Abstract
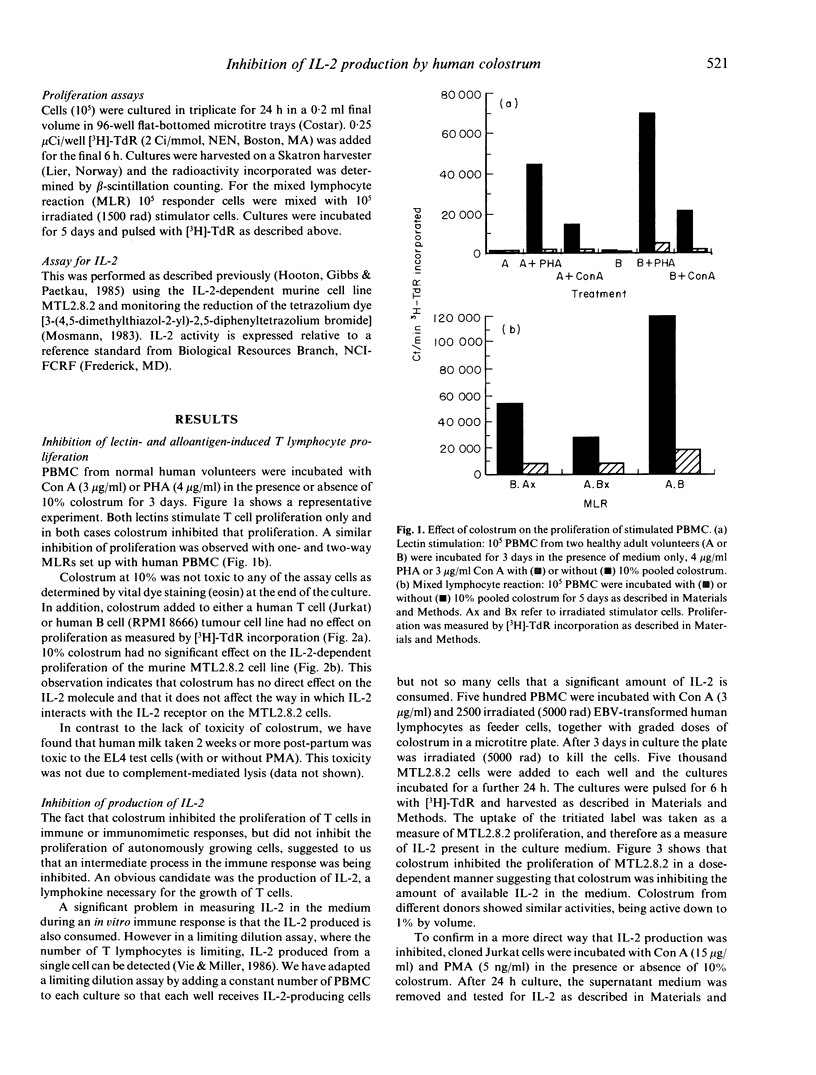
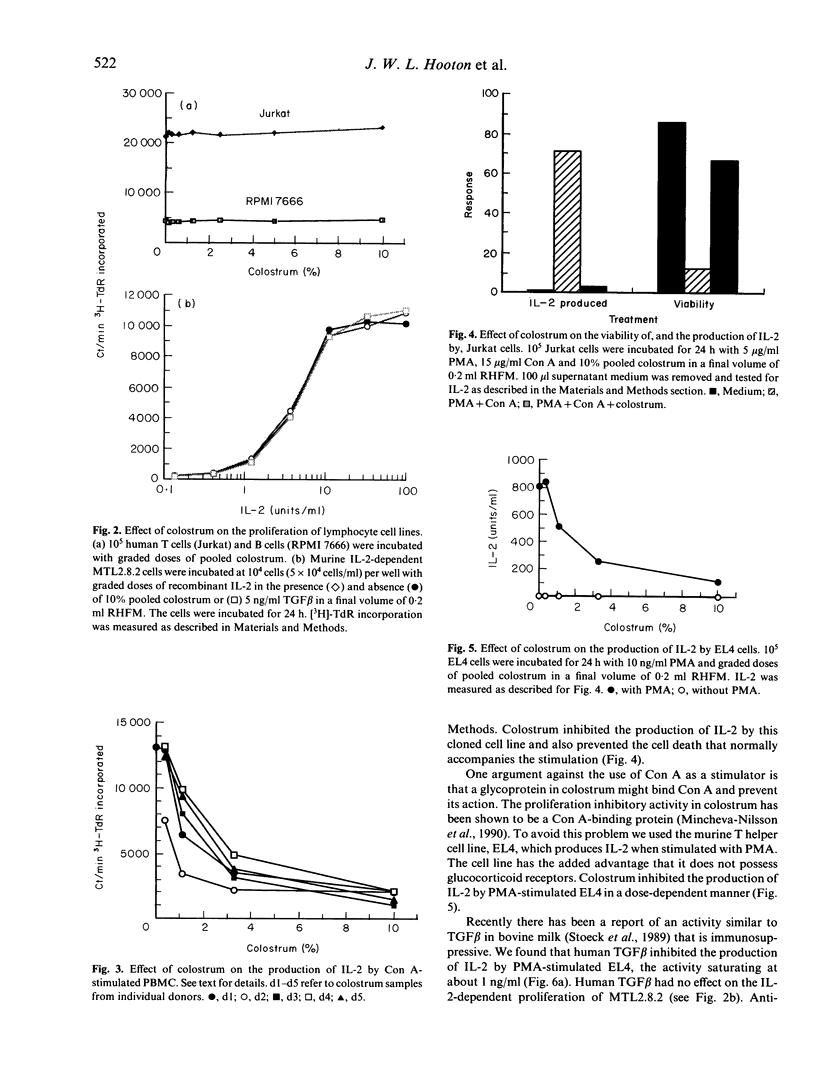
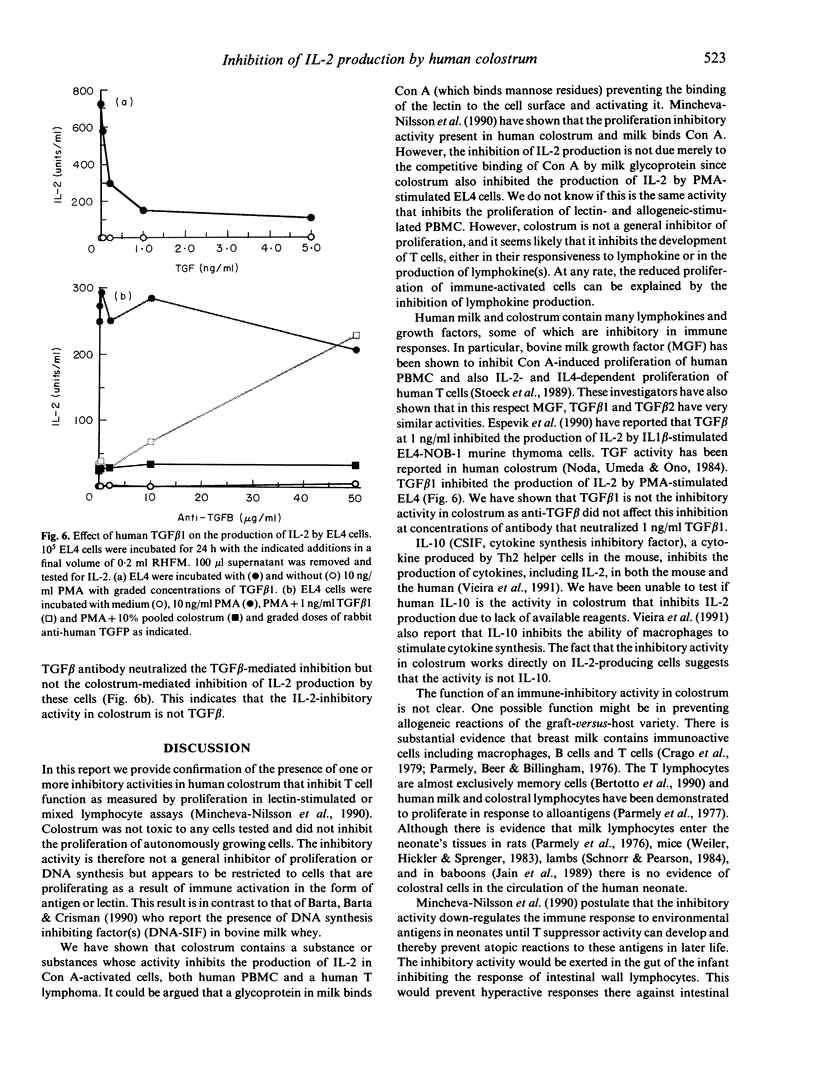
The effect of human colostrum on T cell immune function was investigated. Colostrum inhibited the proliferation of human T cells activated by allogeneic, concanavalin A (Con A) or phytohaemagglutinin (PHA) stimulation. Colostrum also inhibited the production of IL-2 by Con A-activated human peripheral blood T cells and by Con A-activated Jurkat cells, a human T lymphoma line. Similarly, human colostrum inhibited the production of IL-2 by EL4 cells, a murine thymoma line, when stimulated with phorbol myristate acetate. The inhibitory activity was not cytotoxic and could not be neutralized by antibody to transforming human growth factor beta.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bertotto A., Gerli R., Fabietti G., Crupi S., Arcangeli C., Scalise F., Vaccaro R. Human breast milk T lymphocytes display the phenotype and functional characteristics of memory T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Aug;20(8):1877–1880. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crago S. S., Prince S. J., Pretlow T. G., McGhee J. R., Mestecky J. Human colostral cells. I. Separation and characterization. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Dec;38(3):585–597. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espevik T., Waage A., Faxvaag A., Shalaby M. R. Regulation of interleukin-2 and interleukin-6 production from T-cells: involvement of interleukin-1 beta and transforming growth factor-beta. Cell Immunol. 1990 Mar;126(1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(90)90299-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooton J. W., Gibbs C., Paetkau V. Interaction of interleukin 2 with cells: quantitative analysis of effects. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2464–2473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain L., Vidyasagar D., Xanthou M., Ghai V., Shimada S., Blend M. In vivo distribution of human milk leucocytes after ingestion by newborn baboons. Arch Dis Child. 1989 Jul;64(7 Spec No):930–933. doi: 10.1136/adc.64.7_spec_no.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Janusz M., Lisowski J. A colostral protein that induces the growth and differentiation of resting B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 1;140(5):1366–1371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mincheva-Nilsson L., Hammarström M. L., Juto P., Hammarström S. Human milk contains proteins that stimulate and suppress T lymphocyte proliferation. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Mar;79(3):463–469. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb08113.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Dec 16;65(1-2):55–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda K., Umeda M., Ono T. Transforming growth factor activity in human colostrum. Gan. 1984 Feb;75(2):109–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabst H. F., Godel J., Grace M., Cho H., Spady D. W. Effect of breast-feeding on immune response to BCG vaccination. Lancet. 1989 Feb 11;1(8633):295–297. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91307-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabst H. F., Spady D. W. Effect of breast-feeding on antibody response to conjugate vaccine. Lancet. 1990 Aug 4;336(8710):269–270. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91802-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmely M. J., Beer A. E., Billingham R. E. In vitro studies on the T-lymphocyte population of human milk. J Exp Med. 1976 Aug 1;144(2):358–370. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.2.