Abstract
The mechanism of neutrophil leucocytosis in cases of Japanese encephalitis is not known. We here report that during Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) infection in mice the splenic macrophages secrete a chemotactic factor that attracts the neutrophils. The peak activity of macrophage derived factor (MDF) was observed on day 7 following infection. The MDF acted in a dose-dependent manner. This chemoattractant was purified by low pressure liquid chromatography and gave a single band of 10 kD on silver stained polyacrylamide gel. The MDF was found to be heat resistant and sensitive to prolonged incubation with proteases.
Full text
PDF
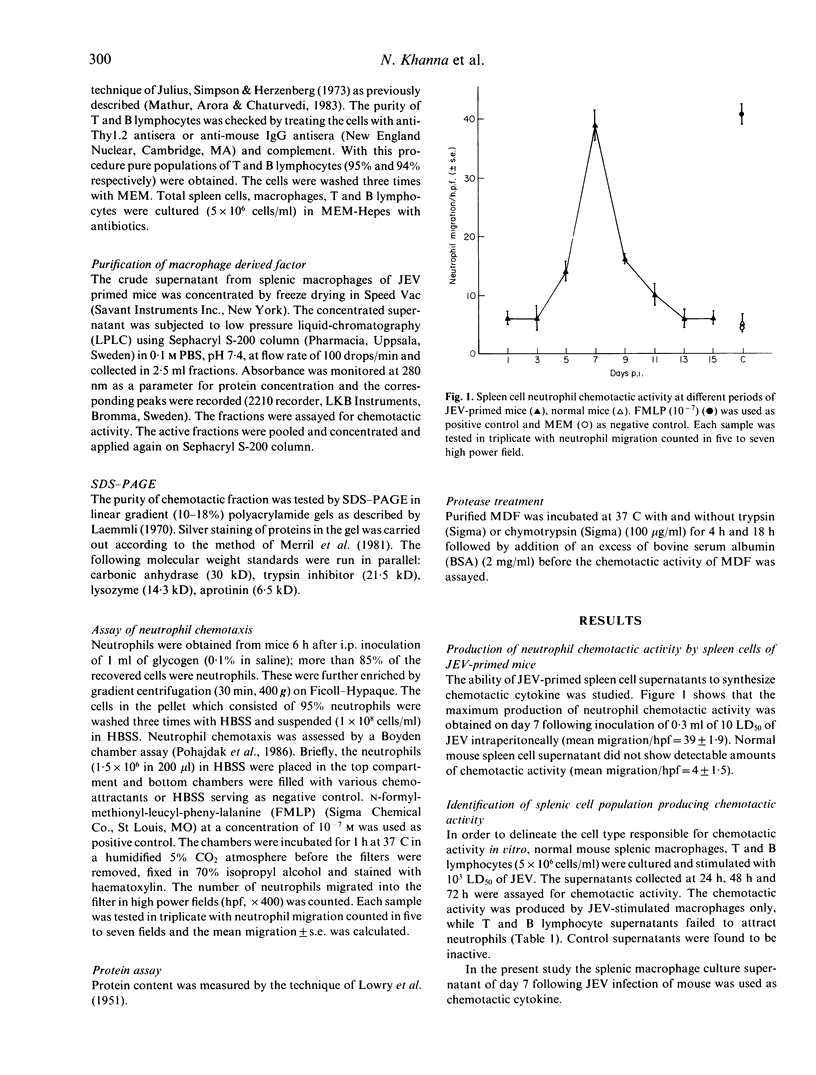
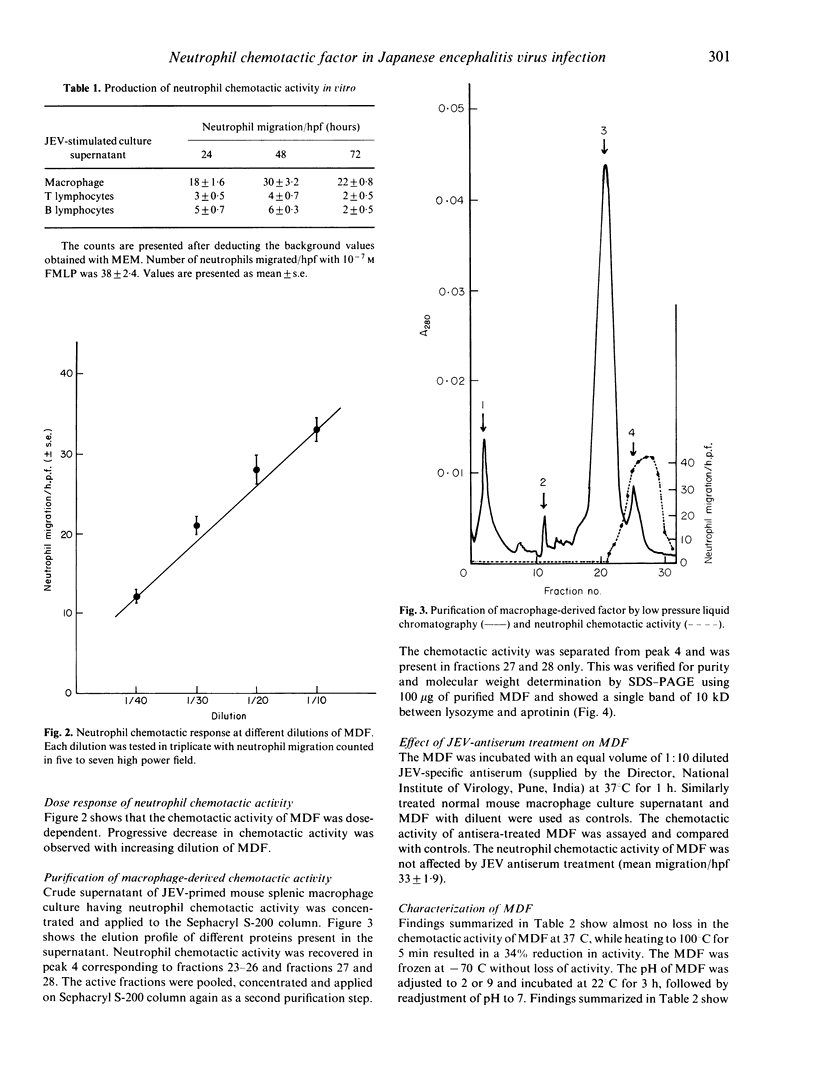
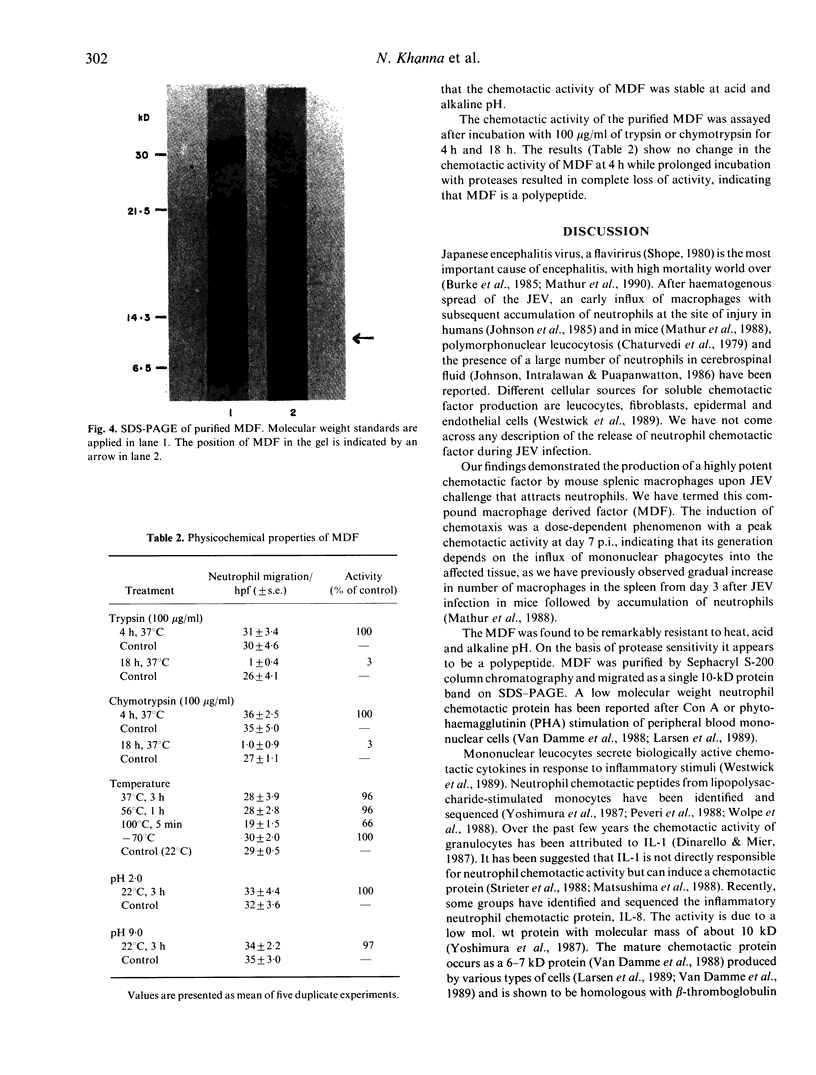

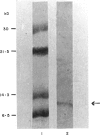
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altman L. C., Chassy B., Mackler B. F. Physicochemical characterization of chemotatic lymphokines produced by human T and B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1975 Jul;115(1):18–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D. S., Lorsomrudee W., Leake C. J., Hoke C. H., Nisalak A., Chongswasdi V., Laorakpongse T. Fatal outcome in Japanese encephalitis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1985 Nov;34(6):1203–1210. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1985.34.1203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaturvedi U. C., Mathur A., Tandon P., Natu S. M., Rajvanshi S., Tandon H. O. Variable effect on peripheral blood leucocytes during JE virus infection of man. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Dec;38(3):492–498. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davatelis G., Tekamp-Olson P., Wolpe S. D., Hermsen K., Luedke C., Gallegos C., Coit D., Merryweather J., Cerami A. Cloning and characterization of a cDNA for murine macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP), a novel monokine with inflammatory and chemokinetic properties. J Exp Med. 1988 Jun 1;167(6):1939–1944. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.6.1939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory H., Young J., Schröder J. M., Mrowietz U., Christophers E. Structure determination of a human lymphocyte derived neutrophil activating peptide (LYNAP). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Mar 15;151(2):883–890. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80364-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. T., Burke D. S., Elwell M., Leake C. J., Nisalak A., Hoke C. H., Lorsomrudee W. Japanese encephalitis: immunocytochemical studies of viral antigen and inflammatory cells in fatal cases. Ann Neurol. 1985 Nov;18(5):567–573. doi: 10.1002/ana.410180510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. T., Intralawan P., Puapanwatton S. Japanese encephalitis: identification of inflammatory cells in cerebrospinal fluid. Ann Neurol. 1986 Dec;20(6):691–695. doi: 10.1002/ana.410200607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathur A., Arora K. L., Chaturvedi U. C. Congenital infection of mice with Japanese encephalitis virus. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):26–29. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.26-29.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathur A., Arora K. L., Chaturvedi U. C. Host defence mechanisms against Japanese encephalitis virus infection in mice. J Gen Virol. 1983 Apr;64(Pt 4):805–811. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-4-805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathur A., Bharadwaj M., Kulshreshtha R., Rawat S., Jain A., Chaturvedi U. C. Immunopathological study of spleen during Japanese encephalitis virus infection in mice. Br J Exp Pathol. 1988 Jun;69(3):423–432. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathur A., Kumar R., Sharma S., Kulshreshtha R., Kumar A., Chaturvedi U. C. Rapid diagnosis of Japanese encephalitis by immunofluorescent examination of cerebrospinal fluid. Indian J Med Res. 1990 Jan;91:1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushima K., Morishita K., Yoshimura T., Lavu S., Kobayashi Y., Lew W., Appella E., Kung H. F., Leonard E. J., Oppenheim J. J. Molecular cloning of a human monocyte-derived neutrophil chemotactic factor (MDNCF) and the induction of MDNCF mRNA by interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor. J Exp Med. 1988 Jun 1;167(6):1883–1893. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.6.1883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peveri P., Walz A., Dewald B., Baggiolini M. A novel neutrophil-activating factor produced by human mononuclear phagocytes. J Exp Med. 1988 May 1;167(5):1547–1559. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.5.1547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohajdak B., Gomez J., Orr F. W., Khalil N., Talgoy M., Greenberg A. H. Chemotaxis of large granular lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(1):278–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strieter R. M., Kunkel S. L., Showell H. J., Marks R. M. Monokine-induced gene expression of a human endothelial cell-derived neutrophil chemotactic factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Nov 15;156(3):1340–1345. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80779-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Damme J., Decock B., Conings R., Lenaerts J. P., Opdenakker G., Billiau A. The chemotactic activity for granulocytes produced by virally infected fibroblasts is identical to monocyte-derived interleukin 8. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Jul;19(7):1189–1194. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Damme J., Van Beeumen J., Opdenakker G., Billiau A. A novel, NH2-terminal sequence-characterized human monokine possessing neutrophil chemotactic, skin-reactive, and granulocytosis-promoting activity. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1364–1376. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westwick J., Li S. W., Camp R. D. Novel neutrophil-stimulating peptides. Immunol Today. 1989 May;10(5):146–147. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90164-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolpe S. D., Davatelis G., Sherry B., Beutler B., Hesse D. G., Nguyen H. T., Moldawer L. L., Nathan C. F., Lowry S. F., Cerami A. Macrophages secrete a novel heparin-binding protein with inflammatory and neutrophil chemokinetic properties. J Exp Med. 1988 Feb 1;167(2):570–581. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.2.570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura T., Matsushima K., Tanaka S., Robinson E. A., Appella E., Oppenheim J. J., Leonard E. J. Purification of a human monocyte-derived neutrophil chemotactic factor that has peptide sequence similarity to other host defense cytokines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9233–9237. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]