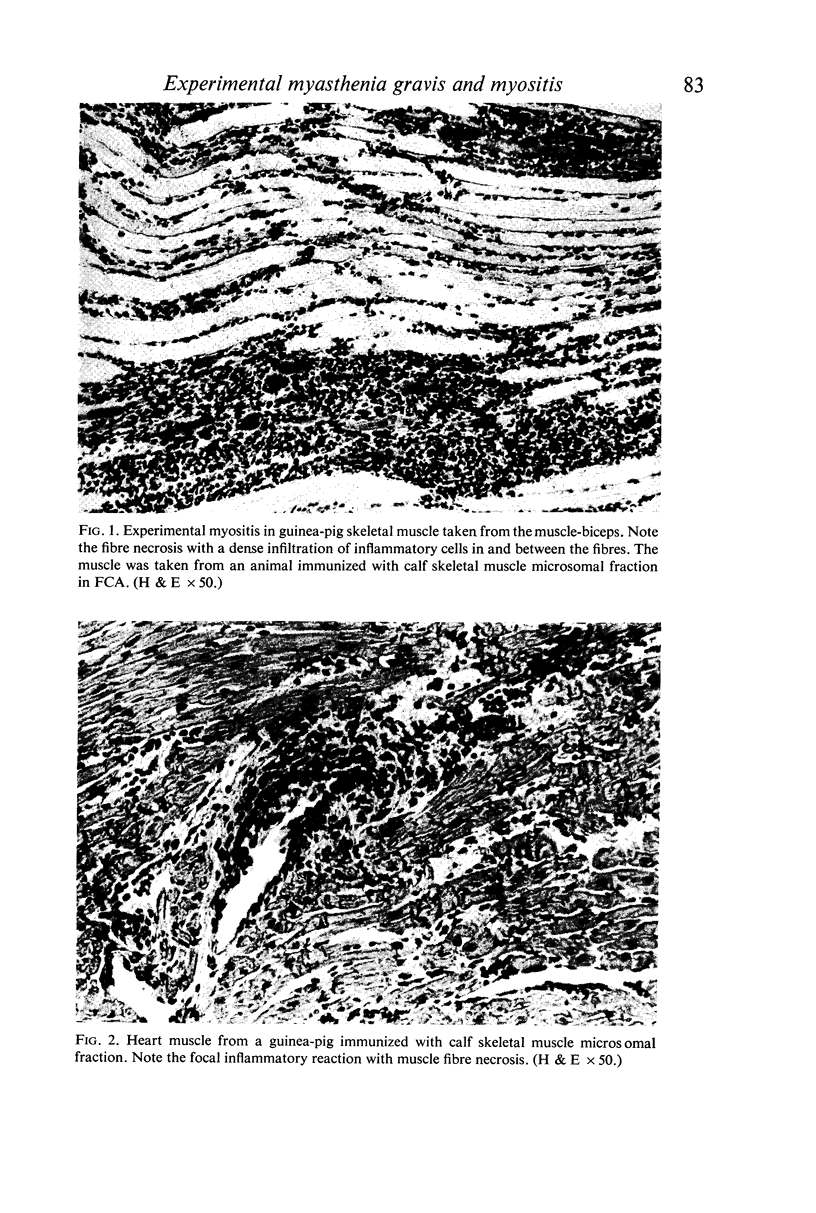
Experimental thymitis and a partial neuromuscular block was produced in guinea-pigs by immunization with the subcellular fractions of calf thymus and skeletal muscle homogenates. A significant incidence of thymitis was observed in guinea-pigs immunized with the soluble or with the microsomal fractions of thymus or of skeletal muscle. The mitochondrial fraction of thymus or skeletal muscle was less effective in producing thymitis. In guinea-pigs immunized with the subcellular fractions of skeletal muscle additional evidence of experimental myositis (60%) and myocarditis (40%) was shown. All three skeletal muscle fractions were equally effective in the production of experimental muscle lesions.