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmely M. J., Reath D. B., Beer A. E., Billingham R. E. Cellular immune responses of human milk T lymphocytes to certain environmental antigens. Transplant Proc. 1977 Jun;9(2):1477–1483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnorr K. L., Pearson L. D. Intestinal absorption of maternal leucocytes by newborn lambs. J Reprod Immunol. 1984 Aug;6(5):329–337. doi: 10.1016/0165-0378(84)90031-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeck M., Ruegg C., Miescher S., Carrel S., Cox D., Von Fliedner V., Alkan S. Comparison of the immunosuppressive properties of milk growth factor and transforming growth factors beta 1 and beta 2. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 15;143(10):3258–3265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapper D., Klagsbrun M., Neumann J. The identification and clinical implications of human breast milk mitogen. J Pediatr Surg. 1979 Dec;14(6):803–808. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(79)80270-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vie H., Miller R. A. Estimation by limiting dilution analysis of human IL 2-secreting T cells: detection of IL 2 produced by single lymphokine-secreting T cells. J Immunol. 1986 May 1;136(9):3292–3297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira P., de Waal-Malefyt R., Dang M. N., Johnson K. E., Kastelein R., Fiorentino D. F., deVries J. E., Roncarolo M. G., Mosmann T. R., Moore K. W. Isolation and expression of human cytokine synthesis inhibitory factor cDNA clones: homology to Epstein-Barr virus open reading frame BCRFI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1172–1176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiler I. J., Hickler W., Sprenger R. Demonstration that milk cells invade the suckling neonatal mouse. Am J Reprod Immunol. 1983 Sep;4(2):95–98. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0897.1983.tb00261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


