Abstract
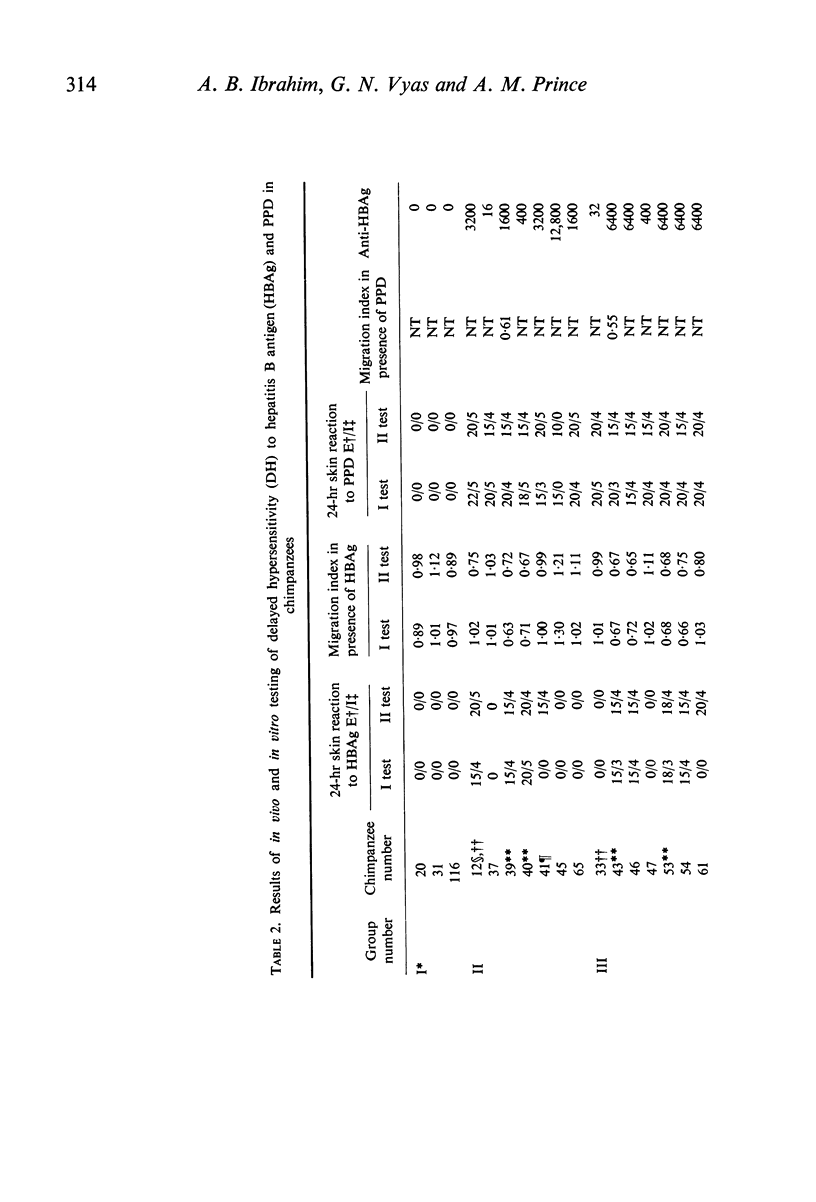
Twenty-eight chimpanzees were divided into six groups according to their history of previous immunization or exposure to hepatitis B antigen (HBAg) and studied for delayed hypersensitivity (DH) to HBAg. Purified HBAg derived from a normal human carrier was used for in vivo skin testing and in vitro leucocyte migration inhibition tests. Of seventeen chimpanzees immunized with HBAg in Freund's complete adjuvant (FCA), nine exhibited positive DH reactions to HBAg with good correlation between the in vivo and in vitro responses. Of the seventeen chimpanzees, fourteen also exhibited positive DH reactions to purified protein derivative of tuberculin (PPD) with marked erythema and induration; the other three exhibited only erythema with no induration. None of the seventeen animals exhibited any immediate reactivity to either HBAg or PPD. Intradermal injection of HBAg-negative human serum failed to elicit DH reactions in four animals who showed positive skin test with purified HBAg; the DH response was thus probably HBAg-specific. Nineteen chimpanzees, including six unimmunized animals, three chronic carriers of HBAg and two which had been injected with HBAg without FCA, failed to show DH response to HBAg. Thus, DH to HBAg was observed only in animals hyperimmunized with HBAg in FCA.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bond H. E., Hall W. T. Separation and purification of hepatitis-associated antigen into morphologic types by zonal ultracentrifugation. J Infect Dis. 1972 Mar;125(3):263–268. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.3.263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILLIS W. D. An outbreak of infectious hepatitis among chimpanzee handlers at a United States Air Force Base. Am J Hyg. 1961 May;73:316–328. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschman R. J., Shulman N. R., Barker L. F., Smith K. O. Virus-like particles in sera of patients with infectious and serum hepatitis. JAMA. 1969 Jun 2;208(9):1667–1670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K., Nakagawa J., Okimoto Y., Nakano H. Chronic hepatitis--migration inhibition of leukocytes in the presence of Australia antigen. N Engl J Med. 1972 May 4;286(18):1005–1005. doi: 10.1056/nejm197205042861817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Bouvier G. L. The heterogeneity of Australia antigen. J Infect Dis. 1971 Jun;123(6):671–675. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.6.671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- London W. T., Alter H. J., Lander J., Purcell R. H. Serial transmission in rhesus monkeys of an agent related to hepatitis-associated antigen. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):382–389. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soborg M., Bendixen G. Human lymphocyte migration as a parameter of hypersensitivity. Acta Med Scand. 1967 Feb;181(2):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1967.tb07255.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vyas G. N., Shulman N. R. Hemagglutination assay for antigen and antibody associated with viral hepatitis. Science. 1970 Oct 16;170(3955):332–333. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3955.332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vyas G. N., Williams E. W., Klaus G. G., Bond H. E. Hepatitis-associated Australia antigen. Protein, peptides and amine acid composition of purified antigen with its use in determining sensitivity of the hemagglutination test. J Immunol. 1972 Apr;108(4):1114–1118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