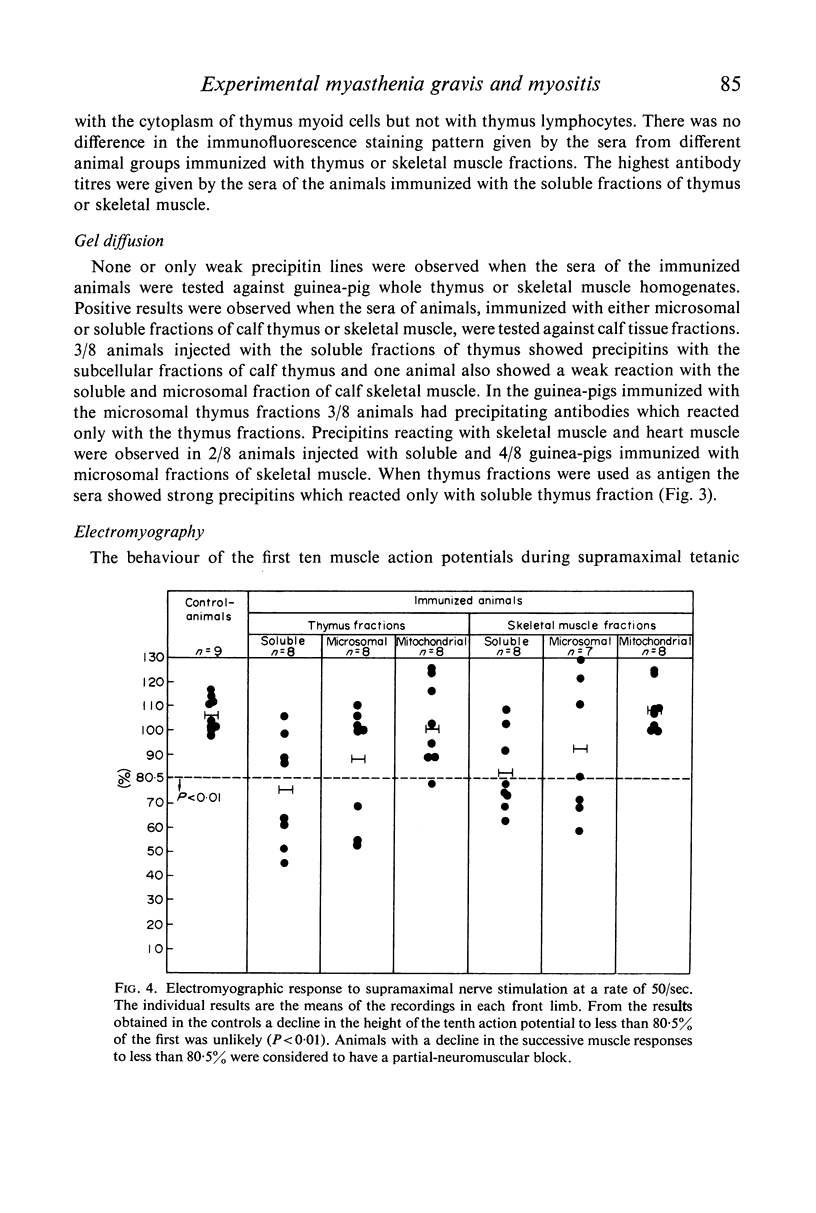
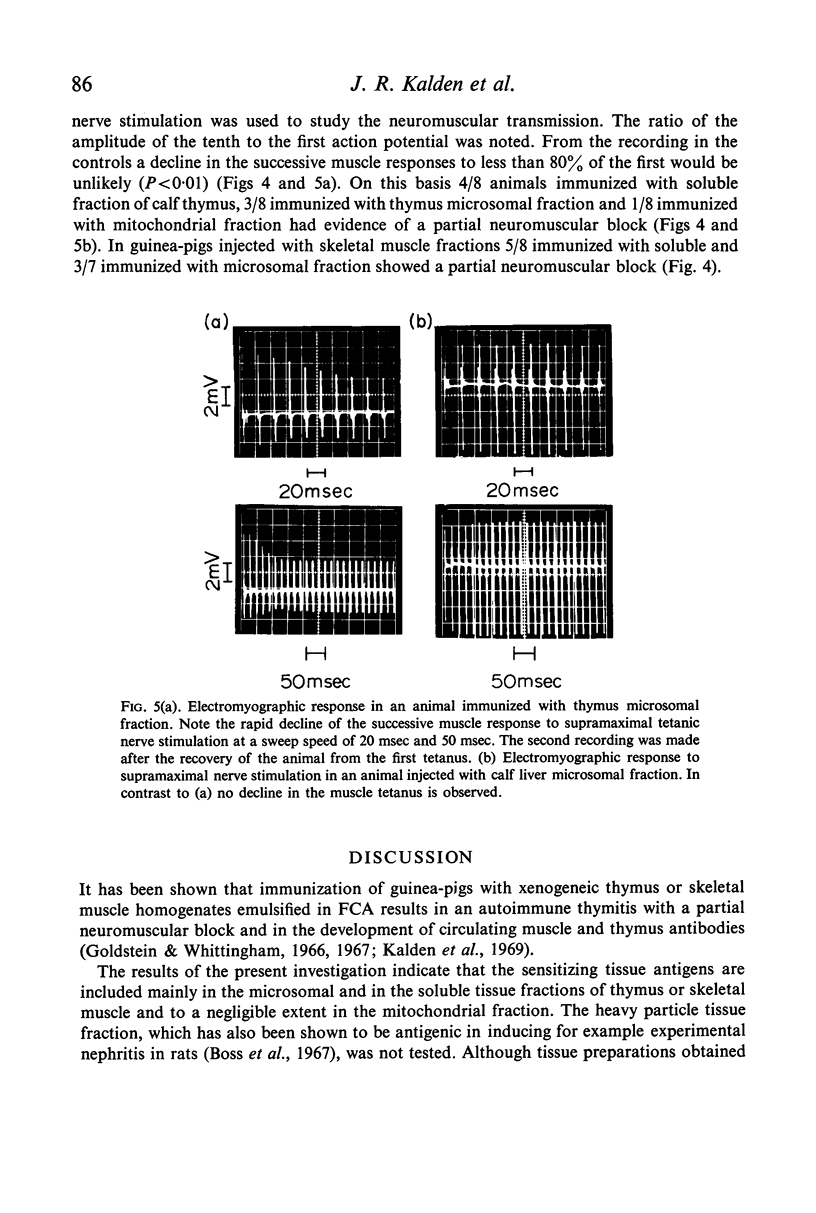
A close correlation was found between the presence of thymitis and the evidence of a partial neuromuscular block. In contrast, a partial neuromuscular block was not observed in animals with experimental myositis but without thymitis. This finding gives further support to the hypothesis that the inflamed thymus is a source of a factor which blocks neuromuscular transmission in experimental myasthenia gravis.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOSS J. H. AUTOIMMUNE RENAL DISEASE. THE PRODUCTION OF AUTOIMMUNE RENAL DISEASE IN THE RAT BY HOMOIMMUNIZATION WITH ORGAN-HETEROLOGOUS MATERIAL. Med Pharmacol Exp Int J Exp Med. 1965;12:345–354. doi: 10.1159/000135572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawkins R. L. Experimental myositis associated with hypersensitivity to muscle. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1965 Oct;90(2):619–625. doi: 10.1002/path.1700900231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenichel G. M. Muscle lesions in myasthenia gravis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jan 26;135(1):60–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb45463.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein G., Hofmann W. W. Electrophysiological changes similar to those of myasthenia gravis in rats with experimental autoimmune thymitis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1968 Oct;31(5):453–459. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.31.5.453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein G., Hofmann W. W. Endocrine function of the thymus affecting neuromuscular transmission. Clin Exp Immunol. 1969 Feb;4(2):181–189. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein G., Strauss A. J., Pickeral S. Antigens in thymus and muscle effective in inducing experimental autoimmune thymitis and the release of thymin. Clin Exp Immunol. 1969 Jan;4(1):3–16. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein G., Whittingham S. Experimental autoimmune thymitis. An animal model of human myasthenia gravis. Lancet. 1966 Aug 6;2(7458):315–318. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)92599-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein G., Whittingham S. Histological and serological features of experimental autoimmune thymitis in guinea-pigs. Clin Exp Immunol. 1967 May;2(3):257–268. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalden J. R., Irvine W. J. Experimental myasthenia gravis. Lancet. 1969 Sep 20;2(7621):638–639. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90342-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalden J. R., Williamson W. G., Irvine W. J. The effect of thymectomy, hemi-thymectomy and sham thymectomy on experimental myasthenia gravis in guinea-pigs. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Apr;6(4):519–530. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalden J. R., Williamson W. G., Johnston R. J., Irvine W. J. Studies on experimental autoimmune thymitis in guinea-pigs. Clin Exp Immunol. 1969 Oct;5(4):319–340. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman B. M., Rushworth G., Wright R. Experimental studies related to autoimmunity in myasthenia gravis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1969 Aug;32(4):281–289. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.32.4.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUTOLO V., D'AMELIO V. Antigen-distribution in rat liver mitochondria. Experientia. 1962 Dec 15;18:556–557. doi: 10.1007/BF02172175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkes J. D. Attempted production of myasthenia gravis in the rat. Br J Exp Pathol. 1966 Dec;47(6):577–585. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYAN K. J. Biological aromatization of steroids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Feb;234(2):268–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sell S., Mascari R. A., Goldblatt P. J. The in vitro effects of goat antisera to rabbit thymocyte subcellular fractions. J Immunol. 1970 Dec;105(6):1569–1574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vetters J. M., Simpson J. A., Folkarde A. Experimental myasthenia gravis. Lancet. 1969 Jul 5;2(7610):28–31. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)92601-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb J. N. Experimental immune myositis in guinea pigs. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1970 Mar;7(3):305–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb J. N. In vitro transformation of lymphocytes in experimental immune myositis. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1970 Apr;7(4):445–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb J. N. Phagocytosis factor in the serum of guinea pigs in experimental immune myositis. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1970 Mar;7(3):317–327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




